This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Dr. CKII Nguyen Quoc Viet - Vinmec Da Nang International General HospitalCoronary artery disease is the number one cause of death from cardiovascular disease. In Vietnam as well as in the world, the rate of coronary heart disease is increasing. Despite great advances in treatment, coronary heart disease remains a major challenge for both physicians and patients. The following article will provide information on early detection and effective treatment of this disease.
1. Early detection of coronary heart disease
Coronary artery disease occurs when one or more branches of a coronary artery become narrowed or completely blocked due to several causes. The most common cause is coronary atherosclerotic plaque (accounting for more than 90%), in addition to some other causes such as coronary artery malformation, trauma, Takayashu disease...
Angina is a muscle sign and most important to recognize coronary artery disease. Pain feels tight, constricted like being pressed by a heavy object or sometimes just feels short of breath when exerting, the patient feels "breath shortened".
Common location of pain: Behind the breastbone, in the middle of the chest or in the heart area. Pain may be local or radiate to the neck, jaw, shoulder, or left arm.
Duration: The pain is usually very short, only 10-30 seconds or a few minutes, even long.
Intensity of pain: It can be mild, go away quickly, or be very intense, "knife-like" pain in the case of a myocardial infarction. Usually, angina can occur when the coronary artery is narrowed by more than 50% of the lumen diameter.
When having symptoms of angina, the patient needs to rest immediately, go to the hospital as soon as possible. Even the slightest exertion can be life-threatening.
2. Risk factors for coronary artery disease
2.1 Unmodifiable risk factors
Age
The risk of cardiovascular events increases with age. Epidemiological studies show that age is one of the most important predictors of disease. You can't shorten your life, but eating right and staying active can help slow down the aging process.
Nguy cơ xảy ra các biến cố tim mạch càng tăng lên khi tuổi càng cao
Sex
Men have a higher risk of coronary heart disease and stroke (about 70%) than women. However, after menopause, the rate of cardiovascular disease increases faster.Genetic factors
Research evidence shows that people with a genetic (familial) factor in cardiovascular disease or stroke have a higher risk of cardiovascular disease than others. Genetic factors also include race.
2.2. Modifiable risk factors
Hypertension
Hypertension is the most common cardiovascular risk factor and also the most well-studied risk factor. Hypertension is considered a silent killer and is the strongest risk factor for cardiovascular events. High blood pressure often has no symptoms and causes a host of dangerous cardiovascular complications. Good treatment of high blood pressure significantly reduces cardiovascular risk.
Increased blood cholesterol
Increased levels of lipids (fats) in the blood (cholesterol and triglycerides) are very common and are one of the most important modifiable risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
Smoke
Smoking (including pipe tobacco) is a proven risk factor for coronary artery disease, stroke, and peripheral vascular disease. Besides, smoking also causes lung cancer and a host of other diseases.
If you smoke, quit immediately, because quitting is a proven measure to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Passive smoking (when you are exposed to secondhand smoke) is equally risky.
Overweight - Obesity
To varying degrees all increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Diabetes and insulin resistance
People with diabetes, especially type II diabetes, have a higher rate of coronary heart disease and stroke than the general population. Diabetes accelerates the process of atherosclerosis and its complications.
Sedentary (sedentary lifestyle)
A sedentary lifestyle is considered a risk factor for cardiovascular events. Regular daily exercise of at least 30 minutes has a significant benefit in reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease.Drink alcohol
Currently, the recommendations say that, if used in moderation, ie no more than one drink (equivalent to 1 can of 5% beer 330ml, or 50ml of 30% alcohol) per day, drinking less alcohol does not cause harm. cardiovascular risk and may to some extent help prevent atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease.

Uống rượu có nguy cơ gây bệnh tim mạch
3. Treatment of coronary artery disease
Once diagnosed with coronary artery disease, the doctor will give you a treatment plan, depending on the cause and severity of the disease in each case. Treatments for coronary heart disease include:
3.1 Recanalization of narrowed coronary arteries
There are two methods of revascularization of the narrowed coronary artery: Percutaneous coronary intervention (e.g. balloon angioplasty, stenting) and coronary artery bypass graft surgery.Percutaneous coronary intervention
Is a rather complicated procedure, in which the doctor uses a specialized catheter threaded from the carpal or femoral artery up to the heart, into the narrowed coronary artery branches. Through that catheter, the doctor can insert a balloon to widen the coronary artery and then place a metal scaffold (called a stent) in the artery, to keep the lumen from narrowing. Coronary stenting procedure is a percutaneous procedure that requires only local anesthesia and does not require anesthesia. The procedure lasts from 45 to 120 minutes, depending on the case.
