This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Le Anh Viet - Radiologist - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International Hospital.1. Introduction to magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a modern medical imaging technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves.Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) images with high contrast, good anatomical details allow accurate detection of morphological and structural lesions in body parts. This helps doctors to evaluate lesions in detail and make an accurate diagnosis, which in many cases is better than other imaging techniques such as ultrasound, X-ray and CT scan. .
The ability to reproduce 3D images, without side effects, is increasingly being specified for many different specialized applications. MRI allows to detect abnormalities hidden behind layers of bone that are difficult to detect with other imaging methods. MRI can provide faster and more accurate diagnosis than X-rays in the diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases.
2. What is magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatitis (MRCP)?
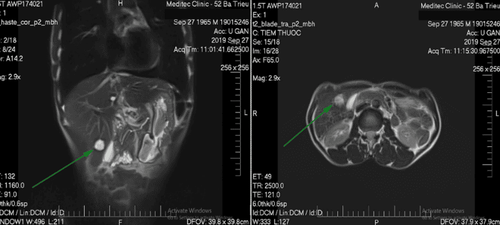
Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is a technique that uses magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to create images of the liver, bile ducts, gallbladder, and pancreas.Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is also known as magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography or MRI of the biliary tree.
Bile-pancreatic magnetic resonance is a valuable technique in the investigation of pancreatic biliary tract disease. Bile-pancreatic magnetic resonance is a non-invasive technique comparable to endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography in detecting and locating biliary obstruction, detecting gallstones.
2.1 Indications for magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography Basically, magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography is mainly indicated for the following cases:
Pancreas
● Evaluation of pancreatic duct dilation or obstruction
Suspicion or development presence of pancreatic duct abnormalities
Assess for complicated acute pancreatitis, chronic pancreatitis, or pancreatitis in general;
Detection of pancreatic tumors by other imaging methods with characterization of suspicious or enlarged but unexplained lesions;
● Follow-up after pancreatic surgery or treatment;
● Assess the situation of fluid accumulation or leakage of pancreatic and peripancreatic fluid;
Gallbladder, biliary tract
Evaluation of biliary tract dilation
Evaluation of cholangiocarcinoma before surgery
Detection and follow-up after treatment for gallbladder or biliary tract cancer
Detecting stones in the biliary tract or gallbladder
● Evaluation of suspected congenital anomalies in the gallbladder or biliary tract.

No radiation
Disease does not require anesthesia
Better identification of the biliary tract above the obstruction
Combined with T1W, T2W helps to diagnose price of extra-biliary tract injury
3. What is magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatitis (MRCP) used for?
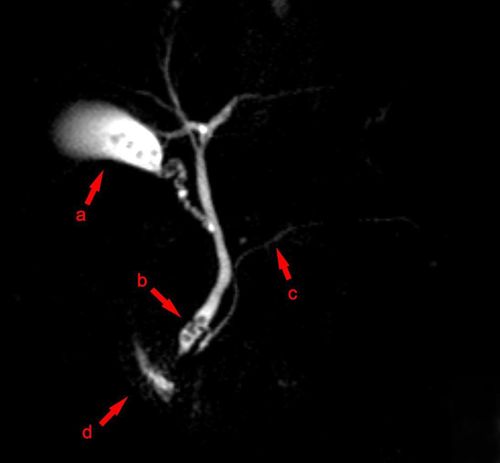
3.1 Bile ducts and nearby structures To learn about the uses of MRCP, let's first learn about the bile ducts and nearby structures:Bile is made in the liver. The liver is located in the upper right abdomen. Bile is secreted from the liver cells and empty into the small bile ducts. The smaller bile ducts fuse together to form the larger bile duct and eventually empty into the common bile duct. Bile from the common bile duct enters the duodenum (the first segment of intestine after the stomach) through an opening called the duodenal papilla.
The gallbladder is located below the liver on the right side of the upper abdomen. The gallbladder is the place where bile concentrates and stores bile between meals. When you eat, the gallbladder contracts to push bile through the cystic duct into the common bile duct and down into the duodenum to help dissolve and absorb fats in food. The pancreas is a gland that secretes digestive enzymes that play an important role in digesting fats and proteins in food. These digestive enzymes are secreted from pancreatic cells into the small pancreatic ducts, then into the main pancreatic duct and empty into the duodenum through the duodenal papilla. In addition, the pancreas also secretes a number of hormones (hormones) such as insulin, glucagon involved in the regulation of blood sugar.
3.2 What is Magnetic Resonance of Pancreas (MRCP) used for? Magnetic resonance pancreatitis is used to:
● Check for diseases of the liver, bile ducts, gallbladder, pancreas such as tumors, stones or inflammation.
Find the cause of pancreatitis.
● Find the cause of abdominal pain.
● Use as a less invasive diagnostic method than endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP).
MRCP can help diagnose the presence of biliary obstruction and the degree of obstruction in most cases. Small calcium stones less than 2 mm can also be seen. Primary sclerosing cholangitis can be diagnosed from the many abnormal narrowings seen in the bile duct.
In patients with recurrent pancreatitis, MRCP may be performed to look for stones, pancreatic divisions, or strictures. Pancreatic magnetic resonance imaging can be used to evaluate parenchymal changes due to pancreatitis or to identify pancreatic cancer.

4. Notes when performing abdominal MRI
To date, there have not been any reported side effects associated with MRI of the pancreas. However, because the MRI machine generates a very large magnetic force, before performing the procedure, the following should be noted:● Patients who have had metal implant surgery such as: Artificial heart valve implantation, vascular stenting coronary , coronary clamp...
● Patient is afraid of tight and closed places, claustrophobia (Claustrophobia)
● Contains metal foreign objects inside the body such as: shrapnel, surgical screws bones, dentures, braces, artificial bone crests...
● Using assistive devices: Pacemakers, defibrillators, hearing aids, automatic drug pumping devices under the skin (with patients treated for diabetes)...
● Mental patients, oversized people, naughty children, uncooperative.
● The patient works directly in the metal mining and manufacturing environment.
Reactions to contrast drugs (very rare)
Vinmec International General Hospital is currently one of the major hospitals with modern equipment and machines for general medical examination and treatment and MRI Accurate, modern for diseases of the brain, cerebrovascular in particular.
Especially, Vinmec International General Hospital is the first unit in Southeast Asia to put into use the new 3.0 Tesla Silent MRI machine from the US manufacturer GE Healthcare.
The machine currently applies the safest and most accurate magnetic resonance imaging technology available today, without using X-rays, non-invasive. Silent technology is very beneficial for patients who are young children, the elderly, patients with weak health or have just had surgery.
Master Doctor Le Anh Viet has 07 years of experience working in the field of diagnostic imaging, performing well in diagnostic imaging techniques. Currently, the doctor is working at the Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.