This is an automatically translated article.
The raw food diet consists of eating mainly unprocessed, plant-based, and preferably organic, whole foods. Some sources say that when following this diet, raw foods should make up 3/4 of the diet.
1. What is the Raw Vegan Diet?
Like a vegan diet, Raw Vegan excludes all foods of animal origin. The Raw Vegan mode then adds the concept or raw foodism, which stipulates that food should be eaten raw or heated to temperatures below 104–118 °F (40–48 °C).
Vegan diets, which consume raw, whole foods often high in fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, whole grains and legumes. Accordingly, promoting health is the main reason why many people choose to follow a vegan or Raw Vegan diet. They believe that raw and minimally heated foods are more nutritious than cooked foods. Alternative meal preparation methods, such as juicing, blending, pickling, salting, are used instead of cooking.
Some advocates also believe that the Raw Vegan diet provides all the nutrients humans need. This is also why supplements are generally not recommended during adherence to this diet.

Chế độ ăn Raw Vegan bao gồm nhiều các loại hạt
2. Benefits of Raw Vegan Diet
Raw Vegan diet brings a lot of health benefits, which can be mentioned as:
2.1. Improve heart health
Vegetarian diets can improve heart health thanks to increased amounts of fruits and vegetables compared to conventional diets. Thereby, helping users lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke This diet also includes lots of nuts, seeds, whole grains and legumes. Studies show that these foods can improve blood cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease. Observational studies show that vegetarians can reduce their risk of high blood pressure by up to 75% and reduce their risk of dying from heart disease by 42%.
The number of studies specific to the effects of the Raw Vegan diet is limited. However, the amount of nutrient-rich plant foods added to this diet may yield similar results.

Chế độ ăn Raw Vegan rất có lợi cho sức khỏe tim mạch
2.2. Reduce the risk of diabetes
Similarly, this effect is in large part due to the Raw Vegan diet that focuses primarily on the addition of fruits and vegetables, which in turn, reduces the risk of type 2 diabetes. In addition, this diet is rich in fiber - a nutrient that has been linked to lower blood sugar and increased insulin sensitivity.
A recent review study linked vegetarian and vegan diets to a 12% reduction in the risk of type 2 diabetes, with a vegan diet being the most effective. What's more, a vegan diet containing high amounts of nuts, sprouted grains, and legumes can help lower blood sugar even further. However, there is still very little research on the Raw Vegan diet. Based on increased fruit and veg intake, a Raw vegan diet may also produce similar results.
2.3. Support weight loss
The Raw Vegan diet can be effective in helping users lose weight and maintain a healthy weight. In fact, studies consistently link Raw Vegan diets, which include veganism, with lower amounts of body fat. In one study, people who followed different raw diets for more than 3.5 years lost about 22–26 pounds (10–12 kg). In another study, people following the Raw Vegan diet had a 7–9.4% lower total body fat percentage than those following the regular diet.

Người béo phì có thể giảm cân nhờ chế độ ăn này
2.4. Improve digestion
The high amount of fiber in the foods used in the Raw Vegan diet can help improve digestion. The Raw Vegan diet is high in soluble and insoluble fiber. Insoluble fiber adds bulk to the body's waste, helping food move faster through the intestines during elimination, reducing the likelihood of constipation.
Besides, soluble fiber is also beneficial, helping to feed the beneficial bacteria in the intestinal tract. These healthy bacteria produce nutrients, such as short-chain fats, that help reduce gut inflammation. They may also help the body improve symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), Crohn's disease, and ulcerative colitis.
3. Popular Raw Vegan Foods
People interpret the Raw Vegan diet and what it means in different ways. Some people will eat some cooked food, while others will not. For some, it's a lifestyle and for others, it's simply a dietary choice. The following foods go well with most Raw Vegan diets:Fruit raw and raw vegetables Dried fruits and vegetables Fresh fruit and vegetable juices Soaked and sprouted beans, other legumes and grains Raw nuts and seeds Raw nut butters, such as peanut butter and almond butter Nut milk , including almond milk Coconut milk Cold pressed olive oil or coconut oil Nutritional yeast Seaweed Dried fruit Green food powder, such as dried wheatgrass or algae Fermented foods, including kimchi and melon cabbage Purified water, not tap water Other organic, natural or unprocessed foods

