This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Quang Duc - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International HospitalBone scintigraphy is a nuclear medicine method that uses radioactive material to record the entire skeletal system of the body. So what is a bone scan for?
1. What is a bone scan?
Bone scintigraphy is a technique that uses radioactive isotopes to create images of bones. The patient is injected intravenously with chemicals capable of emitting radiation. These substances travel from the blood into the bones, accumulating in areas where bone cells are repairing, repairing or breaking down (bone marrow is working), thereby helping to detect bone abnormalities.
2. What is a bone scan for?
Bone scan is indicated in the following cases:
Bone cancer: Diagnosis of bone cancer, or cancer that has spread to the bones such as breast cancer, lung cancer, thyroid cancer, kidney cancer. Unexplained bone pain: Diagnosis of bone pain causing back pain but unknown cause. Trauma: Fracture but not detected by X-ray. Bone lesions and pathologies: Bone scan helps to detect bone cysts, bone tumors, arthritis, infected bone marrow, osteomalacia, osteoporosis, ... Helps locate to perform techniques aspiration, bone biopsy. Monitor and evaluate the response of bone graft surgery, disease treatment by methods such as chemotherapy, radiotherapy, ...
3. Meaning of bone scintigraphy
3.1 Bone scintigraphy helps to detect bone metastases Cancer Organizations and bone systems are very susceptible to being affected and metastasized by cancer. Depending on the type and stage of cancer, the rate of metastasis will vary. Common bone metastases include lung cancer, breast cancer, and prostate cancer.

Initially, bone lesions due to metastatic cancer may not show any symptoms. Then, at a late stage, the cancer spreads to the bone causing symptoms such as joint pain and pain due to spinal cord and nerve compression, which can cause pathological fractures.
Bone scintigraphy is a method to help detect bone metastatic cancer with the advantage of high sensitivity and accuracy, and allows evaluation of the entire skeletal system, compared with other methods such as X-ray. (only detectable lesions that lose 30-50% of bone density), computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging (only detect lesions when metastases cause localized symptoms). Bone scan results are the basis for screening, diagnosing, giving reasonable treatment regimens and monitoring and evaluating the patient's response to treatment of some diseases, especially cancer by different methods. such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
Bone scintigraphy is widely used to help detect bone metastases in lung cancer, breast cancer and prostate cancer.
Breast cancer with bone metastases: Breast cancer is a type of cancer that often metastasizes to bones, the most common bone damage site is the sternum, ribs. Initially, metastases do not cause bone pain symptoms, if early bone scan, combined with clinical examination, X-ray, and laboratory tests, it will help evaluate good breast cancer treatment results. than. Bone metastases: Lung cancer that has spread to the bones can spread to distant sites such as the bones of the extremities. Bone metastases: Bone scintigraphy allows the assessment of prostate cancer metastasized to bone with higher sensitivity and accuracy than other methods.
3.2. Bone scans for diagnosis of bone cancer and bone tumors Bone scans can help diagnose primary bone cancers. However, this technique allows only local bone scintigraphy and does not have the advantage of invasive assessment (compared to magnetic resonance imaging) to consider before surgical treatment. However, in some cases, performing a bone scan will also reveal other bone sites of injury.
For benign bone tumors, bone scintigraphy is performed to aid in the diagnosis when radiographs do not accurately assess the disease.
3.3. Bone scan diagnoses some metabolic diseases in bone Bone scan helps to evaluate the damage of the skeletal system caused by some metabolic diseases in bone. However, it is important to distinguish these lesions from metastatic bone cancer. Some common metabolic diseases in bone such as:
Osteoporosis: Bone scan is performed to survey the entire skeletal system and detect abnormalities of damage caused by osteoporosis.
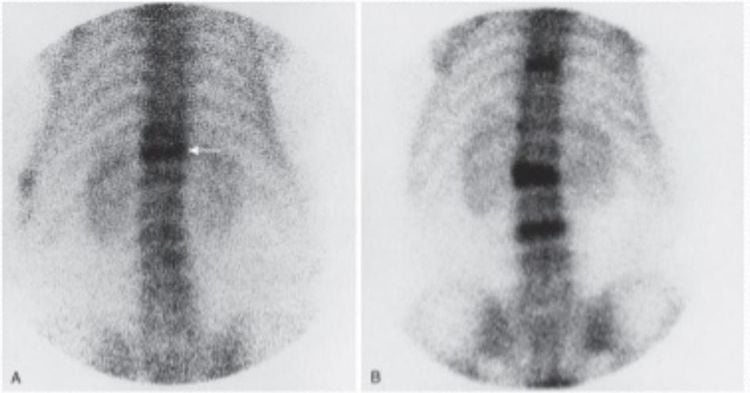
Hyperparathyroidism: The disease often affects the skull, jaw, ribs, and sternum. Perform bone scintigraphy to diagnose hyperparathyroidism because of the higher radioactivity in bone. Paget's disease: The disease usually affects the pelvis, femur, humerus, shoulder blade, and femur. Bone scintigraphy allows assessment of the extent of the lesion. Osteomyelitis: The most common site of osteomyelitis is the metatarsal bone (mainly in diabetics), the axial bone. If you have spinal osteomyelitis, the damage can spread to many other bones by traveling through the bloodstream. Bone scintigraphy is a highly sensitive technique used to diagnose osteomyelitis. Necrotic bone, infarct in the bone: The bone scan image will be different depending on the time of performing the bone scan, the radiation defect when taking in the acute stage of the disease, the increased radioactivity when taking in the disease phase. bone healing. Bone scintigraphy is often used to diagnose necrotic lesions of the femoral head. Bone trauma: In some cases, a bone scan helps to detect trauma caused by other methods such as X-rays. Microshock fracture: The cause of a micro-concussion fracture is an imbalance of bone absorption and replacement. Bone scintigraphy is a highly sensitive technique, allowing early detection of micro-trauma fractures in the bone, making treatment more effective. Unexplained bone pain: Pain occurring in areas such as the low back, accompanied by edema, muscle weakness due to impaired sympathetic nerve reflexes can be detected by bone scintigraphy. Depending on the stage of the disease, the images taken will vary. For the diagnosis of bone pain of unknown etiology, bone scintigraphy is a technique with high specificity but low sensitivity. Postoperative evaluation: In some surgery for bone grafting such as hip replacement, bone scintigraphy is applied to detect inflammation if any.
Bone scintigraphy is a modern imaging method, which is of great significance in detecting lesions such as metastatic bone cancer.
Vinmec International General Hospital uses the SPECT/CT Discovery NM/CT 670 Pro system with the most modern 16-row CT of the world's leading medical equipment maker GE Healthcare (USA), for high quality images. , which helps in early diagnosis of diseases to be investigated.
Vinmec medical staff are experienced, well-trained at home and abroad, so they can advise and support customers during the shooting process, even for foreign customers. Vinmec hospital's high quality service will satisfy customers.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.