This is an automatically translated article.
Intussusception is treated by defibrillation or surgical surgery depending on each specific case. Today, with the advancement of medicine, laparoscopic surgery is widely applied because it has many advantages over open surgery.
Laparoscopic surgery to remove the intussusception and fix the cecum is a highly effective method for children with intussusception to help them recover quickly and avoid complications.
1. What is intussusception?
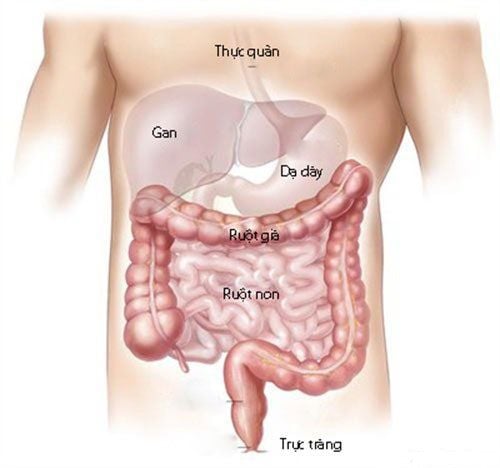
Intussusception is a disease caused by a segment of intestine entering the adjacent segment of intestine, creating intestinal obstruction syndrome according to the mechanism of occlusion and obstruction. Intussusception can occur when the small intestine enters the small intestine or the small intestine enters the colon. Intussusception is a common abdominal emergency in children, especially breastfed babies, rare in adults and easy to miss. Children with intussusception can experience dangerous complications such as: intestinal perforation, intestinal necrosis causing generalized peritonitis, toxic septic shock, and even death if not diagnosed early and treated promptly. time. Treatment of intussusception includes conservative treatment with air or water intubation and surgery. Surgery includes open surgery and laparoscopic surgery. Laparoscopic surgery is applied in some cases to treat acute intussusception, especially in the ileocecal region.
2. Diagnosis of intussusception
Diagnosis is based on the following symptoms:
Children with intussusception have clinical manifestations including:
Children cry intermittently due to abdominal pain. This is the main symptom and assessment of the duration of intussusception. Quit suckling. Vomiting of food just sucked, in some cases later vomiting digested food. Hemoptysis: 6-12 hours after abdominal pain. On examination, the intussusception may be palpable or the abdominal wall is responsive to palpation. Rectal examination showed blood under gloves, palpable tip of the intussusception. Subclinical:
Ultrasound: is the first option that can find images of intussusception such as: In cross section: target image with hyperechoic central region and hypoechoic periphery. On the longitudinal section: Sandwich shape. Colon X-ray with contrast: gradually replaced by ultrasound, almost rarely used to diagnose intussusception.

Trẻ nôn là dấu hiệu của bệnh lồng ruột
3. Treatment of intussusception
3.1. Remove the cage with the inflatable
It should be done as soon as possible.
Contraindications:
Late arrival after 48 hours. Bad condition or shock. There are complications of intussusception such as: bowel perforation, complete bowel obstruction shown clinically as well as X-ray.
3.2. Surgery
When air intubation is not possible, there are contraindications to air intubation, intussusception has a physical cause.
Notes when performing surgery:
Need to prepare before performing surgery such as: Rehydration, electrolytes and acid-base balance, gastric bypass and use of antibiotics to prevent infection. Surgery includes open surgery and laparoscopic surgery. In which, laparoscopic surgery is highly effective in shortening the hospital stay, but requires the facility to have adequate equipment and experienced surgeons.
4. Laparoscopic surgery to remove the intussusception and fix the caecum
Indications for laparoscopic intussusception surgery: When air intubation fails. Patient arrived late after 24 hours. Repeated intussusception (>2 times) with uncertain etiology (laparoscopic intubation combined with diagnosis). Indications for ileocecal fixation: Recurrent ileocecal intussusception more than 2 times. There is no primary cause of intussusception. The cage can be completely removed. Contraindications: The general contraindications of laparoscopic surgery include: coagulation disorders, hemodynamic disorders, severe cardiopulmonary disease. Complete intestinal obstruction or large bowel distention. Peritonitis. Procedure: Place the trocar into the abdomen, pump CO2. Observe the abdomen, evaluate for peritonitis, intestinal obstruction, intestinal perforation or not. Use 2 soft clamps to work on the cage block. With one hand pull the neck of the cage (proximal bowel) away from the tip of the cage (distal bowel). When removing the intussusception, it is necessary to re-check the intussusception for ischemic or necrotic lesions, re-examine the entire intestine to assess the digestive circulation. Stitch the caecum if indicated. Appendiceectomy was performed, and the positions of the cecum, the appendix root and the terminal ileum were fixed to the lateral abdominal wall with undissolved sutures, respectively.
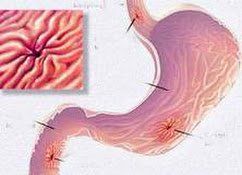
Trước khi phẫu thuật cần quan sát xem có thủng ruột hay không
5. Accidents and handling
Intraoperative complications: General complications such as: complications related to trocar (bleeding, intestinal perforation, mesenteric tear...), intraoperative bleeding and similar management in all other cases. Intestinal perforation due to intestinal traction and conversion to open surgery, suture, laparoscopy or open surgery. Post-operative complications: Incisional infection and wound care. Dissection of the appendix stump after appendectomy causes peritonitis. Paralytic ileus, intestinal obstruction after surgery. To book an appointment for examination and consultation, you can contact Vinmec International General Hospital nationwide or register online HERE.