This is an automatically translated article.
Lung cancer with brain metastases is a common complication of cancer. Approximately 10% of patients newly diagnosed with advanced non-small cell lung cancer have brain metastases. About 40 to 50% of brain metastases come from lung cancer.1. Lung cancer metastasis to the brain
Brain metastases are one of the most common intracranial tumors in adults, accounting for over 50% of all brain tumors. For cancer patients, metastasis to the brain is a common complication, especially in lung cancer, accounting for about 40-50% of lung cancer cases.Previously, patients with brain metastatic lung cancer often had a poor prognosis and rapid death. However, when medicine is increasingly developed along with the development of surgery, radiation therapy, radiation surgery and chemotherapy, it has reduced the mortality rate, extended the survival time, and at the same time improved the quality of life for patients. more sick people.
2. Clinical manifestations of lung cancer metastasis to the brain
Patients who are being treated for any tumor in any location often have neurological symptoms or patients have not been diagnosed with cancer, the first manifestation is craniocerebral symptoms including:Headache: this is Symptoms usually occur in about 40 to 50% of patients with brain metastases. The rate is increasing with multifocal metastasis, large metastatic tumor size or posterior fossa brain metastasis. Headaches are aggravated by movements that increase intracranial pressure such as coughing and sneezing. Classic early morning headaches are uncommon. The characteristics of headache patients that often point to brain tumours include: nausea and vomiting, change in pattern to the previous headache, abnormal neurologic findings, and worsening symptoms. Syndrome of increased intracranial pressure such as headache, nausea, papilledema, impaired consciousness,... Focal neurological signs: present in about 20 to 40% of patients, including motor paralysis, sensory disturbances, cranial nerve palsies, aphasia,... Changes in personality, behavior: this is a subtle sign, the patient is often angry, forgetful... Abnormal mood swings or personality manifests in 30 to 35% of patients. Seizures: New-onset seizures are symptomatic in 10 to 20% of patients. Stroke: Approximately 5% to 10% of acute stroke manifestations are caused by bleeding within the metastatic mass, hyperactivity, invasion, or arterial compression by tumor or tumor cell thrombosis. SEE ALSO: Metastatic brain tumor: What you need to know
Biểu hiện lâm sàng của ung thư phổi di căn lên não
3. Diagnosis of brain metastases lung cancer
Imaging methods will provide useful information, however brain biopsy is necessary in some cases for a definitive diagnosis.3.1 Computerized tomography (CT scan)
Tumor metastases to the brain usually occur in the border between gray matter, white matter in the cerebral hemisphere, with one or more tumors.Before drug injection: lesions are usually copper mass or decrease in density. Sometimes there is a higher density than the adjacent brain parenchyma due to bleeding in metastatic tumors, calcium deposition. After drug injection: nodular, mottled or ring-shaped (ring-shaped) enhancement lesions, often with extensive surrounding cerebral edema. Some cases have a mass effect with signs of compression of the midline and adjacent organs.
3.2 Magnetic resonance imaging
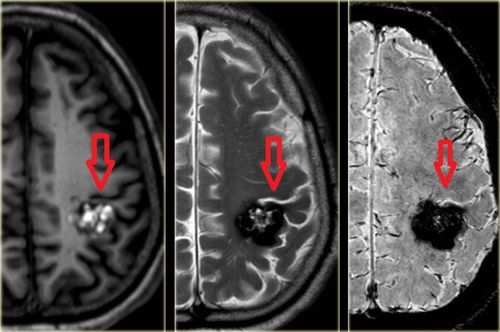
Magnetic resonance imaging is a valuable imaging tool for the diagnosis of brain metastases. Magnetic resonance imaging is more sensitive than CT scan of the brain in finding lesions in patients with suspected brain metastases and in differentiating brain metastases from other CNS lesions.The image of brain metastases lung cancer on magnetic resonance is as follows::
On T1 pulse, copper damage or hypointensity, when there is bleeding in metastatic tumor at early stage, may increase signal. After injection of the contrast agent, the drug is usually ring-shaped, which can be even or mottled. According to many experts, non-enhanced lesions on MRI are very rarely metastatic. On T2 pulses, FLAIR is often hyperintense and has signs of peritumoral cerebral edema. Imaging features on MRI that can help distinguish brain metastases from other intracranial lesions include:
Multifocal appearance. Location at the border of gray matter and white matter. The edge is clear. The amount of angioedema is greater than the size of the lesion. In addition, the diagnosis of primary tumor and tumor spread requires examination, testing, and systemic assessment to identify the primary tumor at the site of lung cancer metastasis to the brain.

