This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Nhu Thu Truc - Obstetrician and Gynecologist - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Currently, the laparoscopic ovarian cyst removal treatment method is increasingly dominant because of its safety, effectiveness, quick handling, and less pain. However, not all cases can be performed laparoscopically.
1. When is laparoscopic surgery to remove ovarian cysts indicated?
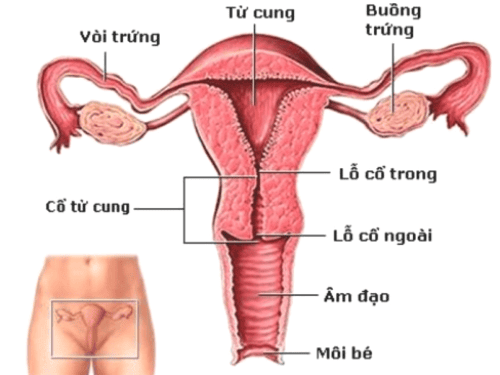
Laparoscopic surgery is the most widely used method today in surgical treatment, removal of ovarian cysts or adnexa. This method is indicated for the following cases:
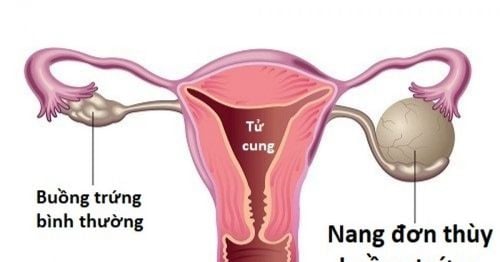
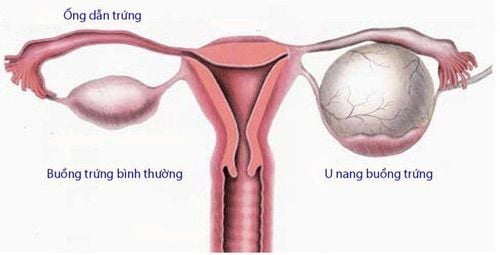
Ovarian tumor is not suspected of malignancy and is not too big, not too sticky. Water cyst next to the fallopian tube. Pyelonephritis of the fallopian tubes. Breast cancer with indications for oophorectomy. With contraindications to laparoscopic ovarian cystectomy or having performed the old surgery many times, it will be forced to open the abdomen to remove it. Contraindications include:
Patients who are in their menstrual cycle or have abnormal bleeding that have not been cured. Have an infection or blood disease. Having medical diseases and contraindications for laparoscopic surgery. The tumor is very sticky, has undergone abdominal surgery many times. Ovarian Cancer .
2. Steps in laparoscopic ovarian cyst removal surgery
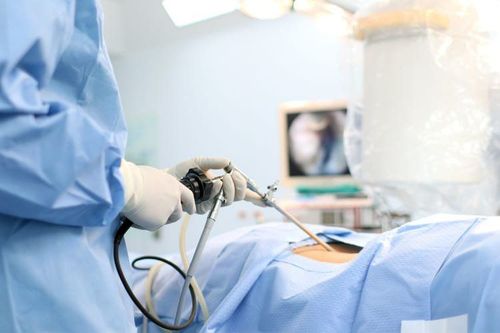
2.1. Preparation for surgery Performing laparoscopic ovarian cystectomy is an obstetrician and gynecologist trained in laparoscopic surgery. It is necessary to prepare a full set of laparoscopic surgery, equipment, facilities, operators and nurses to wear clothes, wash hands, wear hats, and wear sterile gloves.
Before surgery is indicated, the patient should have a complete and specialized examination to assess overall health and detect contraindications. After that, the doctor will consult carefully about the disease, endoscopic technique as well as possible complications. Should operate after about 1 week after menstruation, the patient will be cleaned with an enema 2 hours before surgery, when transferred to the operating room, the patient will be disinfected on the abdomen, covered with a sterile cloth and anesthetized for endotracheal intubation.
