This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Doctor Pham Anh Tuan - Vinmec Stem Cell Research Institute and Gene Technology
Mass Spectrometry (MS) is a technique for measuring the mass to charge-m/z ratio of ions. From the results of that mass and structure, we can know about the biological function of the analyzed molecule. Tandem Mass Spectrometry (MS/MS) also shows chemical components at low or even very low concentrations in the analytical mixture.
Currently, there are fewer mass spectrometry-based diagnostic methods included in clinical routines compared with traditional analytical systems, immunohistochemistry. However, the use of mass spectrometry in clinical diagnosis has increased in recent years. Clinical applications of mass spectrometry include: screening and target analysis, where screening aims to detect biomarkers for disease, toxicology, and pharmaceuticals. In addition, the accuracy, sensitivity and assurance of the results are specific to the target quantitative analyses.
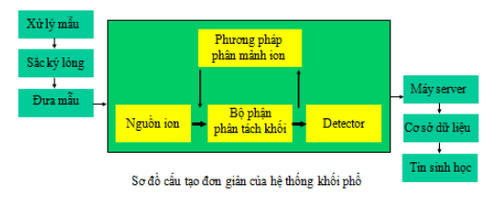
Sơ đồ đơn giản của hệ thống khối phổ
Newborn screening of inborn errors of metabolism (NBS-IEM) is defined as a complete system that includes training; screening; monitor, test and confirm abnormal results; diagnose; treatment; evaluate the effectiveness. OMIN has data on 6,000 genetic diseases in humans, whose genetic disorders must be treated to ease symptoms or protect against the effects of the disease. Newborn screening is appropriate for individuals, families, and society as a whole, as long as screening is started early. And MS/MS has become an important and popular technique in newborn screening for congenital metabolic defects in many advanced countries around the world (Table 1):
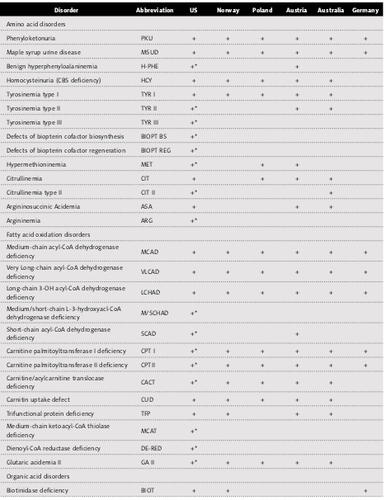
Bảng 1. Sàng lọc sơ sinh các khiếm khuyết trao đổi bằng khối phổ ở một số nước phát triển
Trong việc phát hiện các chỉ số sinh học mới của Hội chứng suy giảm hô hấp cấp trầm trọng (SARS) , MS đã được ứng dụng rộng rãi
MS is also used to analyze and detect new biomarkers for autoimmune diseases, cardiovascular diseases and severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (SARS) or endocrine disorders in women and children.
We all know, vitamin D deficiency will lead to bone disorders as well as other diseases. There are different methods to determine the serum vitamin D concentration, usually by quantification of 25-hydroxyvitamin and the results are always elevated in clinical laboratories. Until recently, this increased parameter was evaluated by immunoassay, but it failed to distinguish 25-hydroxyvitamin D2 and D3. Through Liquid Chromatography-LC-MS/MS, it is now possible to easily distinguish these two substances, thus making diagnosis more efficient with sensitivity. high.
References
Vogesera M., Zhang V., Understanding the strategic landscape surrounding the implementation of mass spectrometry in the clinical laboratory: A SWOT analysis, 2018; 9: 1-6 Kushnir MM, Rockwood AL, Bergquist J: Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry applications in endocrinology. Mass Spectrom Rev, 2010; 29: 480–502 Oyben T: Expanded newborn screening and confirmatory follow-up test- ing for inborn errors of metabolism detected by tandem mass spectrome- try. Clin Chem Lab Med, 2013; 51: 157–76 McKusick-Nathans Institute of Genetic Medicine; Johns Hopkins University. Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man OMIM; 2011. Available from: URL: http://omim.org/ Rousseau F, Giguère Y, Berthier MT et al: In: Prasain JK (ed.), Tandem Mass Spectrometry Applications and Principle. 30, InTech, 2012; 722–50 Pollitt RJ: Newborn blood spot screening: New opportunities, old problems. J Inherit Metab Dis, 2009; 32: 395–99 Chace DH, Kalas TA, Naylor EW: Use of tandem mass spectrometry for mul-tianalyte screening of dried blood specimens from newborns. Clin Chem, 2003; 49: 1797–817 Wallace AM, Gibson S, de la Hunty A et al: Measurement of 25-hydroxyvitamin D in the clinical laboratory: Current procedures, performance characteristics and limitations. Steroids, 2011; 75: 477–88 Herman J, Shushan B: Clinical applications. In: Prasain JK (ed.), Tandem mass spectrometry applications and principle. 29, InTech, 2012; 673–721
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.