Those who have coronary stent implantation
This is the method prescribed by the doctor. When the advanced atherosclerotic plaque narrows the lumen above 70% of the arterial lumen, the coronary artery is not able to supply enough oxygen demand for the myocardium, especially during exercise, exercise or strenuous work. This causes myocardial ischemia, which manifests as angina pectoris and shortness of breath. At that time, it is necessary to visit a cardiologist to examine and prescribe appropriate treatment.
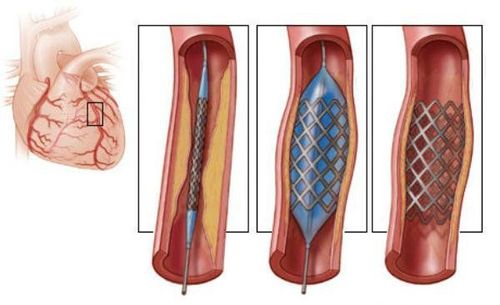
Stent mạch vành
Common types of stents
Conventional stents (or non-medicated stents): Currently less common because of the high rate of restenosis in the stent. Often indicated in very elderly patients to reduce the duration of dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT), reduce the risk of bleeding complications for the patient. Drug-eluting stents: Very popular nowadays. A type of stent that is coated with an anti-proliferative drug on the stent wall to reduce the risk of restenosis in the stent lumen. However, after drug-eluting stents, longer antiplatelet therapy is required (at least 1 year according to current recommendations). Therefore, the risk of bleeding is also higher than with conventional stents. Biological stents: Currently not widely used because of the lack of strong enough research evidence. Besides, the price is also high. Each type has a specific mechanism of action, choosing which type of stent will be based on the doctor's prescription for each specific case. Coronary stenting complications
Although stenting has become simple, it is still an invasive procedure that carries certain risks during the intervention, including: Infection, pain or discomfort at the catheter insertion site. Allergy to anesthetic or contrast agent during insertion. There can also be complications such as stroke, kidney failure. Injury to the artery wall causes stenosis at another site or the stent is not fully expanded or displaced. Coronary artery re-stenosis after surgery due to scar tissue, thrombus development in the stent lumen. These are complications that can reduce the time the stent takes effect. Bleeding due to anticoagulation Drugs that appear sooner or later are complications after stenting and directly affect the outcome of treatment, increasing the risk of re-occlusion.
Surgery to make the aorta-coronary bridge
This is a surgery to re-open coronary blood flow, thereby improving blood flow to the myocardium. During surgery, your doctor will use a "healthy" vein or vein from your own body to connect the aorta to the narrowed coronary artery.
3.2 Medical treatment
After coronary stent implantation, you need to fully comply with the treatment instructions of the specialist to minimize the risk of stent thrombosis as well as reduce later restenosis. Your doctor may give you the following medicines:
Antiplatelet drugs: To prevent blood clots from forming in the coronary arteries. Usually use two types in combination for at least 1 year. Then use one that lasts a lifetime. Beta-blockers: The drug slows the heart rate, lowers blood pressure, reduces myocardial oxygen demand. Prolonged use if there are no contraindications. Blood lipid-lowering drugs: Reduces atherosclerosis, prevents blood clots. Prolonged use if there are no contraindications. Nitroglycerin: The drug relieves chest pain by dilating narrowed coronary arteries, increasing myocardial perfusion, ACE inhibitors: Has the effect of lowering blood pressure, improving heart function. Prolonged use if there are no contraindications. Medicines to treat comorbidities such as hypertension, diabetes...
4. Lifestyle changes to prevent coronary artery disease
A healthy lifestyle can help limit the progression of coronary heart disease. Lifestyle change measures include:
Change in nutrition: Diet with fat, salty foods, weight loss Regular exercise and increased physical activity

Tập thể dục đều đặn để phòng ngừa bệnh động mạch vành
Quit smoking completely including avoiding secondhand smoke (also known as passive smoking) Recognizing and well controlling risk factors for coronary heart disease: hypertension, diabetes sugar, dyslipidemia. Currently, with a team of experienced interventional cardiologists, participating in smooth coordination with related departments, a system of modern and synchronous equipment, and especially with professional support from experts in the field. As a leader in interventional cardiology, Vinmec International General Hospital is ready to perform cardiovascular emergencies as well as program interventions on coronary artery disease (such as acute myocardial infarction, angina pectoris. ..). The hospital ensures the highest expertise to meet the needs of cardiovascular health care for customers.
See more
What is coronary artery? Common diseases of the coronary arteries What you need to know about coronary artery disease Patients with coronary artery stenosis should not smoke