This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Dr., Doctor Tran Nhu Tu and Master, Doctor Le Thi Hong Vu - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Danang International Hospital.
Chest X-ray is an important subclinical test technique, effectively supporting doctors in diagnosing lung diseases such as tuberculosis, pleural effusion, pulmonary embolism....
1. Overview of chest radiography technique
The chest X-ray technique is done in a special room. Use an X-ray tube attached to a large metal rod. Patients will be instructed to remove jewelry, metal accessories, wear a thin shirt and stand in front of a plate containing X-ray film or a special receiver to help record the structure of the chest. Images of the lungs, airways, blood vessels, lymph nodes, heart, and ribs are all evident on the x-ray.Based on this chest X-ray, the doctor can evaluate and then give results about the patient's health status, specifically:
Determine whether the patient has lung problems such as tuberculosis, pneumonia , pleural effusion , lung cancer , atelectasis , acute pulmonary edema , lung tumor , pleural tumor , mediastinal tumor... Check if there is fluid or air inside the pleura, surrounding space lung or not. Whether the rib system is damaged, affected in case of trauma or not. A chest X-ray is usually done during a physical exam and screening for lung disease. The value of radiographs in the diagnosis of lung disease is second only to the diagnosis of bone diseases.
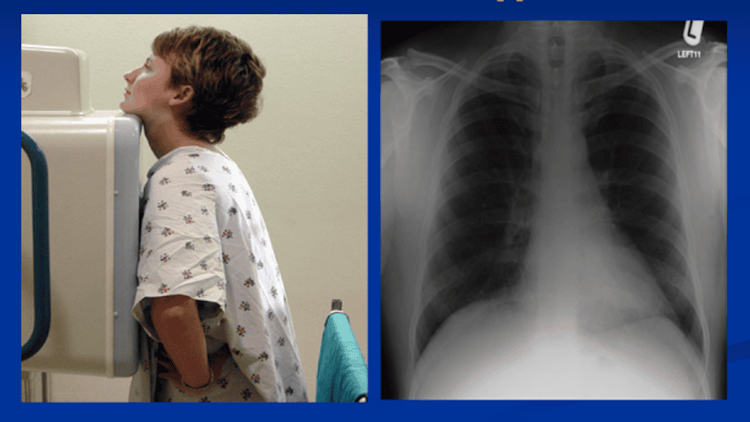
Tư thế chụp Xquang lồng ngực
2. Chest X-ray methods
Straight X-ray: The patient is instructed to take the image in a standing position in the back - anterior direction. If the patient is not able to stand, imaging can be done in the Fowler position (low, semi-standard, standard or elevated position). Should not be taken in the lying position because it will make it difficult to diagnose effusion, pneumothorax.Tilt X-ray: Often used to clarify suspected mass lesions that are difficult to see on straight film. The purpose of lateral imaging is to segment the mediastinum and localize the lesion to lobes and lobes of the lung. If any side injury is suspected, take that side.
Computed tomography (CT) is a particularly effective method to help diagnose lung tumors, mediastinal tumors and bronchiectasis. Especially high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) is very valuable in the diagnosis of bronchiectasis.
In addition to the above methods, there are a number of other chest X-ray methods such as high-voltage imaging, bronchoscopy with contrast pump... but are rarely applied.
Evaluation criteria for a beautiful chest X-ray film
Patient position is suitable: The patient's standing is balanced, without crooked or deviated. On the film, the sternoclavicular joints are symmetrical on both sides, the shoulder blades are outside the lung field. Photo taken when the patient takes a deep breath. Appropriate imaging method: In terms of facilities, KV and mA voltages, if applied to a suitable X-ray tube, will produce an X-ray current of moderate intensity, not too young or too old to help contrast the film. good, not too black or white, from which we can see the shadow of 3, 4 thoracic vertebrae of the patient. He can take all the lung fields, no deviation: The upper photo must take all the C6 cervical vertebrae, the bottom 2 diaphragmatic arches, the two sides capture all the rib cage and the soft part of the chest wall.
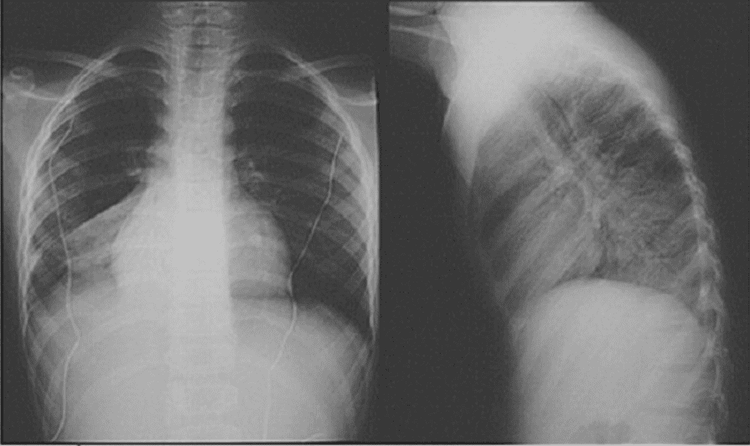
Xquang tim phổi tư thế thẳng và nghiêng
3. Normal chest radiograph and tuberculosis
3.1. Normal chest radiograph In straight lung film: The radiograph shows the medial end of the ribs symmetrically through the posterior spine of the dorsal spine. Pulmonary ridges are also seen about 1cm from the periphery, faintly the dorsal spine behind the heart shadow. Film is taken when the patient inhales, clearly shows the diaphragm across the head in front of the 6th rib, the right shoulder blade separates from the lung field.In the lateral lung film: taken when the patient breathes in, the posterior arch of the ribs overlaps, and the posterior diaphragmatic contours are quite clear.
