This is an automatically translated article.
The article is expertly consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Thi Mai Anh - Doctor of Radiology - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital. The doctor has nearly 10 years of experience in the field of Diagnostic Imaging.Sinusitis is a common disease in all subjects, the disease causes some uncomfortable signs and can also cause dangerous complications. Sinus X-ray is a simple, non-invasive and minimally invasive method to help diagnose sinus disease.
1. Overview of sinus disease
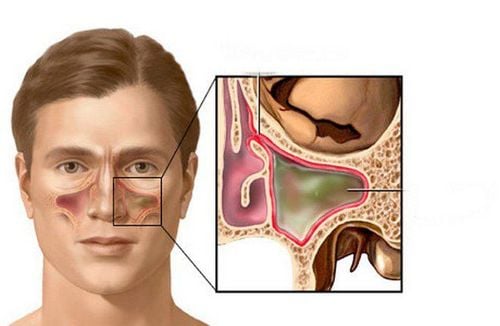
Sinuses are cavities of different sizes inside the bones of the face and skull. Inside the sinus is a layer of epithelium and is connected to the nasal cavity. The sinuses have the function of resonating sound, reducing the weight of the skull, humidifying and warming the air, and providing oxygen to nourish the skeletal system.Sinus structure includes group of anterior and posterior sinuses.
Anterior sinus: Includes maxillary sinus, frontal sinus, anterior ethmoid sinus. This is a group of sinuses that are susceptible to infection and can cause complications to neighboring areas. Posterior sinus: Includes sphenoid sinus, posterior ethmoid sinus. These sinuses are located deeper, so there is less infection. Sinusitis is an inflammation of the lining of the sinuses, which can be caused by many factors such as allergies, viruses, bacteria, fungi... To diagnose sinus disease, people use endoscopic methods and X-rays of the sinuses. Through X-ray images, it is possible to see the inflammatory niches, assess whether the sinusitis has spread to other areas or not.
2. Commonly used sinus X-ray positions
To determine the extent of damage to the sinuses including the anterior and posterior sinuses, it is necessary to perform different imaging positions. Some of the sinus X-ray positions commonly used in disease diagnosis include:2.1. Blondeau position sinus X-ray This position is used to examine the maxillary sinuses, frontal sinuses, and nasal cavities.
Patient position: Lying on the stomach, mouth open as much as possible, placing nose and chin in contact with the radiograph. X-rays will be projected from the back to the front; Note that in order to obtain a correct and clear X-ray image, the film must be balanced between the right and left sides. In order for the stony bones not to obscure the maxillary sinus, it is necessary to bring the two upper edges of the stony bones to the base of the 2 sinuses; If a foreign body is suspected in the sinus, it is necessary to take another position to determine the specific location. Read the results:
Normal: On the film, you can clearly see the light space in the nasal cavity. The bone walls are even and clear. Compared with the orbit, the maxillary and frontal sinuses are evenly lit.
Pathology:
Sinusitis: The image of the maxillary sinus or frontal sinus on the film will be blurred due to swelling or edema of the mucosa. The opening of the nasal cavity is also lost and the nasal sphincter becomes excessively enlarged or narrowed. To evaluate, compare with eye sockets. Translucent sinuses can also be caused by a degenerative condition of the mucosa, thickened mucous membranes, or because there is a lot of purulent fluid in the sinus cavity. In particular, in cases where the bone wall is not clearly visible, there may be a high risk of malignancy.
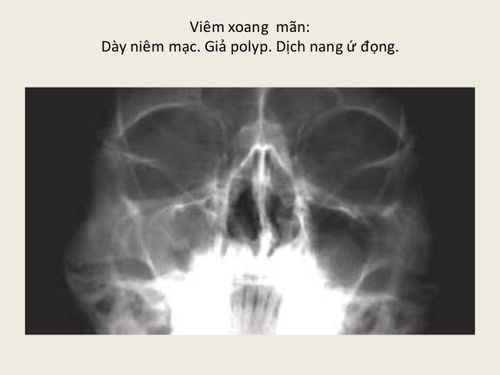
Thông qua hình ảnh X quang xoang, có thể thấy các hốc viêm, đánh giá tình trạng viêm xoang có lan sang các khu vực khác hay chưa
Photographer's position: Lie in a supine position with your head protruding from the edge of the table so that the top of your head can touch the film. X-ray direction goes from top to bottom. Read the results:
Normal: The sinuses are seen with a bright image, the septum can be clearly observed. Pathology: The sinus image is dense or blurred due to thickening of the mucosa or pus or polyps in the sinuses. If the septum of the septum cannot be seen clearly, it may be caused by a nasal polyp or, more seriously, by a malignant tumor that has destroyed and disappeared. 2.3. X-ray of the sinuses in Schuller's position With this sinus position, it helps to diagnose inflammatory diseases in the mastoid sinuses, ear and mastoid disease.
Patient's position: Lie on your side, similar to when taking a cephalometric scan. At the same time, always bend the ear flap forward, so that the new image does not press on the mastoid bone; The incident ray source will be inclined from the 2 ear axis from about 25 to 30 degrees. At this point, the X-ray will shine through the ear canal on the imaging side; Assessment of results:
Normal: Observable on film, the septum and septum are clearly visible.
Pathology:
If the patient has acute mastoiditis, the film image will show the septum is not clear and the cells are completely blurred due to the fluid. If the septum is gone and the septum is blurred, it is a sign of chronic mastoiditis. 2.4. Sinus X-ray Stenvers position Sinus X-ray in this position captures the entire stony bone from the lateral to the medial part of the mastoid process. Often applied to study traumatic brain injuries that cause transverse fractures, osteomyelitis or tumors in the cerebellar pons.
Patient's position: The patient is placed in the prone position, so that the head rests on the table along the upper border of the eye socket, nasal bone and cheekbone. Thus, the vertical plane of the skull makes an angle of 45 degrees with the vertical line without touching the table. The main ray axis in the posterior anterior direction focuses on the contralateral occipital region. Assessment of results:
Normal: Visible on radiographs of parts such as cochlea, inner ear, inner ear canal, vestibule and superior and outer semicircular canal and the apex of the stony bone. However, the posterior semicircular canal is normally not visible.
Pathology:
On the film, there is a fracture line, which means that the patient has a broken bone. If the inner ear canal is dilated, it may be a sign of nerve tumor VIII. Thus, combined with the clinical suspicion of which group of sinuses has the disease, the doctor can prescribe the most accurate position x-ray. A correct and early diagnosis greatly helps in treatment. Increase the effectiveness of treatment.
To protect health and prevent complications, patients need to go to a reputable hospital to conduct examination and treatment as soon as there are signs of sinus disease. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the leading prestigious hospitals in the country, trusted by a large number of patients for medical examination and treatment. Not only the physical system, modern equipment: 6 ultrasound rooms, 4 DR X-ray rooms (1 full-axis machine, 1 light machine, 1 general machine and 1 mammography machine) , 2 DR portable X-ray machines, 2 multi-row CT scanner rooms (1 128 rows and 1 16 arrays), 2 Magnetic resonance imaging rooms (1 3 Tesla and 1 1.5 Tesla), 1 room for 2 levels of interventional angiography and 1 room to measure bone mineral density.... Vinmec is also the place to gather a team of experienced doctors and nurses who will greatly assist in diagnosis and detection. early signs of abnormality in the patient's body. In particular, with a space designed according to 5-star hotel standards, Vinmec ensures to bring the patient the most comfort, friendliness and peace of mind.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.