This is an automatically translated article.
Laryngeal flaccid disease is rare, accounting for only 0.01% of ENT diseases in general. The most noticeable sign is the wheezing sounds of babies right in the first weeks of life.
1. Laryngeal flaccid disease
Laryngeal flaccidity is a congenital abnormality of laryngeal cartilage used to describe cases where the tissue supporting the anatomical structures above the larynx, including the epiglottis and the funnel cartilage, has not developed in time, causing these structures to prolapse. The baby's airway makes a wheezing sound.
Softening of the larynx, a common congenital defect in the glottis and larynx, accounts for 60% of congenital abnormalities of the larynx. The disease causes clinical wheezing, 2 times more boys than girls. The phenomenon of laryngeal softening mainly occurs in the epiglottis and the laryngeal funnel, but also in both structures. This disease is very rare, accounting for only 0.01% of ENT diseases in general.
2. Causes of soft laryngeal cartilage in children
Softening of the larynx occurs when the epiglottis narrows with each inhalation. The specific cause is currently unknown, possibly from many different mechanisms:
Due to anatomical abnormalities Due to the short epiglottis and omega-shaped epiglottis, the epiglottis narrows.
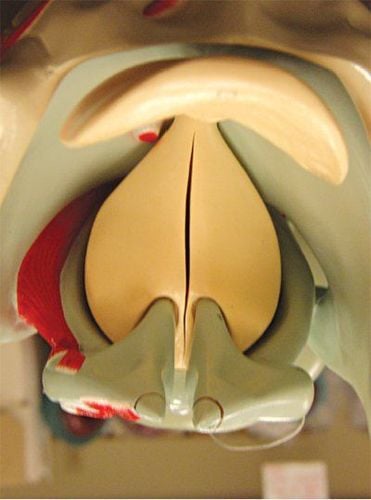
Tình trạng thanh quản bị mềm sụn xảy ra khi vùng thượng thanh môn bị hẹp lại mỗi khi hít hơi vào
Because of the difference between lung size and upper respiratory tract size, there is a situation of contraction or bulging of the muscles of the chest, neck area, most obvious when the child breathes in and out, active This is mild but takes place evenly, continuously, creating a hissing sound.
Incomplete nerve pathways Nerve pathways are not fully mature, so nerve-muscle coordination is incomplete, causing airway tone in this area to be lower than needed. Therefore, it is easy to inflate and deflate, not stable.
3. Symptoms of soft cartilage in the larynx
Baby wheezing for a long time + The baby started wheezing with each breath right after birth. Each breath is wheezing and interrupted when inhaling, sometimes making parents think that the baby is sucking amniotic fluid in the nose that is not clean after birth, causing rhinitis and leading to stuffy and blocked nose. However, if you examine the ears, nose, and throat, you can't see any lesions, nor do you see any discharge.
+ Parents can hear high-pitched wheezing sounds, aggravated when the child is in the supine position, when the child is crying, the child has respiratory infections. More seriously, the child has a slow weight gain, difficulty breastfeeding, sudden pauses in breathing for a few seconds, chest and neck constriction when breathing in, pale skin. These acute symptoms usually last in the first 8 months of life, then disappear on their own.
+ The wheezing will be interrupted every time the child inhales. The whistling sound at first is easy to mistake for a baby's stuffy nose, but it's persistent and there's no mucus in the baby's nose. The timbre of a child's wheezing can be as high as a stridor.
+ Wheezing increases when the child is placed on his or her back, when the child is irritable and fussy, or when there is an associated upper respiratory tract infection. Many cases of wheezing during and after feeding (when the baby is placed on his back, gravity will cause the epiglottis to protrude into the airway more and make the baby wheeze more.)
+ Except at times. with combined laryngitis, the child still plays and sucks as usual.

Trẻ thở khò khè lâu ngày nếu bị mềm sụn thanh quản
Gastroesophageal reflux Up to 80-100% of children with soft laryngeal cartilage have gastroesophageal reflux caused by an obstruction in a part of the glottis, when the child tries to inhale, it will increase the negative pressure at the larynx. Excessive rib cage makes food in the stomach in the baby's abdominal cavity easier to back up into the esophagus (the part of the digestive tract located in the chest). In contrast, children with severe gastroesophageal reflux disease will have pathological structural changes similar to laryngeal softening, especially swelling and bulging of the funnel cartilage.
Other symptoms may be accompanied such as: + Slow weight gain
+ Difficulty suckling
+ Swallowing milk
+ Choking milk
+ Stopping breathing
+ Pulling chest when baby takes a strong breath
+ Cyanosis
+ Ợ fluid acidity in the stomach
Symptoms worsen within the first few months, usually between 4-8 months of age. Most children with laryngospasm will have no symptoms by 12-18 months.
