This is an automatically translated article.
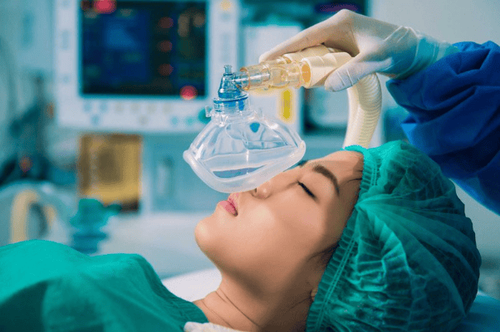
The article was consulted with an Anesthesiologist - General Surgery Department - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Maintenance of anesthesia is the next phase of induction (induction). At this stage, the patient has fallen into a state of sedation, loss of consciousness, loss of sensation, the body gradually stabilizes after the effects of the anesthesia and surgery will often begin at this stage. However, at this stage, patient safety may still be threatened by the effects of surgery and anesthesia as well as manifestations of the patient's underlying disease, thus This requires close monitoring for prevention, early detection and management of complications.
1. What is maintenance anesthesia?
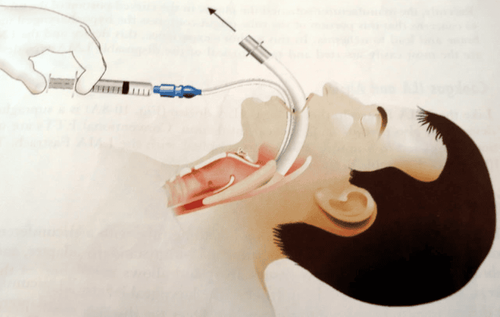
After the induction phase, using anesthetic drugs such as sedatives, hypnotics, analgesics, muscle relaxants, anti-emetics, etc., are enough for the patient to go into a state of temporary loss of consciousness, relieve pain, and intubate. tracheal intubation, followed by a maintenance phase of anesthesia.Maintenance of anesthesia is started right after induction of anesthesia (anesthesia induction), when the patient's condition is stable, lying still, breathing, circulation, muscle relaxation, the surgeon will perform surgery. During this period until the anesthetic is stopped, the patient will gradually regain consciousness.
At this point, even though the patient has fallen into a coma, he still has to use a certain amount of anesthesia by intravenous or inhalation to maintain anesthesia as well as relieve pain and relax muscles suitable for each type of surgery. and lasts for the duration of the surgery..
2. Drugs used to maintain anesthesia
Some drugs are commonly used to maintain anesthesia such as: inhalation anesthetics, intravenous anesthetics, muscle relaxants, analgesics....2.1 Inhalation anesthetics are commonly used Nitrous oxide As an anesthetic colorless, gaseous.
The drug is used in combination with other drugs for anesthesia in major and prolonged surgery.
Nitơ oxit là thuốc gây mê thể khí không màu
Absolutely: Patients with traumatic brain injury causing loss of consciousness, pneumothorax. Relative: Patients with intestinal obstruction, shock, bleeding, hypoxia, heart failure, coronary disease, sickle cell disease. Effects of the drug:
On the central nervous system: With concentrations above 60%, it causes loss of consciousness, mild pain relief, and does not affect the vomiting center. Mild increase in intracranial pressure. The anesthetic effect is weak, so when used in combination with other anesthetics. Cardiovascular: Reduces myocardial contractility, slightly increases heart rate. Blood pressure is less affected. Undesirable effects:
Lack of oxygen when blood concentration is greater than 70% May cause nausea, vomiting. Causing gas expansion in natural cavities. Halogen anesthetics
Are volatile, colorless, liquid anesthetics, including some drugs such as isoflurane, Sevorane, Halothan...
