This is an automatically translated article.
Arterial blood gas testing helps to assess the patient's acid-base balance, ventilation status, and blood oxygenation status. The indicators to evaluate are important such as: pH, PaO2, PaCO2, HCO3,...
1. What is an arterial blood gas test?
Arterial blood gas is a test to evaluate the acid-base balance, ventilation status and blood oxygenation status of the patient.
The test will provide parameters such as blood pH , arterial blood carbonic pressure (PaCO2), plasma bicarbonate concentration HCO3-, arterial blood oxygen saturation (SaO2) and specific pressure fraction of dissolved oxygen in arterial blood (PaO2). Blood gas results are normal when:
pH: 7.35-7.45 PaCO2 : 35-45 mmHg HCO3-: 22-26 mmol/l PaO2: 80-100mmHg SaO2: 95-100%.
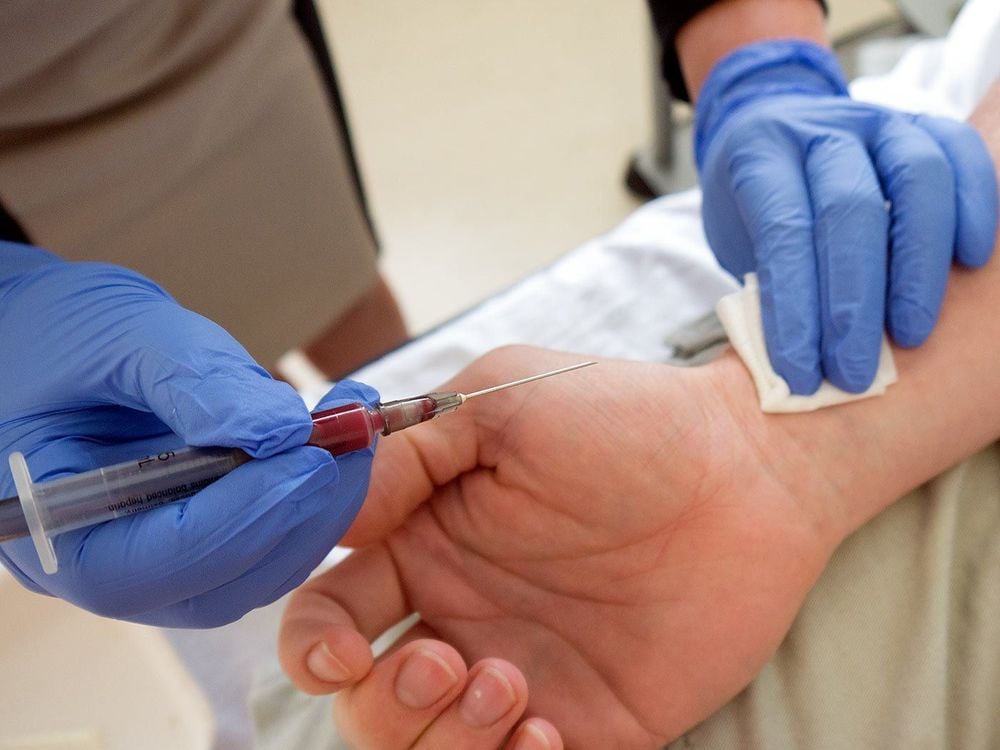
Cách lấy mẫu xét nghiệm khí máu động mạch
2. Meaning of HCO3 in blood gas results
Most of the arterial blood gas results calculate the value of HCO3- and residual alkalinity in order to find out the metabolic causes in acid-base disorders, or the compensatory mechanism of metabolic acid-base disorders. HCO3- and excess alkalinity are particularly useful when the cause of acid-base disturbance is a combination of metabolic and respiratory problems. Laboratory results for normal HCO3- and residual alkalinity may rule out metabolic acid-base disorder.
To evaluate acid-base, it is necessary to consider the following indicators:
pH: Acidic blood when pH < 7.35, alkaline blood pH> 7.45. Within 7.35-7.45 may be normal or mixed acid-base disorder. PaCO2 and HCO3-: To determine whether the acid-base disorder is due to metabolic or respiratory causes.
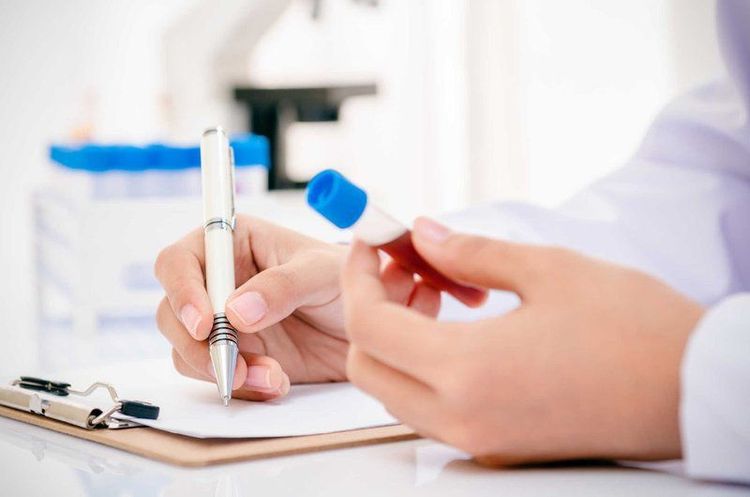
Đánh giá toan kiềm cần dựa vào các chỉ số tiêu chuẩn
Any questions that need to be answered by a specialist doctor as well as customers wishing to perform an arterial blood gas test at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System worldwide. country or register online HERE.
MORE
What is the arterial blood gas test for? PaO2, PaCO2, FiO2 indexes in arterial blood gas test results how dangerous are acute respiratory failure?