This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by BSCK II Phung Thi Phuong Chi - Oncologist - Oncology Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital. The doctor has 20 years of experience in the field of oncology.Ovarian cancer is a disease that often progresses quietly, without many typical symptoms in the early stages. Therefore, the disease is difficult to detect early and treat promptly.
1. What is ovarian cancer?
Ovarian cancer is a malignant tumor in the ovary. Cells in melanoma are abnormal cells that divide not according to the body's needs and are not controlled by the body, easily invade nearby organs and metastasize to distant organs. than.There are many types of ovarian cancer:
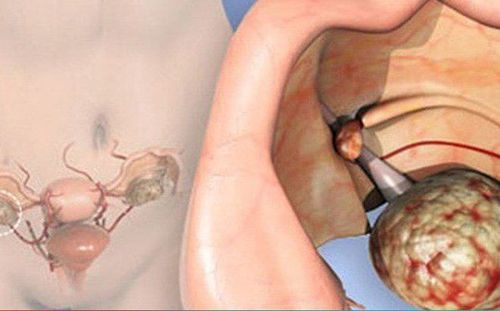
Carcinoma: cancer that originates from the surface of the ovary. Germ cell cancer: cancer that begins in the cells that produce eggs. Tumor stromal cancer: cancer that originates in the ovarian stroma. Ovarian cancer cells often grow outside the ovary and spread to other tissues and organs in the body. Specifically, ovarian cancer cells spread to the peritoneum causing ascites. Cancer cells can also follow the blood to the liver, bones, brain, lungs, ... to form tumors there or by the lymphatic system to attack lymph nodes in the body.
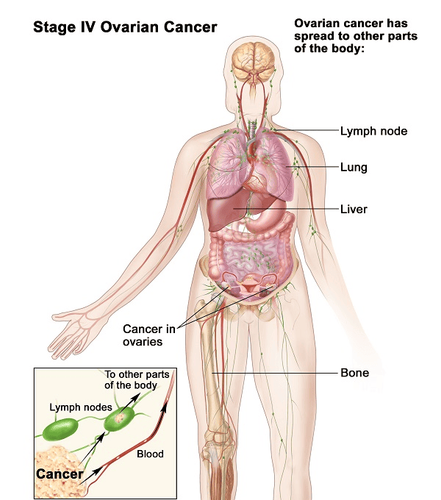
Ung thư buồng trứng có thể di căn tới nhiều cơ quan trên cơ thể
2. Methods of diagnosing ovarian cancer
Commonly used methods to screen for ovarian cancer are:Pelvic examination: including examination of the uterus, vagina, ovaries, fallopian tubes, rectum and bladder,... Patients may have Ovarian cancer if: there is a tumor in the abdomen, there is too much fluid (ascites), or there are signs of metastasis to other organs such as pleural effusion, metastatic tumor in the liver or lung. .. Ultrasound: is a method that uses high-frequency sound waves that cannot be heard by the human ear and shines on the ovaries. The sample obtained from the echoing sound forms an image known as a tone histogram. Tissues, sacs, air cysts, and tumors will give different images on the chart, helping doctors diagnose ovarian cancer effectively. In addition, ultrasound also helps the doctor look at the density, structure, size of the ovaries, characteristics of the blood vessels and cysts if any. The doctor can choose the transvaginal ultrasound (transvaginal ultrasound, inserting the ultrasound probe into the vagina) or transabdominal ultrasound to examine the reproductive organs (tubal, ovary, uterus). bow) and other abdominal organs. CA 125 test: is a blood test that measures levels of CA-125 – an ovarian cancer biomarker that is often found to be higher than normal in women with epithelial ovarian cancer. However, doctors do not completely rely on this test for ovarian cancer because many other causes also cause high levels of CA-125 in the blood, such as endometriosis and adnexitis.

Xét nghiệm CA-125 chẩn đoán ung thư biểu mô buồng trứng

Bác sĩ lấy mẫu mô buồng trứng qua sinh thiết để chẩn đoán ung thư
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.