4. Classification
4.1. Mild grade Inspiratory wheezing without complications of severe airway obstruction, does not affect the nursing infant, and has no other associated symptoms. These children often fuss with the nanny but have no other health problems and usually clear up on their own after 12-18 months of age. If the child has mild laryngomalacia, it is still very important to pay attention to monitor the signs and symptoms of bad progress to promptly bring the child to a medical facility.
4.2. Moderate Child is classified into this category when the following symptoms are present:
Wheezing on inhalation No milk Airway obstruction (due to soft larynx) Difficult feeding but does not affect the child's steady weight gain History been hospitalized multiple times for airway obstruction Gastro-oesophageal reflux (vomiting acid in the stomach) These children also resolve on their own by 12-18 months of age but may require treatment for reflux. stomach - esophagus. Even if the child is classified as a moderate disease, it is still very important to pay attention to monitor the signs and symptoms of worsening in order to promptly bring the child to a medical facility. 4.3. Severe Grade Children in this category often may need surgery to correct. Doctors will recommend surgery if the child has any of the following symptoms:
Shortness of breath, life is threatened Occurrences of cyanotic breaths The chest is pulled and the neck area, too, gets worse when breathing Needs to breathe need to breathe oxygen Continued cardiopulmonary disease caused by prolonged hypoxia Unable to gain weight because of difficulty feeding
5. Subjects at risk of disease
Premature babies Neuromuscular diseases Associated respiratory tract damage: soft tracheal cartilage, subglottic stenosis...
6. Complications of laryngeal softening
Severe airway obstruction, life-threatening. Complications of epiglottitis, tracheostomy. Children slowly gain weight. Aspiration pneumonia.
7. Caring for children with soft laryngeal cartilage
Laryngeal softening disease currently has no specific remedy, parents can give their children vitamin D and calcium supplements. Therefore, this disease is very difficult to prevent because the cause is not clear.
When taking care of children, parents should pay attention to:
Limit children lying on their backs. Under the effect of gravity, the more laryngeal cartilage tissue protrudes into the child's airway, the more wheezing the child becomes. For newborns, you should let the child lie on his side, sometimes turning over to help him feel less tired, and for older children, he will lie down in the position that he feels most comfortable to breathe.

Hạn chế cho trẻ nằm ngửa để trẻ dễ thở
Breastfeeding properly Some babies with soft larynx will find it difficult to suckle. Therefore, mothers need to be alert when breastfeeding to adjust the amount of milk to suit the baby's sucking capacity, avoiding the very dangerous phenomenon of choking.
Cleaning the nose and throat before going to sleep Before going to bed, remember to clean the baby's nose with physiological saline solution so that the baby's nose is open, helping the baby breathe easier. Children with soft laryngeal cartilage or breathing through the mouth when sleeping, you should apply lip balm to your baby to avoid dry, chapped lips, and breastfeeding will be very difficult.
Enhance resistance Minimize respiratory diseases because children with soft laryngeal cartilage wheeze more when suffering from these diseases. When children enter the age of weaning, parents should add foods containing a lot of vitamin C to help strengthen resistance and prevent common respiratory infections.
Periodic examination Check and monitor the health status of children periodically. If the child has soft laryngeal cartilage leading to weight loss, apnea, aborting, ..., the child must be taken to a medical center for timely support. Parents should periodically send children to the hospital to measure the saturation of fresh oxygen in the blood.
Lifestyle There is no need to abstain from any food nor restrict any physical activity of the child. Give your child regular vaccinations to prevent other diseases.
Softening of the larynx is common in young children and infants. Most children with laryngospasm will have no symptoms by 12-18 months. However, for severe cases, parents should still have a thorough understanding of the pathological knowledge to best care for the child.
As a key area of Vinmec Health system, Pediatrics Department always brings satisfaction to customers and is highly appreciated by industry experts with:
Gathering a team of top doctors and nurses in Pediatrics : consists of leading experts with high professional qualifications (professors, associate professors, doctorates, masters), experienced, worked at major hospitals such as Bach Mai, 108.. Doctors All doctors are well-trained, professional, conscientious, knowledgeable about young psychology. In addition to domestic pediatric specialists, the Department of Pediatrics also has the participation of foreign experts (Japan, Singapore, Australia, USA) who are always pioneers in applying the latest and most effective treatment regimens. . Comprehensive services: In the field of Pediatrics, Vinmec provides a series of continuous medical examination and treatment services from Newborn to Pediatric and Vaccine,... according to international standards to help parents take care of their baby's health from birth to childhood. from birth to adulthood Specialized techniques: Vinmec has successfully deployed many specialized techniques to make the treatment of difficult diseases in Pediatrics more effective: neurosurgery - skull surgery, stem cell transplantation. blood in cancer treatment. Professional care: In addition to understanding children's psychology, Vinmec also pays special attention to the children's play space, helping them to have fun and get used to the hospital's environment, cooperate in treatment, improve the efficiency of medical treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.