This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Truong Nghia Binh - Obstetrician-Gynecologist - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Da Nang International General Hospital.
A lot of women don't realize the birth of a baby isn't complete until the placenta is completely removed from the uterus. In most cases, this process will happen after the baby is delivered vaginally (naturally), however, in other cases, this process does not occur spontaneously, leading to present A part of the placenta is not completely pushed out but remains in the uterus.
1. What is post-partum lactation?
After giving birth, the pregnant woman will have a placental abruption to remove all the placenta from the uterus. However, in some cases, the placenta is not completely removed, but remains in the abdomen, which will adversely affect the health of the pregnant woman. Therefore, after giving birth, pregnant women need to pay attention to the signs of placental remnants for timely detection.If the placenta remains inside the uterus, the consequences can be life-threatening, leading to infection and even death.
2. Causes of retained placenta
There are three main reasons leading to placental abruption:Uterine Atony: This is the main cause of placental abruption because the uterus does not contract enough or stops contracting to push the placenta out. from the uterus. Placenta entrapment: Occurs when the placenta separates from the uterus but gets stuck behind a closed cervix, when the cervix begins to close before the placenta is completely removed. Placenta previa is a placenta that does not attach to the fundus of the uterus, but part or all of the placenta attaches to the lower uterine and cervical regions, obstructing the path of the fetus during labor. There are 4 types of placenta previa: low-lying placenta (placental margin adheres to the lower uterine segment, not yet within the cervix), margin-attached placenta (placental margin adheres to the endocervical foramen), pre-placental placenta. semi-central (placenta partially covers the cervical opening), central previa (placenta completely covers the internal cervical opening). Placenta percreta is when part or all of the placenta invades and cannot be separated from the uterine wall. Normally, after birth, the placenta will separate from the uterine wall and come out, but when the placenta is attached, the placenta cannot detach from the uterus and is the cause of postpartum hemorrhage. bleeding disorders, residual vegetables... even death for the mother.
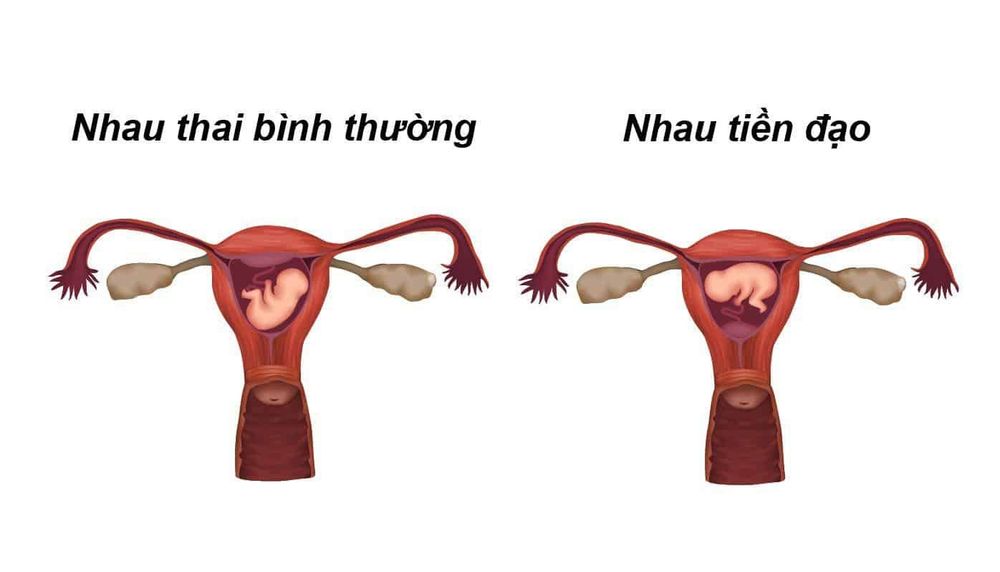
3. Risk factors for placental survival after birth
Preterm birth or giving birth before the 34th week of pregnancy. Lobulated placenta. History of placenta previa Has had 5 births Pregnancy after 35 years of age Stillbirth Prolongs the first or second stage of labor Women with a history of uterine surgery If the woman has any weakness If you have any of the above risk factors, talk to your doctor for advice on health care and ways to prevent miscarriage.4. Symptoms of residual placenta after childbirth need attention
When there is a missing placenta in the body, women will experience symptoms within a day after giving birth, including:Fever The most recognizable sign of placental abruption is heavy bleeding after delivery. Many people often mistake it for translation. However, blood due to retained placenta is black, has an unpleasant odor, and is accompanied by persistent dull pain in the lower abdomen. Bad odor in vaginal discharge Persistent bleeding Severe cramps and spasms Delayed milk
5. Treatment of residual placenta after birth
Manual placental removal: The doctor does this in the delivery room or operating room. The doctor will place a urinary catheter to drain urine and empty the bladder, and give you intravenous antibiotics to prevent infection. You will also receive local, spinal, or epidural anesthesia. The doctor will then place his hand inside the uterus to remove the placenta. You may need more intravenous medication after a manual placental ablation to help the uterus contract. Controlled cord traction: This technique is performed when the placenta is separated from the uterus, but still cannot come out. In this case, the doctor will gently pull the umbilical cord to help the placenta get out of the uterus and body. Curettage is a procedure performed by a gynecologist to clean the uterus from the remains of an incomplete abortion, the placenta after a normal delivery, or a vaginal birth.
Hysterectomy: In the case of the placenta percreta, where the placenta grows deep into the uterus, a hysterectomy may be required if necessary to save the woman's life. However, when a hysterectomy is performed, the woman cannot become pregnant in the future. Your doctor will also prescribe some oral antibiotics after any of the treatments above to prevent or treat an infection. Ensuring that the placenta has completely come out of the uterus, whether it is a vaginal birth or a cesarean section, depends not only on the mother's condition but also on the qualifications of the obstetrician-gynecologist as well as the care. postpartum for mothers. With the Maternity Package at Vinmec International General Hospital, mothers and babies will be cared for and monitored not only before and during childbirth, but also after birth. Mother's health will be restored fastest, avoiding complications later.
To know more about the maternity packages of Vinmec International General Hospital, you can call hotline 0243 9743 556 or register online HERE
Specialist I Truong Nghia Binh Has over 13 years of experience in the field of obstetrics and gynecology, has high expertise and long experience in diagnosing and treating obstetrics and gynecological diseases such as:
Screening for mother and baby diseases Before birth, chorionic villus biopsies, amniocentesis.. Ultrasound to screen for fetal malformations (3D, 4D ultrasound) Follow-up, birth control in cases of normal delivery, difficult birth Examination and treatment of pre-eclampsia diseases, placenta previa, pregnancy with complicated medical conditions... Cesarean section for first, second, third time caesarean section... Examination and treatment of gynecological diseases. Examination and consultation of infertile couples
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.