Phương pháp điều trị ung thư phổi di căn não
4. Methods of treating brain metastatic lung cancer
4.1. The principles of treatment
The basic principle in the treatment of lung cancer metastasized to the brain is to combine local treatment (treatment of metastatic cancer lesions in the brain) and systemic treatment of primary lung cancer causing brain metastasis. The treatment of brain metastatic tumors is very necessary, especially for cases where signs of compression, brain edema appear... Because this is the cause of high mortality and should be a top priority. must handle. However, the treatment of metastatic brain tumors of lung cancer is still only local treatment, not treating the root cause, and the risk of metastatic recurrence is very high. Systemic treatment of primary lung cancer should be carried out in combination with local treatment. Accordingly, the treatment is based on the following factors:The type of tumor and the disease stage of the primary tumor. Neurological status of the patient. The extent of the spread of the primary tumor. Disease prognostic score. For patients with brain tumors that have not been identified as primary tumors, a brain tumor biopsy should be performed if the patient's conditions allow.
4.2. Surgical treatment
Indicated in the following cases:Tumor resection with a solitary brain tumor with mass effect. If there is no primary extracranial lesion, a diagnostic biopsy is required. Purpose of surgery:
Removal of part or all of the tumor Biopsy of the tumor to confirm the histopathological diagnosis or find genetic mutations if present.
4.3. Brain tumor radiation therapy
Brain tumor radiotherapy is a mainstay treatment for brain metastases, aimed at local control of metastatic tumors and other metastases not detected on imaging. There are 2 methods of brain radiation therapy, including:Whole brain radiation therapy
Indicated for cases of multifocal brain metastases (> 3 foci), or cases that cannot be operated on or radiosurgery due to technical conditions, equipment or contraindications, or widespread disease, poor general condition. Radiotherapy dose: The usual dose is 30Gy in 10 fractions (3Gy/day x 10 days). Other dosing patterns include 20Gy in 5 fractions, 37.5Gy in 15 fractions and 40Gy in 20 fractions. Brain tumor radiosurgery
Indicated for cases of brain tumor metastasis in one or 3 foci and tumor size <5cm, combined treatment with surgery or whole brain radiation therapy and the remaining lesions or recurrence after treatment such as: whole brain radiation therapy, surgery, chemotherapy. Radiation dose: Depending on tumor size as follows <2cm is 24Gy, 2-3cm is 18Gy, 3-4cm is 15Gy. However, the specific dose of radiation therapy depends on the individual patient's condition or the location of the lesion, the number of lesions and the type of histopathology. For patients who have received prior whole-brain radiation therapy, the recommended dose should be reduced by 30%.

Xạ trị khối u não nhằm kiểm soát tại chỗ khối u di căn và các ổ di căn khác tại Vinmec
4.4. Internally medical treatment
Symptomatic treatment:Corticosteroid therapy: used when increased intracranial pressure or paralysis. Usually dexamethasone dose 4mg, dose 4-8 vials/day, intravenous injection. Or use methylprednisolone 4-16mg, take 2-4 tablets a day, drink at 8 am after having a full meal. In some cases of brain edema lesions, methylprednisolone 40mg, 1-2 vials/day, can be used intravenously or mixed with 250ml of 0.9% NaCl solution intravenously. Synacthene can be used 1mg intramuscularly, 1 vial each time, 1-2 vials per week. Before stopping the drug, it is necessary to gradually reduce the dose of corticosteroids. Antiepileptic: if there is no seizure, then no prophylactic treatment is recommended. The commonly used antiepileptic drugs are depakine 500mg orally 1-3 tablets per day or tegretol 200mg 1-2 tablets per day, depending on the patient's response to the appropriate maintenance dose. Rehabilitation: exercise, speech. Pain relief treatment: when the patient has symptoms of headache or pain in other locations. Chemotherapy (systemic treatment)
Chemotherapy is a systemic treatment indicated for both primary tumors and metastatic brain lesions. Systemic treatment can be chemotherapy, targeted therapy, endocrine, immunological,... This treatment is carried out according to the systemic treatment regimen of the primary tumor combined with other treatment methods. in situ brain metastasis.
In summary, brain metastases lung cancer is a common complication, accounting for about 40-50% of lung cancer cases. The disease often has a poor prognosis, so cancer patients need regular health checkups. Especially when there are abnormal symptoms, it is necessary to immediately go to a medical facility for timely examination and treatment.
Department of Oncology - Radiation Therapy of Vinmec system is focused on carefully investing in expertise and equipment, bringing satisfaction to patients.
The leading team of domestic and international doctors: the doctors are all highly qualified, experienced, conscientious and knowledgeable, having worked in major hospitals of Vietnam, Korea, Russia, are trained specialized training in the country and abroad to bring the most effective and new treatment regimens to patients. Intensive technique, effective treatment of difficult cases: is the first and only hospital in Vietnam to successfully deploy robotic surgery. CT scan accurately detects cancer even when there are no symptoms. Applying advanced gene technologies to early detect the risk of 16 most common cancers. Deploying autologous immunotherapy and thermotherapy in combination with cancer treatment to effectively prevent recurrence. Continuously working for the community: always accompanies the community in free screening programs for common cancers: Breast, cervical, colorectal, etc. Thousands of patients cannot be screened for cancer, join hands with the community to fight back the dreaded cancer. To register for examination and treatment with the leading doctors of the Department of Oncology - Radiation Therapy, please register on the website, or register for an online examination.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.