This is an automatically translated article.
Hemorrhage is a condition in which there is heavy bleeding after giving birth. Up to 25% of deaths are directly related to haemorrhage and it is the most common cause of maternal death after birth. In addition to the common postpartum haemorrhage, there is another type called late postpartum hemorrhage that occurs between one and two weeks postpartum.1. How can I tell if my postpartum bleeding is abnormal?
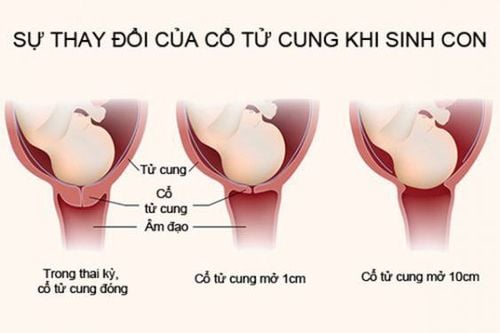
All new mothers experience vaginal bleeding soon after giving birth, as the uterus sheds its thick layer of tissue from pregnancy. This type of bleeding and discharge is called Lochia (postpartum bleeding). The discharge is usually bright red at first but will gradually lighten in color and decrease in number over the first few days.However, some women experience heavy bleeding after giving birth and need to be monitored and treated in medical facilities. This excessive bleeding is called postpartum hemorrhage. Heavy bleeding that occurs within the first 24 hours after birth is considered primary postpartum hemorrhage. About 1 percent of postpartum women experience severe bleeding beyond 24 hours to 12 weeks after giving birth, this is known as late postpartum or delayed postpartum hemorrhage. On average, late bleeding usually occurs one to two weeks postpartum.
Therefore, after giving birth, if the mother has bright red bleeding that lasts more than a few days after giving birth, she should contact a doctor at medical facilities. As this could be a sign of another medical problem. In addition, you should also seek medical attention immediately if you have bleeding that drenches an entire tampon within an hour or if you have a blood clot larger than a golf ball.
Get emergency medical help if you are bleeding heavily or have any unusual symptoms, including:
Lightheadedness Fatigue Fast heartbeat or palpitations Rapid or shallow breathing Cold sweats Confusion
2. Causes of late postpartum hemorrhage?
2.1. Causes of Late Postpartum Bleeding Late postpartum bleeding can happen if your uterus doesn't contract normally after you give birth. Sometimes this happens when pieces of the placenta or amniotic sac remain in your uterus after delivery. In addition, an infection can also cause delayed postpartum bleeding.You may have a higher risk of postpartum hemorrhage if you have a systemic clotting disorder. It may be hereditary or develop during pregnancy due to complications such as severe preeclampsia or HELLP syndrome or placental abruption. In addition, bleeding can also cause clotting problems, leading to even heavier bleeding. Sometimes a late postpartum hemorrhage can't find a specific cause.
2.2. Risk factors for postpartum hemorrhage Having a risk factor does not mean that you will definitely have postpartum bleeding, but it can increase your risk. Some factors like:
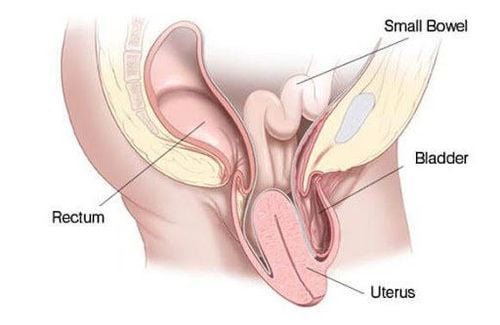
You are more likely to have postpartum hemorrhage than other women if you have had postpartum bleeding in a previous birth. Asian and Hispanic women are also more likely to have postpartum hemorrhage than women of other races. Uterine: This is the most common cause of postpartum bleeding. It occurs when the muscles in a woman's uterus contract after giving birth. Uterine contractions after birth help stop bleeding at the site where the placenta separates from the uterus. The placenta develops in the uterus and provides the fetus with food and oxygen through the umbilical cord. You may have uterine atony if your uterus is stretched or enlarged with twins or a large baby (more than 8 pounds, 13 ounces). Postpartum haemorrhage can also occur if you have had many babies, have been in labor for a long time, or you have too much amniotic fluid. Placental abruption: This occurs when the placenta separates from the uterine wall before birth. The placenta may separate partially or completely. Comb placenta, comb placenta: These conditions occur when the placenta grows too deep into the uterine wall. Placenta previa: This condition occurs when the placenta lies very low in the uterus and covers all or part of the cervix. The cervix is the opening of the uterus located at the top of the vagina. Placental abruption: This happens if the placenta is not ejected from the uterus within 30 to 60 minutes after childbirth. Even if you pushed the placenta soon after giving birth, your doctor will still have to check to make sure there is no placental tissue left in the uterus. If placental tissue is missing and not removed from the uterus, it can immediately cause bleeding.