Các loại trái cây, rau củ được khuyến khích bổ sung vào chế độ ăn Raw Vegan
Raw eggs Raw fish, such as sushi or sashimi Other raw or dried meats Unpasteurized and unpasteurized milk and dairy products homogenize Foods to avoid on a Raw Vegan diet include:
All fully cooked or processed foods Refined oils Table salt Refined sugars and flours Coffee, tea and wine Pasta VIEW MORE: 24 healthy vegetarian ideas
4. Notes and risks when applying the Raw Vegan diet
Besides the benefits, the application of a Raw Vegan diet may have some risks as follows:
4.1. Nutritional imbalance
One of the prerequisites for a good vegetarian diet is to ensure that the diet always provides all the vitamins and minerals needed by the body. Users can supplement by consuming fortified foods or supplements to compensate for nutrients in low amounts in the diet.
Accordingly, Vitamin B12 is an example of a nutrient most likely to be deficient in a Raw Vegan diet. Getting too little of this vitamin can lead to anemia, nervous system damage, infertility, heart disease, and poor bone health. Although anyone can have low vitamin B12 levels, vegans who don't take supplements are at a higher risk of developing a deficiency. In fact, one study found that 100% of participants following a Raw Vegan diet consumed less than the recommended 2.4 mcg of vitamin B12 per day. Furthermore, more than a third of the participants were vitamin B12 deficient at the time of the study. However, the use of supplements is generally not recommended on a Raw Vegan diet, as the body can get all the nutrients it needs from raw foods alone. This can increase the risk of nutrient deficiencies.
The Raw Vegan diet is also low in calcium and vitamin D. Advocates of this diet often do not use iodized salt, which can cause an iodine deficiency in the body.

Người ăn kiêng có thể bị thiếu hụt vitamin và khoáng chất
4.2. Decreased muscle and bone quality
Certain aspects of the Raw Vegan diet can lead to weaker muscles and bones. For starters, this diet tends to be low in calcium and vitamin D - two nutrients essential for strong bones.
In one study, people following a Raw Vegan diet had lower bone mineral density and content than those following a standard diet. Some people who eat a Raw Vegan diet can get enough vitamin D from sun exposure. However, older adults, those living in northern latitudes, or those with darker skin may not be able to consistently produce enough vitamin D from sun exposure alone.
Furthermore, a Raw Vegan diet tends to provide very little protein - often less than 10% of total calories consumed per day. Despite such a low protein level, it could theoretically be sufficient to meet the basic biological needs of the body. Some evidence links higher protein intake with stronger bone density. Similarly, protein is also important for maintaining muscle mass.
4.3. Increase the rate of tooth decay
Raw Vegan diets may also increase the likelihood of tooth decay. This can be especially true of all diets that include lots of citrus fruits and berries. These fruits are thought to be more acidic and more likely to wear down tooth enamel. In one study, 97.7% of people who followed a Raw Vegan diet experienced some degree of tooth wear, compared with only 86.8% in the control group. However, more studies are needed before definite conclusions can be drawn.
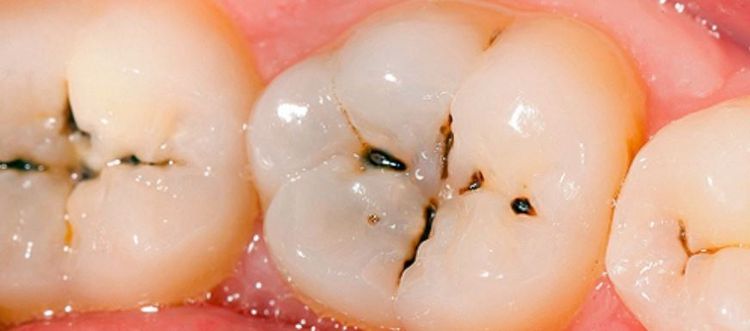
Sâu răng có thể xảy ra với người ăn chế độ Raw Vegan
4.4. Reduced fertility
In some cases, the Raw Vegan diet can reduce fertility. In one study, 70% of women following a Raw Vegan diet had irregular menstrual cycles. Furthermore, it was observed that the higher the roughage ratio, the stronger the effect. The researchers calculated that women who ate only raw foods were seven times more likely to experience amenorrhea than other women. The scientists note that one of the main reasons that the Raw Vegan diet can affect a woman's fertility is that the diet is so low in calories. This can cause women to lose too much weight, reducing their chances of menstruating.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: Healthline.com, Womenshealth.com