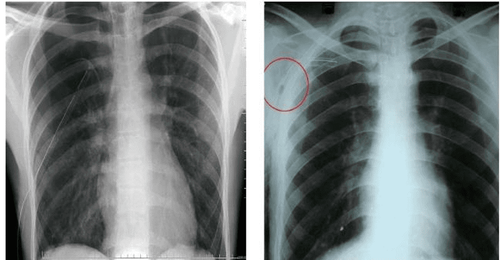
3.2. X-ray picture of pulmonary tuberculosis The condition of pulmonary tuberculosis shown on X-ray is different according to each stage, specifically:
Primary infection: The most typical picture is a dumbbell shape formed by a primary TB infection, lymphatic ducts. vascular and hilar lymphadenitis. Early infiltrates : X-ray image shows uneven opacities, nodules, small nodules; The borderline is not clear and appears to be suprapulmonary. Chronic: The chest radiograph shows fibrous nodules, collapsed lung, cavernous, nodular... Tuberculosis: The lungs appear scattered with small fuzzy dots like millet seeds covering both lungs.
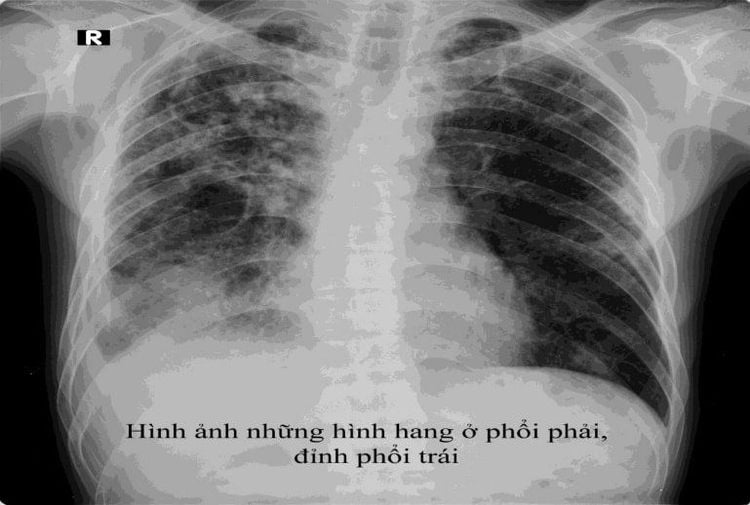
Hình ảnh Xquang lao phổi
Chest X-ray is one of the basic tests in the diagnostic approach of patients with suspected pulmonary embolism, further study of chest radiograph results can help improve the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism and other complications. other lung diseases.
In general, chest X-ray is considered an available, affordable, simple diagnostic method, but plays an important role in identifying specific clinical conditions such as pneumothorax. This is also one of the most widely used testing and evaluation methods by many hospitals and medical facilities today.
Dr. Tran Nhu Tu with over 20 years of experience, of which 3 years as Deputy Head of the Paraclinical Department - Hoa Vang Hospital, 16 years as Deputy Head of Imaging Department at Da Nang Hospital, 4 years as Head of Department Diagnostic imaging at Da Nang Obstetrics - Pediatrics Hospital; Dr. Tu makes accurate diagnoses, minimizes errors based on acquired images, and is ready to serve patients 24/24 in emergencies and emergencies.
Dr. Tu has participated in domestic and foreign training courses such as: Master of Radiology, Research Fellow in Diagnostic Imaging at Hanoi Medical University, Diagnostic Imaging at CHU Reims - France, Electricity interventional radiology at Winterthur hospital - Switzerland, interventional radiology at Singapore General Hospital... before being the head of the Department of Diagnostic Imaging at Vinmec Danang Hospital as it is now.
Master doctor Le Thi Hong Vu has good English, has participated in many short-term and continuous training courses on annual diagnostic imaging. The doctor has more than 7 years of experience as a doctor in the field of diagnostic imaging, especially ultrasound.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
Recommended video:
Periodic health check at Vinmec: Protect yourself before it's too late!
SEE MORE
Relationship between X-rays and Pregnancy In what case is X-ray of the uterus and fallopian tubes (HSG scan) done? Mammomat Inspiration Mammography - An effective "assistant" in the diagnosis and treatment of breast tumors