This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by MSc Huynh An Thien - Department of Medical Examination and Internal Medicine, Vinmec International General Hospital Da Nang.
Ataxia (ataxia) is the term for a group of disorders that affect coordination, balance, and voice. Ataxia affects any part of the body, but people with ataxia have difficulty in certain activities such as: Walking and balancing, speaking, swallowing, activities that require high concentration such as write and eat, look. The symptoms and severity of ataxia depend on the cause of the ataxia.
1. Classification of ataxia
There are 3 main groups of ataxia:
Acquired ataxia: Due to causes such as trauma, stroke, brain tumor, multiple sclerosis, nutritional deficiencies or other causes that damage the brain and nervous system . Hereditary ataxia: Slow progression over many years, caused by genetic mutations inherited from parents, most commonly Friedreich's ataxia. Late-onset idiopathic cerebellar ataxia: Brain damage increases over time for unknown reasons
2. Causes of ataxia
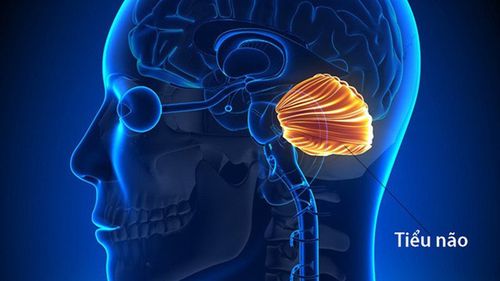
Ataxia is usually caused by damage to a part of the brain called the cerebellum. However, ataxia can also be caused by disorders of the spinal cord and nerves.
2.1 Spinal cord The spinal cord is a bundle of long nerves that run along the vertebrae and connect the brain to all other parts of the body.
2.2 Cerebellum The cerebellum is responsible for regulating the following activities:
Walking and balance Extremity coordination Eye movements Speech Cerebellar damage can be the result of trauma, disease (acquired ataxia) or cerebellar degeneration/spinal degeneration due to genetic causes (hereditary ataxia).
In some cases, no cause can be found as to why the cerebellum and spinal cord are damaged (slow-onset idiopathic cerebellar ataxia)
2.3 Acquired ataxia
Acquired ataxia Causes of acquired ataxia include:
Traumatic brain injury (eg after a traffic accident) Nervous infection: Meningitis, encephalitis Viral infection: Measles, pertussis can CNS infection (although very rare) Certain conditions that impede blood supply to the brain eg: Stroke, bleeding in the brain or transient ischemic attack Cerebral palsy : Occurs as the brain develops abnormal or previously damaged (during infancy). Multiple Sclerosis: Damage to nerve fibers of the central nervous system. Prolonged alcohol abuse Hypothyroidism Vitamin B12 deficiency Brain tumors Neurotoxic substances such as mercury or some solvents can cause ataxia if exposed to excessive amounts Side effects of certain medications such as benzodiazepines can may cause ataxia. 2.4 Inherited ataxia Acquired ataxia is caused by errors in genes. There are two main types of inherited ataxia, including:
Autosomal dominant ataxia: Friedreich's ataxia and Ataxia-telangiectasia (Episodic ataxia) and spinocerebellar ataxia (Spinocerebellar ataxia).

3. Diagnosis of ataxia
If you or your child has unexplained symptoms such as impaired coordination, balance, difficulty walking, or difficulty speaking or swallowing, seek medical attention. Doctors will explore and do some tests in diagnosing ataxia as follows:
3.1 History and medical history The doctor may ask about family history of ataxia. In addition, the doctor also asked about the progression of symptoms as well as preliminary assessment of the patient's ability to coordinate movements, balance and walking. The doctor may ask about the patient's history of alcohol and other drug use because alcohol abuse and certain medications can cause symptoms similar to ataxia. 3.2 Tests that may be performed Some tests may be ordered to rule out other causes of ataxia, such as infection (may be blood or urine tests). Gene testing: Includes blood tests and DNA tests for known genetic mutations that cause ataxia. Genetic testing can now detect mutations in Friedreich's ataxia, ataxia-vasodilatation, and most papillary ataxia. Brain imaging: Brain imaging helps to detect brain abnormalities that can cause ataxia. The 2 most commonly used indications are brain MRI and computed tomography. Other tests: A lumbar puncture to detect infection or other abnormalities. Nerve conduction and electromyography studies to evaluate electrical activity in nerves and muscles; electroencephalogram. Video endoscopy takes continuous X-rays that are taken while swallowing different foods and drinks. Electrocardiogram or echocardiogram.
4. Treatment of ataxia
Treatment of ataxia depends on the cause and type of ataxia.
Sometimes the causes of ataxia can be treated to improve or prevent progression. However, in most cases this is not possible and the doctor can only treat the symptoms to relieve the symptoms.
4.1 Speech and language therapy Speech therapy has a role in treating the 2 most common symptoms of ataxia, slurred speech and problems with swallowing
Physiotherapist will give advice on how to voice Yours is clearer.
Methods may include:
Changing positions to improve voice quality Performing exercises to strengthen muscles when speaking Speak slowly to emphasize each word Use breathing techniques to improve If your voice worsens, you may consider using a speech-assisted device such as a laptop connected to a speech synthesizer. The therapist can advise you on the equipment available.
Treatment of dysphagia, the doctor may instruct you to do exercises that stimulate the nerve that controls the swallowing reflex and increase muscle strength when swallowing. You can see a dietitian who uses foods that are easy to swallow.
4.2 Physiotherapy Helps maintain functional activities of the arms and legs; prevent muscle weakness or spasticity. Include physical exercises to help build strength and reduce muscle loss. 4.3 Treatment of ataxia with known cause Ataxia due to vitamin E deficiency: Vitamin E supplementation Intermittent ataxia: Acetazolamide and avoidance of stress, alcohol and caffeine Acquired ataxia: Depends on the cause. Examples of antibiotics for ataxia due to infection. With severe brain damage such as stroke or traumatic brain injury, the disease may not be completely cured. In such cases symptom control is the goal of treatment. In addition, patients should also combine the treatment process with psychological examination methods to help the treatment results to be more effective and faster.
Master Doctor Huynh An Thien has strengths and experiences in examination, consultation and treatment of neurological diseases; respiratory and endocrine-metabolic diseases
Before being a neurologist at the Department of Medical Examination and Internal Medicine - Vinmec International Hospital Da Nang, Dr. Thien used to have long working experience at the hospital Hue Central
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.