This is an automatically translated article.
Laparoscopic surgery to remove adhesions for people with empyema is aimed at breaking all the nooks and crannies, combined with early lung peel, to prevent complications.1. Purpose of laparoscopic surgery to remove adhesions for people with empyema
Pleural endoscopy is a procedure in which the doctor minimally penetrates the patient's pleural space to view the pleural space and structures in the chest to detect whether the patient is injured or not and is often used in endoscopic removal of adhesions due to pleural effusion.Laparoscopic surgery to remove adhesions for people with empyema is aimed at breaking all the nooks and crannies, combined with early lung peel.
2. Indications and contraindications for endoscopic adhesion removal for people with empyema
Indications for endoscopic removal of adhesions for people with empyema in the following cases:Drainage of solid pus, many pseudomembranous membranes but failed irrigation method The patient is exhausted, loses resistance or has a prolonged infection, fever pleural drainage combined with antibiotic use is not effective. Contraindicated endoscopic adhesion removal for people with empyema in the following cases:
Patients with severe systemic disease; Cardiovascular abnormalities such as: heart failure, arrhythmia, ischemic cardiomyopathy, heart valve. Hemodynamic instability; empyema is a relative contraindication. The patient has thickened pleural adhesions. Patients with coagulopathy with prothrombin ratio <60% and platelets <60G/L. The patient coughs a lot and cannot control the cough.

Bệnh nhân ho nhiều, không dứt được cơn co ho có chống chỉ định với mổ nội soi gỡ dính cho người bị viêm mủ màng phổi
3. Steps to perform endoscopic techniques to remove adhesions for people with empyema
Step 1: Full surgical facility, meeting the requirements of thoracic and vascular surgery; Monitor arterial blood pressure, venous blood pressure, oxygen saturation, breathing rate, electrocardiogram; endoscope; Laparoscopic surgery kit.Step 2: Anesthetize the patient, flatten the lung on the patient's side by isolating the lung by endobronchial.
Step 3: Depending on the location of the fluid collection cavity, place the trocar, then remove the pus and break the pleural adhesions, removing most of the pus and pseudomembranous surface, especially the diaphragm.
4. Monitoring and handling of accidents
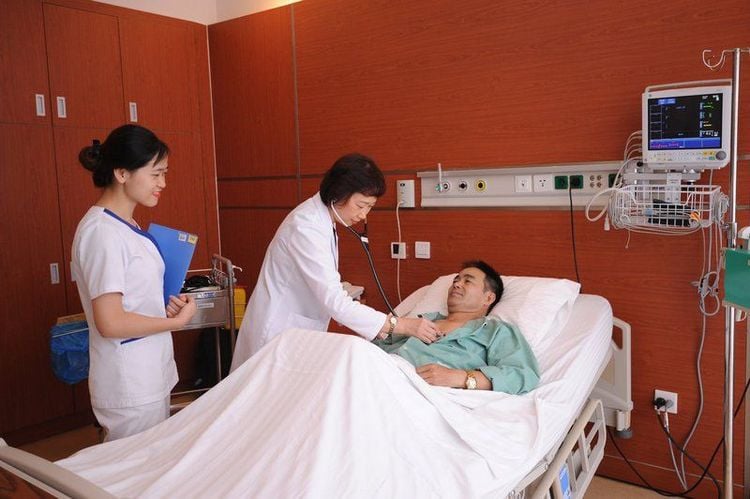
Sau khi mổ bệnh nhân cần được hút rửa màng phổi trong 3-4 ngày
Pain relief, sputum suction to avoid lung collapse. Active respiration after surgery. Aspiration pleural lavage in 3-4 days after surgery. Management of complications:
Drainage should be closely monitored to detect bleeding, if bleeding, re-operate to stop bleeding. It is necessary to detect atelectasis early so that the patient can practice breathing, vibrate, loosen phlegm, change the dressing, take care of the wound, treat with antibiotics if there is an infection. Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit. and hospital treatment.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
SEE MORE
Find out information about empyema Signs and causes of pleurisy How is pleurisy diagnosed and treated?