This is an automatically translated article.
Laparoscopic surgery are minimally invasive interventions to perform surgery. In the past, this technique was commonly used for gynecological surgery and gallbladder surgery. Over the past 10 years, laparoscopic surgery has replaced nearly all open abdominal surgeries.
1. What is Laparoscopic Surgery?
Laparoscopic surgery is a type of surgery to check for problems, diseases inside the body's cavities, such as the abdomen, chest or reproductive system of a woman.
Laparoscopic surgery is done using small tubes called endoscopes. The tubes are all inserted into the body through very small incisions. These are cuts in the skin that sometimes heal undetected. The functions of these tubes include:
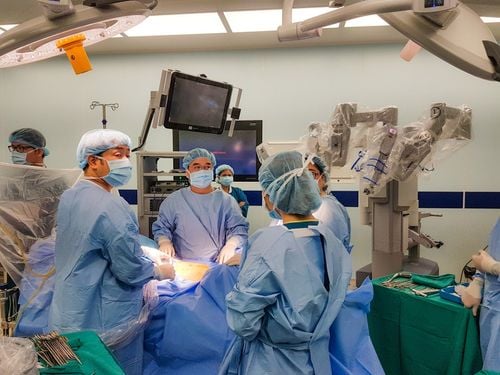
Attach a light source and a camera to send images to an external video monitor, allowing the surgeon to both observe and manipulate. Putting manipulation tools into the surgical field such as scissors, forceps, electric knives... Laparoscopic surgery is called minimally invasive surgery. Thanks to this method, the patient has a shorter postoperative hospital stay, the ability to recover faster, less pain and smaller scars, more aesthetic than traditional surgery.

Thông qua phẫu thuật nội soi, bác sĩ vừa tiến hành phẫu thuật vừa quan sát được
2. What are the roles of laparoscopic surgery?
For patients with abdominal or thoracic symptoms for which physical examination and imaging tests such as X-rays or ultrasound cannot provide a definitive answer, endoscopy may be used. used for diagnosis, called diagnostic endoscopy. That's when you have:
Tumors and abnormal growths Blockage in body structures Unexplained bleeding Infection. On the contrary, if the endoscopic technique is used to treat the disease by surgical measures, it is called surgical laparoscopy. Indications of laparoscopic surgery in pathologies in the abdomen, urogenital, thorax such as appendicitis, biliary tract infections due to stones, thoracic sympathectomy in the treatment of hyperhidrosis due to sympathomimetic. ..
For women, laparoscopy can be used both to diagnose and to treat the following conditions:
Uterine fibroids form inside or outside the uterus Ovarian cysts form inside or on the surface of the ovary Endometriosis Genitourinary prolapse Removal of an ectopic pregnancy Total hysterectomy Tubal ligation for contraception Treatment of urinary incontinence .
3. Steps performed in laparoscopic surgery
Laparoscopic surgery is usually performed in a hospital and includes the following steps:
Before laparoscopic surgery, the patient will be examined and do preoperative tests like any other routine surgery On the night before surgery During laparoscopic surgery, the patient is instructed to fast, drink and clean the body with an antiseptic solution On the day of laparoscopic surgery, the patient will be changed into hospital clothes The patient will be arranged to lie on the operating table with proper position The patient will be given general anesthesia and mechanical ventilation through an endotracheal tube or an epidural to block sensation in the lower half of the body When ensuring that the patient is fully anesthetized In total, the surgeon makes a small incision just below the navel to insert the first laparoscope with a camera attached, which captures and transmits images onto an external monitor Other small incisions are also made to insert the instruments. instruments into the operating room, conducting exploration, diagnostic investigations, or surgical interventions During this process, a gas is injected and o to expand the surgical field, making it easier for the surgeon to see inside the patient's body as well as easy to manipulate After the endoscopy is over, the endoscopes are withdrawn, the air will be removed cancel. The incisions will be closed with a target or non-absorbable suture and bandages. The patient will be transferred to the recovery room, the breathing tube will be removed and waiting to be awake before returning to the rest room.

Phẫu thuật nội soi nên được thực hiện ở các bệnh viện uy tín, an toàn
4. Possible risks after laparoscopic surgery
Different from traditional open surgery, laparoscopic surgery makes very small skin incisions, postoperative recovery time is shortened and less painful. However, laparoscopic surgery still contains potential risks due to trauma in the body cavity:
Bleeding incision Hematoma in the abdomen, chest Incision infection Peritonitis Injury to internal organs around Traction Adhesives Heals bad scars Complications from anesthesia. Therefore, although laparoscopic surgery is the minimal intervention, the patient also needs to be closely monitored in the postoperative period in order to detect complications early and intervene in a timely manner.
The problem of wound care after endoscopic surgery is somewhat simpler than traditional surgery, however, the patient still needs to be scheduled for a follow-up appointment for a comprehensive evaluation of the surgery.
Compared with traditional open surgery, when applying laparoscopic surgery, patients usually have less pain, shorter recovery time and less scarring. With these advantages, laparoscopic surgery has been the preferred method of choice. Therefore, it is necessary to find out and consider choosing reliable and professional medical facilities to conduct endoscopy and effectively treat the disease with the lowest level of trauma.
With outstanding advantages in facilities, modern machinery system, Vinmec International General Hospital is increasingly appreciated in the performance of laparoscopic surgery techniques to treat many different diseases.
The medical team performing the surgery are highly qualified and experienced, ready to handle even when unexpected complications occur. After surgery, the patient will be cared for and closely monitored, rested in a high-quality ward of international standards, providing maximum support for the recovery process.
Customers who need medical examination and treatment can directly go to Vinmec Health System nationwide or book an appointment online HERE.
MORE:
What is Laparoscopic Surgery? Why is laparoscopic surgery more and more popular? Learn about robotic laparoscopic surgery Robotic surgery "blows away" prostate cancer for Japanese doctors
Close-up of prostate cancer treatment with robotic laparoscopic surgery