This is an automatically translated article.
The Schatzki ring is essentially a circular membrane of the mucosa and submucosa of the esophagus. The Schatzki rings appear as thin membrane structures that do not contain any muscular buffering but have the potential to cause narrowing of the esophageal lumen. Accordingly, Schatzki's ring is sometimes found as an explanation for dysphagia, choking on upper gastrointestinal endoscopy.
1. What is the Schatzki ring of the esophagus?
Richard Schatzki was a famous radiologist who described a ring-like structure in patients with dysphagia in papers between 1953 and 1963, and that structure later bore its name. he.
Accordingly, the ring of Schatzki esophagus is described as a circular membrane of mucosa and the submucosa is seen at the squamous junction of the distal esophagus, appearing as a thin membrane structure that does not contain any any muscle layer that has the potential to cause narrowing of the esophageal lumen. Histologically, the ring of Schatzki has an upper surface covered with squamous epithelium and a lower surface covered with columnar epithelium, often associated with a hiatal hernia of the esophagus.
Epidemiologically, Schatzki rings are found in 6% to 14% of barium radiographs. This structural abnormality is noted as the most common cause of intermittent dysphagia for solids and solids in adults.
2. Etiology and pathophysiology of Schatzki's ring
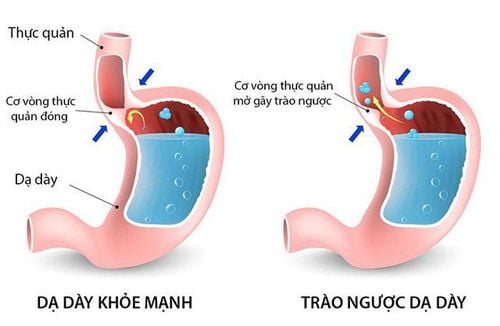
Precisely because the Schatzki ring is associated with a hiatal hernia, gastroesophageal reflux is thought to be the cause. Indeed, many theories have been accepted that the creation of a Schatzki ring is the body's response to repeated exposure to acid and is a natural way to prevent the development of Barrett's esophagus. At the same time, studies have shown that Barrett's esophagus is less common in the presence of a ring of Schatzki, especially long-segment Barrett's esophagus.
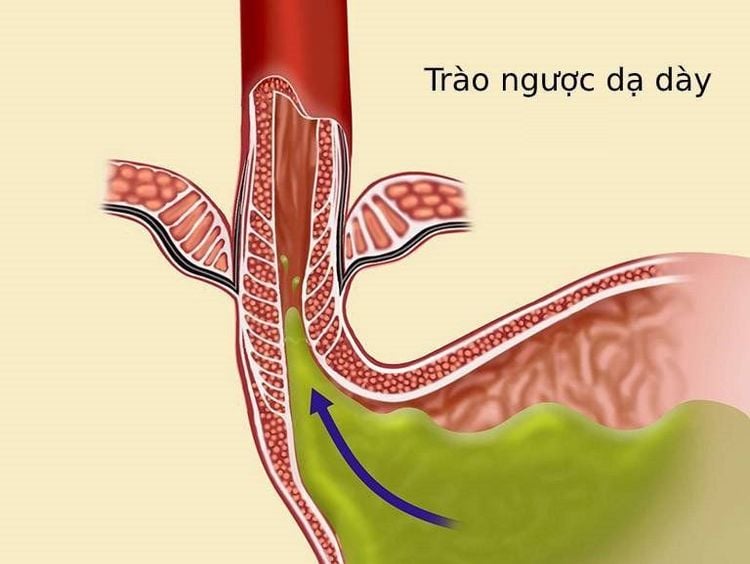
Trào ngược dạ dày thực quản có thể là nguyên nhân gây vòng đai Schatzki
3. How do I diagnose a Schatzki belt?
Most Schatzki rings cause no symptoms if over 25 mm in size. When smaller in size, the main symptom occurs is dysphagia and can lead to acute dysphagia due to pinched food. These manifestations are often related to poor chewing and are sometimes described as a sensation of food sticking in the chest.
Accordingly, once a patient presents with symptoms suggestive of a Schatzki ring, the initial study to evaluate this condition is barium esophagography. To do this, the patient is asked to swallow a substance such as a marshmallow or a barium tablet to gauge the diameter of the ring. However, the indicated tool is intended to guide upper gastrointestinal endoscopy to assess Schatzki ring size as well as treat local symptoms concurrently in patients. If the finding is incidental and the patient is asymptomatic, no treatment is needed.
Furthermore, even though Baryte esophagography is difficult to detect, endoscopy is still recommended to rule out other causes of esophageal stricture, especially esophageal malignancy. Endoscopic mucosal biopsy should also be performed if there is an irregular Z-line at the gastroesophageal junction for histological evaluation of Barrett's esophagus. Even a Schatzki ring biopsy can be performed as a local interventional treatment.
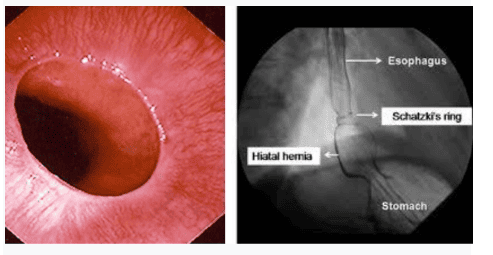
Vòng đai Schatzki có thể được chẩn đoán qua nội soi hoặc XQuang
4. Measures to treat Schatzki .'s ring
The goal of treatment is to reduce the diameter of the Schatzki ring to improve narrowing of the esophagus, allowing food to pass through the esophagus unimpeded. The general principle of treatment is to break the ring of Schatzki by dilating the esophagus or removing the ring with biopsy forceps. In it, for biopsies, residual tissue can lead to recurrence later.
After intervention, patients need to be maintained on some acid-reducing medication such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), especially if Schatzki's ring ablation has been performed.
Overall, Schatzki ring is a benign condition and when symptomatic it can be effectively treated. Patients usually have a good prognosis and symptoms improve rapidly after treatment. Recurrence can occur up to 64% in the first 2 years, thus requiring repeat esophagectomy.
In summary, the Schatzki ring is a band of tissue that can form in the lower esophagus, resulting in narrowing of the esophageal lumen. While some people with Schatzki rings have no symptoms, others have persistent difficulty swallowing or feel that food is stuck in their chest. At this time, upper gastrointestinal endoscopy is a suitable indication, both for diagnosis and for therapeutic intervention. At the same time, lifestyle changes and acid-suppressing therapy can help relieve symptoms of Schatzki's ring.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.