Drugs used in maintaining anesthesia in surgery in adults and children children, outpatient anesthesia
Contraindications:
Absolute: Personal or family history of malignant hyperthermia, Halogen sensitivity, Porphyria relative: Pregnant women, people circulatory volume deficiency disease. Effects of the drug:
Effects on the central nervous system: Loss of consciousness, the drug has no analgesic effect, inhibits the respiratory center, temperature and vasomotor, reduces oxygen consumption for brain cells. Cardiovascular: Decrease myocardial contractility slightly, increase heart rate, reduce myocardial oxygen consumption. Respiratory: Bronchiectasis, decreased tidal volume and respiratory rate. Has little effect on the liver, causes muscle relaxation and reduces intraocular pressure. Undesirable effects:
May cause complications of edema, laryngospasm leading to respiratory failure Vomiting and nausea Malignant fever.
Tác dụng phụ của thuốc gây mê nhóm halogen có thể gây suy hô hấp
Thiopental Indicated for induction and maintenance of anesthesia in combination with other drugs.
Contraindications:
Absolutely: Lack of resuscitation facilities should not be anesthetized for outpatients. Porphyrin metabolism disorder, bronchial asthma, history of allergy to Barbituric Relative: Liver failure, renal failure, coronary failure, severe heart failure. Anemia, malnutrition. Effects:
Has sedative, sedating, anesthetic effects depending on dose, no analgesic effect. Increased perfusion of brain cells. Cardiovascular: Decreased myocardial contractility, increased heart rate, increased coronary output, increased myocardial oxygen demand. Respiratory: Inhibition of the respiratory center, decreased tidal volume. Decreased blood flow to the liver and kidneys, possibly across the placenta, causing hypothermia. Undesirable effects:
Irritation, muscle tremors at the induction of anesthesia, cough, vomiting and nausea.
Thuốc mê đường tĩnh mạch được tiêm trực tiếp vào cơ thể
Contraindications :
Absolutely: disorders of porphyrin metabolism. Lack of means of resuscitation. Cerebrovascular accident, increased intracranial pressure, brain aneurysm. Coronary heart failure, high blood pressure, new myocardial infarction. Preeclampsia, eclampsia. Relative: hyperthyroidism. Addiction to alcohol and drugs. Epilepsy, schizophrenia. Eye surgery. Deep organ surgery, pharynx, bronchial surgery. Effects of the drug:
On the central nervous system: Anesthesia, analgesia, increased muscle tone. Cardiovascular: Increased arterial blood pressure, increased heart rate, increased cardiac output, increased myocardial oxygen demand. On the respiratory system: Reduce salivation, increase bronchial secretion in young children, do not lose respiratory reflexes, bronchiectasis. The drug can cross the placental barrier, but does not affect the fetus, causing increased intraocular pressure. Side effects: Causes vomiting and nausea, increased salivation, decreased or stopped breathing, hallucinations, stimulant psychosis.
Other safer intravenous anesthetics, sedation and sedation, less side effects, used more frequently in new anesthetic maintenance techniques such as TCI, TIVA are:
Propofol Etomidate
3. Possible complications during the maintenance of anesthesia
As with any phase of anesthesia, complications can arise during maintenance. Complications that can occur during the maintenance of anesthesia include:Hypoxia: The cause of hypoxia may be upper airway obstruction, upper airway obstruction, artificial respiration measures. Or the patient's position during surgery is not good, causing hypoventilation, imbalance of ventilation in the lungs, lung damage due to surgical manipulations or anesthesia, nitrous oxide anesthesia when the concentration is greater than 70% is dangerous. muscle is deprived of oxygen. Manifestations: Decreased Sp02, cyanosis, arrhythmia,... Excess C02: Due to obstruction of the respiratory tract, decreased pulmonary ventilation causes C02 retention, due to increased C02 production during malignant high fever, decreased absorption of C02 in exhaled air due to poor quality of calcium absorption, using nitrous oxide anesthetics over 70%. Patients have signs of systolic blood pressure increased, diastolic blood pressure decreased, pulse rapid, sweating. At this time, it is necessary to find the cause and increase ventilation to eliminate C02 through the airways.

Thừa CO2 gây ảnh hưởng trực tiếp tới huyết áp của người bệnh
The use of modern machines to monitor complications during surgery has helped to monitor, detect early and significantly reduce complications due to complications in the period. this caused.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.