This is an automatically translated article.
Lenvatinib is a cancer drug that belongs to the group of tumor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Patients treated with lenvatinib should be supervised by a physician experienced in the use of antineoplastic regimens.
1. What does Lenvatinib do?
Lenvatinib belongs to a group of drugs that act as tyrosine kinase inhibitors, used in the treatment of cancer. Drugs that slow or interfere with the growth of cancer cells.
2. How to use Lenvatinib?
Patients should read the drug information leaflet carefully before starting lenvatinib.
Take Lenvatinib by mouth as prescribed by your treating doctor, usually once daily. Swallow the capsule whole at a time.
Lenvatinib may have different packaging and dosage instructions based on your medical condition. To avoid dosage errors, consult your pharmacist for correct use. Dosage is also based on the patient's response to treatment, laboratory test results, and patient weight.
Use Lenvatinib regularly to maximize the most benefit from it. Do not increase your dose or use Lenvatinib for longer than prescribed because then not only will your condition not improve faster, but your risk of serious side effects will increase.
Because Lenvatinib has the potential to be absorbed through the skin and lungs, and may cause harm to the unborn baby, women who are pregnant or suspect that they may be pregnant should not use Lenvatinib or breathe dust from the capsule. .
Thuốc Lenvatinib làm chậm hoặc can thiệp vào sự phát triển của các tế bào ung thư
3. Side effects when taking Lenvatinib
Patients taking Lenvatinib may experience dry mouth, hoarseness, nosebleed, fatigue, weight loss, headache, muscle and joint pain, trouble sleeping, change in appetite, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting or loss of appetite. Nausea and vomiting are at risk of getting worse. In some severe cases, your doctor may prescribe medication to prevent or relieve nausea. In addition, to limit the feeling of vomiting, patients should eat many small meals, do not eat before taking the drug or limit too heavy activities.
Vomiting or diarrhea that doesn't stop can cause severe dehydration. Talk to your doctor as soon as possible if you notice any symptoms of dehydration, such as dry mouth, unusually frequent thirst, dizziness or lightheadedness.
To relieve dry mouth, suck on hard candies (sugar-free) or shaved ice, chew gum (sugar-free), increase water intake, or use a saliva substitute.
Patients treated with lenvatinib may experience pain or sores in the mouth and throat. Therefore, you should brush your teeth carefully / gently, avoid using mouthwash containing alcohol, regularly rinse your mouth with cool water mixed with baking soda or clean salt. It is best to eat soft or moist foods.
In addition, lenvatinib may lead to temporary hair loss. Hair will grow back normally once the medication is stopped.
People using Lenvatinib have an increased risk of some serious side effects. Even so, the benefit to patients from taking lenvatinib still far outweighs the risk of side effects.
Taking Lenvatinib can cause high blood pressure. Patients should have their blood pressure checked regularly and let their doctor know if the results are abnormally high. In this case, your doctor may control your blood pressure with medication.
Lenvatinib has a risk of leading to a decrease in blood calcium levels. Your doctor may recommend tests during treatment and instruct you to take calcium and vitamin D supplements.
Tell your doctor right away if you notice any serious side effects, including: Signs of kidney problems (such as change in the amount of urine, unusual foamy urine). often), signs of heart failure (such as shortness of breath, swelling in the ankles/feet, fatigue, unusual or sudden weight gain), symptoms of an underactive thyroid (such as weight gain, sensitivity cold weather, slow heart beat), muscle spasms, redness/pain/swelling/blistering on palms or soles, easy bleeding/bruising, slow healing of wounds.
Patients should seek medical attention immediately if any very serious side effects occur, including: symptoms of a heart attack (such as chest/jaw/wing pain) left arm, shortness of breath, unusual sweating), signs of stroke (eg, weakness on one side of the body, difficulty speaking, sudden loss of vision, confusion), stomach/intestinal problems (such as bloody stools, tarry stools, stomach-abdominal pain, vomiting blood, vomit that looks like coffee grounds), fast/irregular heartbeat, dizziness, fainting.
Lenvatinib has rarely led to serious liver problems (possibly fatal). Patients should seek immediate medical attention if they have any symptoms of liver damage, including: Persistent nausea/vomiting, loss of appetite, stomach/abdominal pain, yellowing eyes, jaundice, dark urine .
