This is an automatically translated article.
Congenital heart disease is a malformation that newborns are likely to have right from birth, accounting for about 1%, of which monoventricular congenital heart disease is the rarest congenital heart disease but not should be ignored because there is a very high risk of heart failure in children. To treat this pathology, the Fontan surgery method is quite popularly applied today, helping patients to improve the condition of congenital heart disease in the form of one ventricle.
1. Congenital heart disease with one ventricle
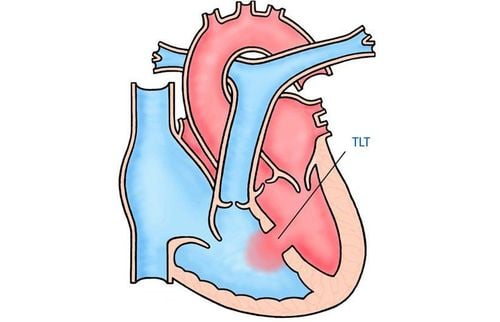
Congenital heart disease with one ventricle is a pathology of the group of congenital heart diseases, caused by the phenomenon that the two atrioventricular valves of the neonate join together into the ventricle chamber, or one atrioventricular valve appears together in the atrioventricular cavity. the seventh. According to another explanation, when having a single-ventricular congenital heart disease, the child's heart does not have the presence of the mitral foramen and the tricuspid foramen, causing hypoplasia of the left heart or the condition of the heart. Pulmonary valve is not associated with right ventricular hypoplasia. Therefore, this type of congenital heart disease usually has only one ventricle of the right size to be able to take care of the function of pumping blood throughout the body. The causes of congenital heart conditions in newborns have been studied and are believed to be largely due to congenital heart disease that is passed on from family members to young children, or it may be because during pregnancy, the mother mothers who use a lot of alcohol, are addicted to drugs or infected with certain viruses. In particular, single-ventricular congenital heart disease has a lower rate than other congenital heart diseases and tends to occur more in boys than in girls.
When you have a congenital heart disease in the form of a single ventricle, the patient has some symptoms such as:
Tâm thất thường có 2 đường vào là biểu hiện bệnh tim bẩm sinh dạng một tâm thất
Left heart hypoplasia Lack of pulmonary valve orifice Closed interventricular septum There is asymmetry of the atrioventricular canal. Identical syndrome, single ventricle. No mitral valve, tricuspid valve, ventricular septal defect, double incompatibility Ventricles often have 2 entrances. Clinically, children may show some symptoms as follows: Shortness of breath, sweating, not feeding. milk. Squat appears hypoxic cyanotic episodes Increased pulmonary circulation: First murmur, mid-systolic left sternal border, becomes smaller if the foramen is narrow, T1 is normal, T2 is split, if there is a lot of blood in the lungs, a murmur can be heard. diastole at the apex of the heart. Pulmonary stenosis: left II intercostal systolic murmur, normal T1, small, simple T2.
2. Fontan surgery

Phương pháp phẫu thuật Fontan chỉ được điều trị cho bệnh nhân trong độ tuổi 4-15 tuổi
For pediatric patients with single-ventricular congenital heart disease who meet the necessary conditions, Fontan surgery will be indicated, which is a fairly effective treatment for this pathology, and is performed after when the patient had a 2-way aortic and pulmonary artery anastomosis. The necessary conditions to be able to perform Fontan surgery are:
Patient must be between the ages of 4 and 15 Electrocardiogram results in sinus rhythm Blood capable of emptying the aorta Pulmonary artery pressure right < 15 mmHg Pulmonary resistance must be < 4 Wood units/m2 The following parameters are within the normal range: McGoon and Nakata Cardiac function test did not detect abnormality The atrioventricular valve does not have stenosis or abnormality. open Pulmonary aortic shunt is absent. Before performing surgery, it is necessary to prepare the patient and prepare the surgical instruments according to the following standards:
Explain to the patient's family about the surgery to be performed. Conduct enemas cleaning for pediatric patients. Before surgery, it is necessary to bathe with water to break Betadine 2 times, change clean clothes. Use Betadine soap to beat chest Prepare full equipment including ventilator, cardiopulmonary system, monitor, cannula, specialized thread, defibrillator... Carry out Fontan surgery in the following order :

Hình ảnh bác sĩ chuẩn bị gây mê cho bệnh nhân
Place patient in supine position. Undergo general anesthesia Place a 3-bore catheter in the central venous line, which is the right internal jugular vein, 1 intravenous line in the periphery The arterial line is the radial artery Perform urinary catheterization and nasogastric catheterization. 1 line to monitor the temperature of 2 organs anus and oesophagus Use systemic anticoagulant for the patient is Heparin Skin incision along the sternum. Remove adhesions and suture the pericardium. Perform dissection of the inferior vena cava, close to the diaphragm Place the aorta, superior vena cava, and inferior vena cava to connect with arteries and veins of the cardiopulmonary machine. Thread lacs to perform ligation of 2 veins Start setting up cardiopulmonary bypass and ligation of 2 veins. Infusion of cardioprotective solution into the arterial base Run cardiopulmonary machine, perform 2 venous ligation. Clamp the aorta and administer cold aortic root, inject cold water into the pericardium and initiate opening of the right atrium. Longitudinal opening of the Goretex vessel Suture the Gore- tex vessel to the right atrium Connect the right pulmonary artery to the rest of the superior vena cava Open the window of the Goretex vein into the right atrium Perform the closure of the right atrium and venous drainage circuit. For extracardiac shunts, catheterize the aorta, inferior vena cava, and arteriopulmonary resuscitators (cardiopulmonary catheters) Thread and ligation of the inferior vena cava Run cardiopulmonary bypass and inferior vena cava resection Cut the inferior vena cava from the atrium Right, close right atrium Perform artificial Goretex vascular windowing with right atrium Constrict or cut pulmonary artery trunk Run a cardiopulmonary bypass machine Stop cardiopulmonary bypass, remove tube, perform neutralization Hemostasis for patient Post-sternal pericardial drainage Place electrodes on the heart Close the incision in accordance with the anatomical layer sequence After surgery, it is necessary to monitor and promptly handle dangerous complications, including:
Sau phẫu thuật cần theo dõi tình trang bệnh của bệnh nhân
Monitor vital signs including pulse, blood pressure, breathing rate, temperature. Monitor arterial blood gas and oxygen saturation Take a chest film for the patient to monitor Chest drainage needs to save on several factors such as the amount of fluid drained, the nature of the drainage fluid, once every 1 hour. Monitor patient's heart failure status If the patient has atelectasis, instruct the patient to breathe with balloon, stimulate, cough and bronchoscopy Monitor Fontan's circulatory failure on the patient after surgery If There is bleeding in the first 2 or 3 hours after surgery with red blood, the amount of 200ml/hour through drainage, it is necessary to have surgery again and stop the bleeding Before leaving the hospital, give the patient an echocardiogram and after 6 months, make an appointment. The patient was re-examined for an ultrasound examination. Fontan surgery is a surgical treatment to treat congenital heart disease in the form of a single ventricle, based on creating a bridge outside the heart by artificial vessels to help patients recover quickly. When there are signs of congenital heart disease, the family should pay attention and take the patient to a medical facility for examination, diagnosis and appropriate treatment indications.
To protect heart health in general and detect early signs of myocardial infarction and stroke, customers can sign up for Cardiovascular Screening Package - Basic Cardiovascular Examination of Vinmec International General Hospital . The examination package helps to detect cardiovascular problems at the earliest through tests and modern imaging methods. The package is for all ages, genders and is especially essential for people with risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.