Nếu mô nhau thai bị thiếu và không được lấy ra khỏi tử cung thì ngay lập tức nó có thể gây chảy máu
Tăng huyết áp thai kỳ là một trong số những yếu tố nguy cơ gây xuất huyết muộn sau sinh
3. What is the treatment for late postpartum hemorrhage?
If your postpartum bleeding becomes life-threatening, you will need to be hospitalized until the bleeding is under control and your vital signs are stable.First, your doctor will give you a physical exam and start intravenous fluids to give you fluids and medicine to help your uterus contract more quickly. You may be given antibiotics if your doctor suspects you have an infection that can lead to late postpartum bleeding.
You will also need to have an ultrasound done to check if any pieces of placental tissue are left in your uterus. If any tissue remains, you may need to have a type of obstetric technique called dilation and curettage to remove any remaining tissue.
Your doctor may also place a small "balloon" in your uterus. This balloon puts pressure on the wall of the uterus to insert blood vessels and help with blood clotting. This balloon is usually left in overnight, along with a catheter to keep your bladder from draining urine.
In some cases (like if the bleeding doesn't stop or your vital signs are unstable) you will need a blood transfusion. Rarely, abdominal surgery or hysterectomy is needed to stop bleeding.
Once the bleeding is under control, you will continue to receive intravenous fluids and medications (usually an additional 24 hours) to help your uterus contract.
The medical team will monitor your recovery closely to make sure heavy bleeding does not continue and watch for signs of infection. You may also continue to need antibiotics.

Bạn có thể dùng thuốc kháng sinh nếu bác sĩ nghi ngờ bạn có nhiễm trùng
4. What is the recovery like?
You may feel tired at first, so don't try to get out of bed on your own while you're still in the hospital.When you get home, it's important to get plenty of rest, drink enough fluids to stay hydrated, and eat nutritious foods. In addition to taking vitamins and folic acid, it's likely that your doctor will prescribe some iron supplements to prevent or treat anemia caused by excessive blood loss.
Currently, there is no completely optimal treatment in the treatment of severe postpartum haemorrhage, especially late postpartum hemorrhage. Therefore, prevention of postpartum hemorrhage is the best option to protect the health of pregnant women. Preventive measures include:
Good management of pregnancy Detecting high-risk pregnancy Good technique delivery, no prolonged labor Postpartum follow-up within the first 6 hours, especially within 2 hours Postpartum To implement the above measures well, you should choose reputable medical facilities to monitor pregnancy, childbirth, labor, and postpartum care.
After 9 months and 10 days of heavy weight, pregnant women go into labor and face a level of labor pain comparable to 20 broken ribs at the same time. In order for the birth to go smoothly and safely, pregnant women need to understand: How the labor process takes place, how long it usually takes to have a normal delivery or caesarean section, and best protect the health of the baby. fetus. Methods to relieve pain during childbirth, limit pain and relieve psychological pressure during labor. The way to push and breathe during childbirth is usually the right way so that the labor takes place quickly, the pregnant woman does not lose strength during childbirth. How to control postpartum uterine contractions in the shortest time. How to take care of the perineal suture does not cause infection and dangerous complications. Early postpartum re-examination to detect dangerous abnormalities such as residual placenta, missing gauze. Take care of the newborn until full month healthy.

Quản lý thai kỳ tốt là biện pháp tốt nhất phòng các tai biến sản khoa
In addition, a complete "painless delivery" service during and after birth using non-morphine epidural and neuromuscular anaesthesia. During the birth process, the mother will be guided by the midwives on how to push and breathe properly, the baby will be born in just 10-15 minutes. After birth, the baby will be cared for in a sterile room before being returned to the mother.
Pregnant women will rest in a high-class hospital room, designed according to international hotel standards, 1 mother 1 room with full facilities and modern equipment. Mothers will be consulted by nutritionists on how to feed the baby before being discharged from the hospital. Postpartum follow-up with both mother and baby with leading Obstetricians and Pediatricians.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference sources: babycenter.com, marchofdimes.org