This is an automatically translated article.
Articles written by MSc, BS. Dang Manh Cuong, Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
Lung cancer screening is very important, helping to detect the disease at the earliest stage, a great support for effective and cost-effective treatment. Low-dose CT lung scan is one of the imaging techniques used in effective lung cancer screening. This technique helps detect even very small nodules in the lungs, making early diagnosis effective.
1. What is lung cancer screening?
Screening is a screening process done to detect disease before symptoms appear. The aim of screening is to detect the disease at its earliest stage and treat it as early as possible.
Screening tests may include testing to check for blood and other body fluids, genetic testing to look for genetic markers associated with disease, and imaging to create patterns image inside the body. These tests are generally valid for the general population. However, because each individual's requirement for a particular screening is dependent on factors such as age, sex, and family history.
In lung cancer screening, people who are at high risk for lung cancer but have no signs or symptoms of the disease will have a low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) scan of the lungs. This is a tomography technique that combines special X-ray equipment with a computer to create multiple cross-sectional images or images of the inside of the body. LDCT produces images of sufficient quality to detect many abnormalities while using up to 90% less ionizing radiation than conventional chest CT scans.
In the past, two other techniques have been used to check for lung cancer: chest x-ray and sputum cytology. A chest X-ray creates images of the heart, lungs, airways, blood vessels, and bones of the spine and chest. Sputum cytology is a test in which a sample of sputum (sputum when a patient coughs) is viewed under a microscope to detect cancer cells. However, the use of chest X-ray and sputum cytology did not reduce the risk of death from lung cancer.
2. Who should be considered for lung cancer screening?
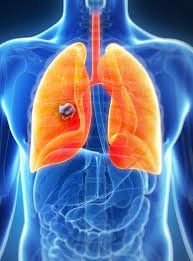
Lung cancer is cancer that forms in the tissues of the lungs, usually in the epithelial cells of the airways (trachea-bronchi). Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death in the United States and worldwide. Approximately 85% of lung cancer deaths occur in current or former smokers. The most common type is non-small cell lung cancer. Lung cancer that is found early (before it has spread to other parts of the body) is often more successfully treated. But unfortunately, when lung cancer is diagnosed, sometimes the disease has spread beyond the lungs.
3. Risk factors for lung cancer
Anything that increases an individual's chance of developing the disease is called a risk factor. Risk factors for lung cancer often include:
History or current heavy smoking; Exposure to asbestos dust, radon, radioactive material or other carcinogenic agents; Personal or family history of lung cancer; Certain chronic lung diseases; Old.
4. Why get screened for lung cancer?
4.1 National Lung Screening Trial Current recommendations for lung cancer screening come after the publication of a large, randomized clinical trial funded by the National Cancer Institute called the Clinical Trial. National Lung Screening (NLST).
NLST was performed to determine whether low-dose lung CT scans could reduce lung cancer mortality in people at high risk for the disease. The trial studied more than 53,000 men and women ages 55 to 74 with current or former heavy smokers at 33 sites across the United States. Each participant was randomly assigned to be screened with low-dose CT (LDCT) or standard chest X-ray once a year for three consecutive years. The trial found a 15 to 20 percent reduction in lung cancer deaths among trial participants screened with LDCT.
4.2 New Screening Proposal Based on this and other NLST results, the National Cancer Network, the American Lung Association, the American Society of Thoracic Surgeons, the American Society of Clinical Oncologists United States, the American College of Chest Physicians, the American Thoracic Society, and the American Cancer Society recommend that individuals at high risk for lung cancer consider annual screening with computed tomography. low dose lung.
5. What are the benefits and risks of lung cancer screening?
5.1 Benefits Because computed tomography can detect even very small nodules in the lungs, low-dose CT lung CT is particularly effective for diagnosing lung cancer at its earliest and most treatable stages. . CT scan is very rapid, so it is suitable for patients with difficulty breathing. CT scan is painless and non-invasive. No contrast agent required. There is no radiation left in the patient's body after the CT scan. The X-rays used in low-dose lung CT scans have no immediate side effects and do not affect any metal parts of your body such as pacemakers or artificial joints. Low-dose chest CT produces images of sufficient image quality to detect many abnormalities using up to 90% less ionizing radiation than conventional chest CT scans. Lung cancer screening with low-dose CT lung has been shown to reduce lung cancer deaths in high-risk patients. When cancer is found by screening, it is often in its early stages, and patients may need to undergo minimally invasive surgery and remove less lung tissue.
5.2 Risk A false-positive result occurs when a screening finds an abnormality but no lung cancer is found. Abnormal findings may require additional examination to determine if cancer is present. These tests, such as a follow-up CT scan or more invasive tests in which a portion of lung tissue is removed (called a lung biopsy). A CT scan that is probably normal even with lung cancer is called a false-negative result. A person who receives a false negative test result may delay seeking medical attention. Not all cancers detected by LDCT will be detected in the early stages of the disease. Screening for lung cancer may not improve your health or help you live longer if the disease has spread beyond the lungs to other areas of the body. There is a theoretically small risk of cancer from low dose radiation exposure. See the Safety page for more information on radiation doses.
6. What if an abnormality is found in a low-dose CT lung scan?
Lung cancer usually occurs as a lung nodule or an area of abnormal tissue in the lung. The majority (more than 95%) of these nodules do not represent cancer but are instead scarred areas in the lungs from previous infections or small lymph nodes. If your low-dose lung CT scan reveals a nodule larger than a certain size, your doctor will likely recommend a follow-up low-dose CT scan several months later to check if the nodule has changed in size. are not. In cases where the nodule is growing or suspicious, the doctor may recommend further evaluation with a more advanced examination such as a contrast-enhanced CT scan and/or removal of a small portion of the nodule (called a biopsy). lung). The pathologist can analyze cells from the biopsy sample under a microscope to determine if the nodule is malignant (cancerous) or benign.

If the nodule is cancerous, additional blood tests and imaging methods may be recommended to determine the tumor's stage. Additional imaging tests often include additional computed tomography (CT) scans of the body and may include bone scans or PET/CT scans. Treatment options and outcomes depend on the stage of the tumor.
Lung cancer screening is the most effective measure for you to detect and promptly treat lung cancer, protect your health and life. Currently, at Vinmec international general hospitals, there is a lung cancer screening package with many outstanding advantages such as: A team of highly qualified and experienced doctors; Having a full range of specialized facilities to diagnose the disease and stage it before treatment: Endoscopy, CT scan, PET-CT scan, MRI, histopathological diagnosis, gene-cell testing... There are full range of main treatment methods for cancer: surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, stem cell transplant....
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: radiologyinfo.org