This is an automatically translated article.
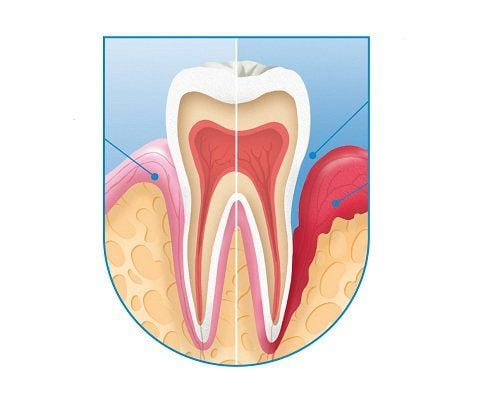
Root canal surgery is to remove the pathological organization around the root and apex of the tooth. At the same time, during the surgery, the doctor also removes the extra root canal and extra canals around the root (if any), thereby giving you strong teeth and helping to prevent diseases. about teeth.
1. Indications and contraindications of root canal surgery
1.1 Indications Root canal surgery is indicated in the following cases:
The tooth is inflamed around the apex despite previous good endodontic treatment.
Teeth with inflammation around the apex, have had poor endodontic treatment and can be re-treated for the following reasons:
Occlusion of the root canal, The canal is too curved, There are Posts and cones in the canal, Small instruments in the canal broken marrow. The tooth has periapical inflammation and the endodontic treatment cannot be completed due to the following reasons:
Foreign body pushed into the apical area, The lower wall of the pulp chamber is perforated, Root perforation, Fracture in the lower third of the tooth. tooth. Dental deformities (such as teeth within teeth). In the above cases, if after root canal surgery but the apical foramen is not sealed, it is necessary to reverse seal, this is mandatory.
The purpose of reverse sealing is to prevent the exit of bacteria and pulp necrosis products from remaining in the canal.
1.2 Contraindications Contraindications of root canal surgery include:
Contraindications to intraoral surgery include: Patient age, systemic problems (such as cardiovascular disease, acute leukemia), tuberculosis,...) The patient has a severe periodontal condition (such as deep gum pockets, much bone loss), Short tooth roots, The position of the tooth root is closely related to the anatomical structure (such as the lower canal, the maxillary sinus). , chin hole, incisor hole or large palatal foramen) that can cause damage during surgery.
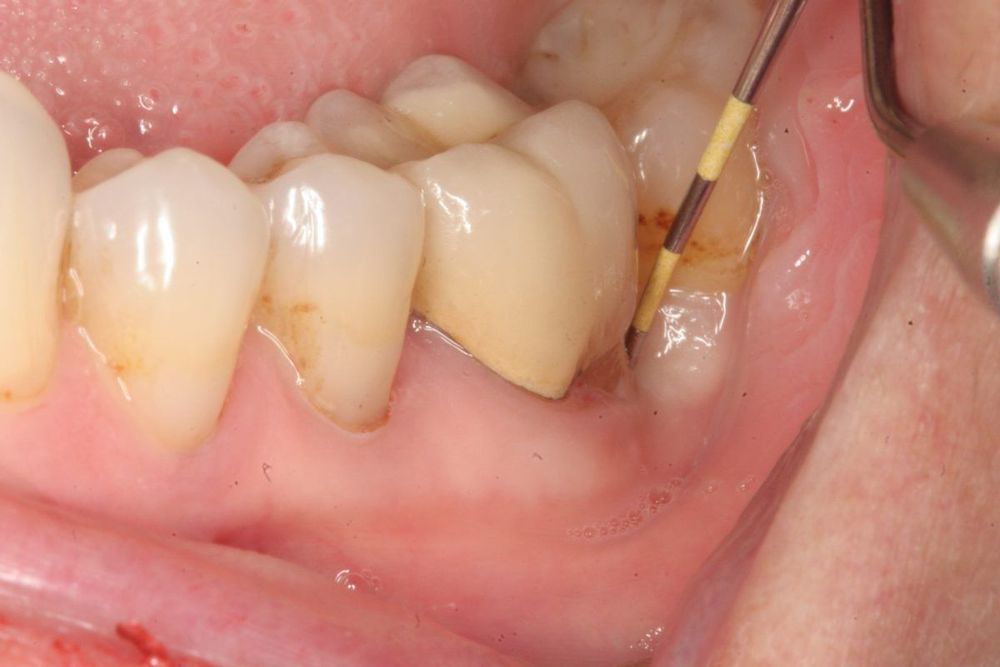
Phẫu thuật cắt cuống răng được chỉ định khi răng bị viêm quanh cuống răng dù đã được điều trị nội nha tốt trước đó
2. The process of performing root canal surgery
2.1. Step 1: Design the flap
To design a suitable flap, it is necessary to rely on the following factors:
Position of teeth Position of dental pocket. Prosthetic tooth restoration. Area of damage around the root of the tooth. Currently, in root canal surgery, there are 3 types of flaps commonly used: triangular flap, semicircular flap and trapezoidal flap.
The semicircular flap is indicated by dentists to be used in the case of root cutting with small lesions, located in front of the jaw door to facilitate later wound healing, as well as to avoid bad scars. However, the incision must be located away from the edge of the lesion so that when the wound is closed, the flap will lie above the healthy bone.
2.2. Step 2: Locate and expose the tooth root
If apical lesions have perforated the vestibular bone, this makes it easier to locate and expose the apex.
If the vestibular bone is thin, but has not been perforated, the doctor can use a probe to remove the covering bone, thereby accurately determining the position of the tooth root.
If the vestibular bone is thick, the doctor can position the apex with a canal wand or a root canal gauge to determine the length of the root. Then, the doctor will use a circular drill to create a bone window, through which to expose the tooth root.
For cases where the tooth root is damaged and the bone is thin, the drill can be used to expand the bone to a large enough size to remove the pathological organization in the root and then cut it.
2.3. Step 3: Cut the root of the tooth
The dentist will use a cylindrical drill with a 45 degree angle to cut the root of the tooth about 2-3 mm. Then cure again to remove the pathological organizations around the apex, especially the posterior ones.
However, if the canal is not completely sealed, the next step is to do a reverse fusion.

Bác sĩ sử dụng mũi khoan trụ với mặt nghiêng 45 độ để cắt cuống chân răng khoảng 2-3 mm
2.4. Step 4: Reverse solder
After the pathological organization around the tooth root has been scraped, the dentist will use a small piece of cotton soaked in medicine to put into the bone socket to stop the bleeding.
Then, the doctor will use a small round drill to create a sinus of about 2mm in the canal, followed by a reverse apex drill for the sealant to adhere to it.
2.5. Step 5: Wash the wound and close the flap
After the reverse fusion is completed, the doctor will use isotonic saline serum to irrigate the wound. Then repeat the X-ray to check if the binder is left in the damaged area. Once the examination is complete, the doctor will sew the flap to close and end the root canal surgery.
Your doctor will schedule a follow-up appointment in 6-12 weeks.
Dentistry department at Vinmec International General Hospital is proud of being a prestigious and quality medical system chain. Owning a system of leading modern dental equipment in the country; gathers a team of good doctors in the field of dentistry, dedicated and thoughtful in examining and treating thousands of cases of periodontitis successfully; All dental services are performed according to strict infection control standards, ensuring safety, minimizing sensitivity and maximum hygiene for customers.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.