This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Le Thao Tram - Doctor of Diagnostic Imaging - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital
fitz-hugh-curtis syndrome is a chronic complication of pelvic inflammatory disease. Patients usually present with right upper quadrant pain or chest pain on the background of pelvic inflammatory disease. The diagnosis can be confirmed by the presence of Chlamydia trachomatis (most common) or Neisseria gonorrhoea in the peritoneal fluid.
1. What is fitz-hugh-curtis syndrome?
Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome (FHCS) - perihepatitis is a sticky inflammation of the liver capsule and peritoneum without affecting the liver parenchyma. This is a chronic complication of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). This syndrome was originally described by Arthur H Curtis in 1930 and Thomas Fitz-Hugh Jr in 1934.
Epidemiologically, the incidence of mild to moderate pelvic inflammatory disease in women may be approximately 4 %. Rates may be higher in genital tuberculosis. It most commonly occurs in women of childbearing age, although rare cases have been reported in men.
Pathologically, this syndrome is thought to result from direct intraperitoneal spread to the perihepatic region by primary pelvic inflammation or infection.
2. Clinical manifestations of fitz-hugh-curtis . syndrome
Patients usually present with right upper quadrant pain or chest pain on the background of pelvic inflammatory disease.
The diagnosis can be confirmed by the presence of Chlamydia trachomatis (most common) or Neisseria gonorrhoea in the peritoneal fluid. Trichomonas vaginalis, Ureaplasma urealyticum and Mycoplasma hominis are less common causes of Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome. In tuberculosis endemic countries, Mycobacterium tuberculosis may be the predominant causative agent of this syndrome.
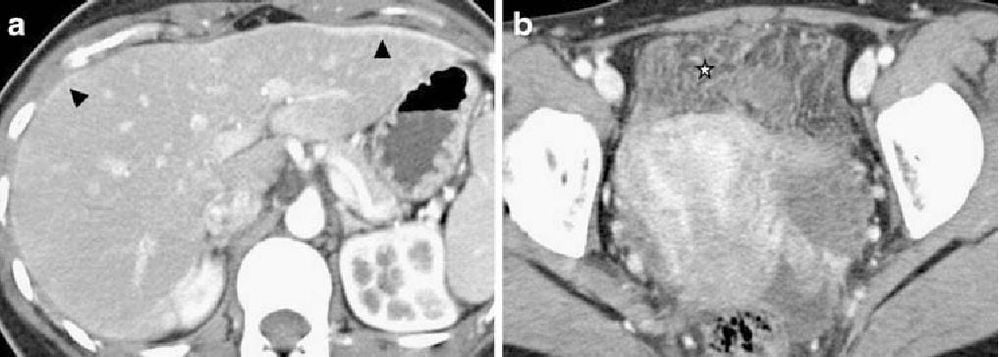
3. Imaging features of fitz hugh curtis . syndrome
The CTScan imaging medium will show inflammation in the pelvic and perihepatic areas. Specifically:
With the pelvis: May show an adnexal abscess, pus-filled fallopian tubes, pelvic fluid. For the perihepatic area: Inflammatory bands can be seen, fluid along the right colonic groove and around the liver, liver capsule thickening, gallbladder wall thickening, inflammatory changes around the biliary tract, transient liver parenchymal perfusion abnormalities can be seen. Differential diagnosis:
Peritoneal carcinomatosis: Shows more peritoneal nodules and has a solid component, shows clear pelvic malignancy on imaging, and has other clinical manifestations. Appendicitis: A differential diagnosis is required from the above syndrome, but appendicitis itself can be a possible complication.
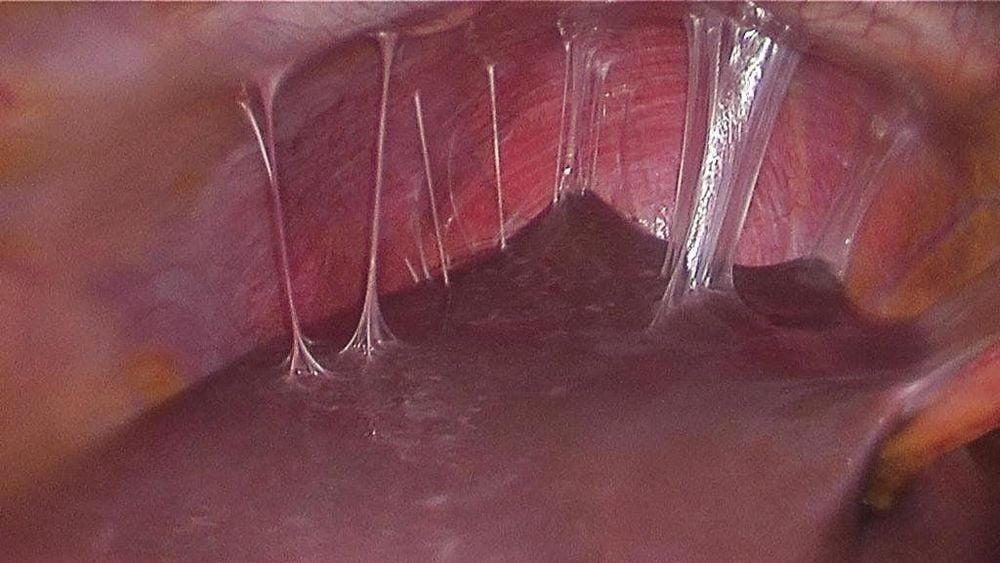
In summary, fitz-hugh-curtis syndrome is a sticky inflammation of the liver capsule and peritoneum without affecting the liver parenchyma. Patients usually present with right upper quadrant pain or chest pain on the background of pelvic inflammatory disease.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: semanticscholar.org, radiopaedia.org