2.2. Procedures The steps for laparoscopic surgery to remove ovarian cysts are as follows:
Inflate the peritoneal cavity (through a needle or a trocart). Insert the light into the abdomen. Examination to assess the status of the ovarian tumor to see how mobile and attached it is to surrounding organs. If it is sticky, it must be removed. When removing the adhesive, pay attention to avoid the tumor breaking. If the prognosis is difficult when endoscopic resection, it must be switched to open surgery. For laparoscopic ovarian cyst removal:
Use a single-pole knife to make an incision on the surface of the tumor about 2cm long, close to the healthy ovary. Use a small forcep to place one side of the tumor incision and pull it up. Using a pick, gradually remove the tumor from the tumor shell. When you have reached the bottom of the tumor, depending on the condition of the tumor, do one of the following two ways: If the tumor is small, the prognosis is not to bleed, then remove the tumor. If the risk of bleeding in the tumor stalk is high, use a 2-pole electric knife to burn the tissue at the bottom of the tumor, use scissors or a single-pole knife to cut the tumor stem. Take the specimen through the bag and send it for testing for pathology to check the nature of the tumor, benign or malignant. Check for bleeding, if necessary, stop bleeding with a double-pole knife. Withdraw the trocart, suture the abdominal incision. For laparoscopic tumor resection:
Use a double-pole knife and burn the tumor stalk from the lumbar-ovarian ligament. Use scissors or a unipolar knife to cut the stem of the tumor. Take the specimen into the bag and send it to the laboratory for pathology to check the nature of the tumor, benign or malignant. Check for bleeding and, if necessary, stop the bleeding with a double-pole knife. Examine the opposite ovary. If the tumor is suspected to be cancerous, a small piece of the opposite ovary is removed for histopathological examination. Withdraw the trocart, suture the abdominal incision. Note: If the tumor is large, aspirate the fluid and proceed as above. For laparoscopic appendectomy:
Examine and assess the condition of the appendix to see if it is attached to surrounding organs. If it is sticky, it must be removed, while removing the adhesive, be careful not to break the fluid. Use a double-pole knife and burn the pedicle of the tumor including the broad ligament and the mesenteric-ovarian mesentery. Using scissors or a single-pole knife, cut the stalk of the lumbosacral ovary and the broad ligament. Take the specimen into the bag and send it to the laboratory for pathology. Check for bleeding and, if necessary, stop the bleeding with a double-pole knife. Withdraw the trocart, suture the abdominal incision.
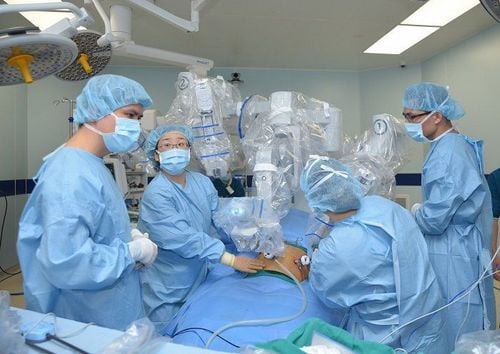
3. Complications and management when laparoscopic surgery to remove ovarian cysts
In general, complications and management of laparoscopic ovarian cyst removal are the same as those of conventional laparoscopy. If bleeding cannot be stopped, switch to open surgery. This endoscopic method has few complications, good effect, patients can be discharged after 24-48 hours of follow-up.
4. Why should laparoscopic ovarian cyst surgery be performed at Vinmec?
Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital has applied laparoscopic surgery since 2018 in the treatment of ovarian cysts. This method achieves a treatment efficiency of over 95% with the treatment of infertility, gynecological pathology, performed by experienced doctors such as:
Master. Thai Bang, has over 14 years of experience in obstetrics and gynecology, prenatal diagnosis and assisted reproduction. Doctor. Doctor Ngo Thi Uyen, has more than 20 years of experience in the field of Obstetrics and Gynecology, especially in the examination and surgery of ovarian cysts, uterine fibroids, and benign breast tumors. Doctor Mykhailo Dudik with 8 years of experience working in many international hospitals, especially has strengths in examination and treatment in the field of obstetrics and gynecology.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.