This is an automatically translated article.
The article is made by Master, Doctor Ton Nu Tra My - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
Breast cancer is a malignancy with a high mortality rate in women. Diagnosis and staging play an important role in treatment. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy is one of the means of distinguishing between benign and malignant tumors.
In breast cancer, the first mammographic magnetic resonance imaging technique was applied using the phosphorus atom (P31) metabolised in the breast lesion, thereby detecting the increased metabolism in the mass. Cancer helps increase the ability to diagnose, distinguish cancerous or noncancerous lesions and monitor response to treatment. Currently, magnetic resonance imaging (MRS) uses the atom of Hydrogen (H1) because it is more sensitive than the Phosphorus atom.
1. Designation
There is a suspected cancerous breast tumor requiring further assessment of tumor metabolism. Evaluation of response to treatment for breast cancer.
2. Contraindications
2.1. Absolute contraindication
Contraindications related to magnetic resonance imaging: implantation of metal-based electronic devices such as pacemakers, defibrillators, cochlear electrodes, automatic subcutaneous continuous injection machines, immobilization devices Intracranial metal fixation, eye socket, blood vessel < 6 months, thoracic metal foreign body, severe disease condition requires emergency resuscitation equipment for monitoring and treatment. Contraindications related to contrast agents: renal failure with glomerular filtration rate < 30 mL/min, pregnancy or lactation

Chống chỉ định tuyệt đối chụp cộng hưởng từ phổ tuyến vú đối với phụ nữ đang cho con bú
2.2. Relative contraindications
Metal surgical instruments > 6 months Fear of the dark, fear of narrow spaces, fear of loneliness.
3. Mammography Magnetic Resonance Imaging Procedure
3.1 Preparation before proceeding
Performer: radiologist and radiologist specialized in radiology. Equipment: resonator 1.5 Tesla or larger Medicine: can be used to support sedation in cases of patients with fear of the dark, claustrophobia. Patient: can have a light meal, it is not necessary to fast before the scan. Instructions and explanations of what to do before filming begins. Patient removes contraindicated items.
3.2. Steps to conduct a mammogram
3.2.1 Patient's position
Lying on your back on the magnetic resonance imaging table Positioning the signal receiver Adjust the table to the sewing chamber and locate the chest area to be examined Adjust the controller to capture breathing, reduce image noise.

Bệnh nhân nằm ở tư thế ngửa trên bàn chụp cộng hưởng từ
3.2.2. Pulse sequences before injection of magnetic contrast agent
Capture initial positioning. The sequence of T1W pulses in the horizontal plane to take a wide field of view includes: ganglion fossa, supraclavicular and anterior chest wall muscle. T2W pulse sequence with transverse fat removal. T1W pulse sequence with transverse fat removal. Diffusion B800 – B1000 Diffusion Pulse Imaging.
3.2.3. Pulse sequences after injection of magnetic contrast agent
Dynamic pulse sequence: T1W pulse sequence with fat removal after injecting magnetic contrast agent with dose of 0.1 Gadolinium/kg body weight, injection rate of 2ml/sec at 1 minute, 2 minutes, 3 minutes, 4 min, 5 min in cross-section. The T1W pulse sequence is delayed in the longitudinal plane. Plot the average curve graph to evaluate drug elimination kinetics at the lesion site.
3.2.4. Spectral pulse sequences at the lesion site
Pulse spectrum in the area with the enhancement mass to evaluate the metabolic rate of the suspected lesion through Choline, Lipid and Lactate peaks.
Many reports have described the association of breast cancer with broad-spectrum peaks centered around = 3.2 ppm. This peak is mainly derived from free choline, phosphocholine and glycerophosphocholine and is commonly referred to as total choline (tCho).
Studies show that total choline (tCho) is increased in melanoma.
However, mammography magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) is technically challenging. Because breast tumors often have many foci, relatively small, mixed with fatty tissue in the breast. For these reasons, mammogram magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) is less commonly used in clinical practice than brain MRS or prostate MRS.
3.3. Read the results of the mammogram with magnetic contrast injection
Films must meet the requirements of clearly showing anatomical structures such as glandular tissue, anterior and posterior fat layers, nipples, skin, chest wall muscles, axillary fossa and supraclavicular areas. Determine whether there is a lesion, mass, cystic lesion, structural disorder, thickened skin, retraction, degree of infiltration into adjacent structures such as chest wall muscle. Investigate the ganglion groups.
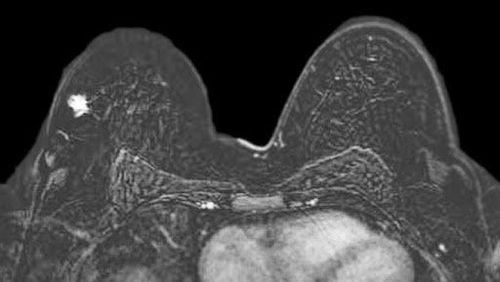
Thông qua hình ảnh, bác sĩ chuyên ngành đọc tổn thương, mô tả trên máy tính có lưu trữ phim chụp và đưa ra kết luận
Assess the enhancement kinetics of the lesion site: whether the lesion is enhancing. Progressive, plateau, or excretory infiltration. Evaluation of the level of metabolism is based on the comparison ratio of Choline, Lipid, Lactate levels over the scans during treatment. A doctor specializing in radiology is the person who reads the lesion, describes it on a computer with stored film, and makes a conclusion whether or not it is necessary to inject the next contrast agent. Print the film and diagnostic results. More expertise on results and recommendations for testing if needed
4. Follow-up during and after magnetic resonance imaging
During magnetic resonance imaging, closely monitor vital signs (pulse, blood pressure, breathing rate), consciousness and focal neurological signs of the patient.
Trong quá trình chụp cộng hưởng từ theo dõi huyết áp của người bệnh
5. Complications and treatment direction
Some patients with agoraphobia, solitude, or claustrophobia may be fearful and agitated. The technician or doctor needs to guide and encourage the patient to comfort or use sedatives in case of indication.
For adverse events related to contrast agents, it is necessary to recognize them early to diagnose and manage complications of contrast injection.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space. Customers when choosing to perform tests here can be completely assured of the accuracy of test results.
Master. Dr. Ton Nu Tra My is currently a Doctor of Radiology, Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital. Dr. Tra My used to be a lecturer in the Department of Diagnostic Imaging, Hue University of Medicine and Pharmacy and had a long time working at the Department of Diagnostic Imaging, Hue University of Medicine and Pharmacy Hospital.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, customers can call Hotlines of hospitals or register online HERE.
Articles refer to the source: NCBI