There have been cases of Lenvatinib causing a serious brain condition called RPLS (Reversible Posterior White Matter Syndrome). Patients should seek immediate medical attention if they notice any symptoms of RPLS, including: Persistent headache, seizures, sudden vision changes, mental/mood swings (eg. , confusion).
Serious allergic reactions to Lenvatinib are very rare. However, see your doctor immediately if you notice any symptoms of an allergy.
4. Caution when using Lenvatinib
Before having treatment with lenvatinib, tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are allergic to the drug, or to any other allergies.
In addition, patients should list to their doctor or pharmacist their medical history, especially: Liver disease, kidney disease, high blood pressure, history of heart attack / stroke, ever severe dehydration.
Lenvatinib has a risk of affecting heart rate (QT interval prolongation). A prolonged QT interval can cause tachycardia or irregular heartbeat (in some cases fatal) and transient symptoms (such as dizziness, fainting) that require immediate medical attention.
The risk of QT prolongation may be increased if you have certain medical conditions or are taking other medicines that prolong the QT interval. Before using lenvatinib, tell your doctor or pharmacist of all the medicines you are taking and if you have any of the following conditions: Certain heart problems (heart failure, slow heartbeat, QT interval prolongation in ECG results), family history of certain heart problems (QT interval prolongation, stroke).
Hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia can also increase the risk of QT prolongation, especially if you take certain medications (such as diuretics) or if you have conditions such as sweating. much, diarrhea or vomiting.
Lenvatinib may cause slow or difficult wound healing. So before having surgery, talk to your doctor about the risks and benefits if you are taking lenvatinib. Your doctor may then ask you to temporarily stop your lenvatinib treatment at least 1 week before surgery. Ask your doctor for specific instructions on when to stop and when to restart treatment with lenvatinib. Tell your doctor if you have a wound that won't heal or won't heal.
Older adults may be more sensitive to the side effects of lenvatinib, especially prolongation of the QT interval.
Because lenvatinib can be absorbed through the skin and lungs and cause harm to an unborn baby, women who are pregnant or suspected of being pregnant should not use lenvatinib or breathe dust from the capsule.
Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or planning to have a baby in the near future. Lenvatinib may affect an unborn baby. Your doctor may ask you to take a pregnancy test before you start taking lenvatinib. Talk to your doctor about safe forms of birth control while using lenvatinib and for at least 30 days after stopping treatment. If you become pregnant, tell your doctor right away about the risks and benefits of Lenvatinib.
It is not known whether lenvatinib passes into breast milk. Because of the risk of possible adverse effects in the neonate, breast-feeding while using lenvatinib and for at least 1 week after stopping treatment is not recommended.
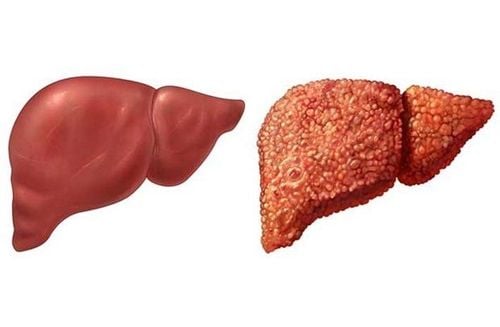
Hãy nói cho bác sĩ hoặc dược sĩ biết về tiền sử bệnh bản thân, đặc biệt là bệnh gan, bệnh thận
5. Interaction between Lenvatinib and other drugs
Drug interactions can affect the way the drug works or increase the risk of serious side effects. Therefore, patients should list all products they are taking (including prescription/nonprescription drugs, including herbal products) and share this information with your doctor and pharmacist. . Do not take, stop or change the dosage of any medicine without your doctor's approval.
6. Precautions when taking Lenvatinib
Do not share Lenvatinib with other drugs.
Patients should have a complete set of tests before and while you are taking Lenvatinib as directed by your doctor (such as blood pressure, electrocardiogram, urine protein, kidney / liver / gland function. thyroid, blood mineral levels). Follow-up appointment as scheduled.
If you forget to take a dose and it is more than 12 hours before your next dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it is less than 12 hours for the next dose, skip the missed dose. Do not arbitrarily supplement by doubling the dose.
Knowing the information about Lenvatinib before using it always brings positive effects and reduces risks for patients. Besides, if you have any questions, customers can send questions to Vinmec International General Hospital to receive in-depth advice from a team of doctors and pharmacists with many years of experience.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: webmd.com