This is an automatically translated article.
Hydrocephalus is a disease that can leave many serious sequelae in children, even leading to death. Early diagnosis and treatment of hydrocephalus will help children have a chance for normal mental and motor development. Among the treatment methods, laparoscopic surgery to break the floor of the third ventricle is the optimal choice at present.
1. Overview of hydrocephalus
1.1 What is hydrocephalus? Hydrocephalus is also known as hydrocephalus. This is an excess of cerebrospinal fluid that forms in the ventricular system of the brain, which can increase intracranial pressure. Hydrocephalus can occur at any age but is more common in infants and people over 60 years of age.
Common causes of hydrocephalus are: Heredity, developmental disorders (vertebral fractures and brain herniation), intracerebral hemorrhage, head trauma, brain tumor, complications of preterm birth (hemorrhage, inflammation, etc.) meningitis , infection, ...) or due to a blockage of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain.
1.2 Symptoms of hydrocephalus Hydrocephalus symptoms are different in each different subject. Specifically:
Symptoms of hydrocephalus in infants: Abnormally large head circumference, thin scalp, tight and bulging fontanel, scalp veins, bones separating in the child's head, vomiting, drowsiness , excitability, convulsions, loss of appetite, skewed eyes,...; Symptoms of hydrocephalus in children: Abnormal head circumference, nausea, vomiting, headache, fever, blurred or double vision, balance disorder, drowsiness, excitability, movement or slow pronunciation, poor coordination, inability to concentrate, seizures, loss of appetite, loss of sensory motor function, difficulty staying awake or waking up,...; Symptoms of hydrocephalus in young and middle-aged people: Headache, loss of coordination or balance, difficulty staying awake or awake, loss of bladder control, impaired vision and cognitive skills; Symptoms of hydrocephalus in the elderly: gait disturbance, loss of coordination or balance, headache, memory loss, loss of bladder control, etc.
1.3 Diagnosis and treatment of hydrocephalus
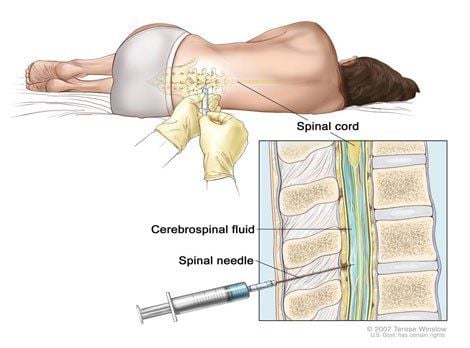
Hình ảnh trẻ bị não úng thủy
To diagnose hydrocephalus, your doctor will review your medical history, perform a neurological exam, perform tests such as ultrasound (for infants), computed tomography (CT scan), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). (MRI).
There are many treatments for hydrocephalus. Specifically, direct treatment of the causes of cerebrospinal fluid obstruction or indirect treatment by directing the fluid to another place (a space in the body such as the peritoneal cavity, pleura, pericardium, ...) . Indirect therapy is performed by implanting a catheter that diverts excess cerebrospinal fluid from the brain, to the peritoneal cavity. However, this method has many potential complications such as bleeding in the brain, infection and blocked drains. At the same time, the patient may have to have many surgeries, causing great harm to health, prolonging the hospital stay and increasing the cost of treatment
An alternative treatment method is laparoscopic surgery to break the floor Endoscopic third ventriculostomy uses a flexible endoscope with a small camera to look inside the ventricular system, breaking the floor of the ventricles, allowing the surgeon to create a new path for blood flow. CSF. The advantages of this method of treatment are short duration (about 30-40 minutes), small lesions, less pain, and reduced risk of complications and infections.
After hydrocephalus treatment, the patient's neurological function will be assessed. The ability to recover will depend on the cause of the disease, the extent of damage caused by hydrocephalus. At the same time, the patient is continuously monitored through tests such as CT scan, MRI scan, X-ray,...
2. Details of laparoscopic surgery to break the floor of the third ventricle
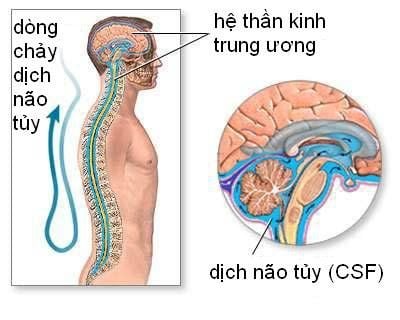
Phẫu thuật nội soi phá thông sàn não thất III
Laparoscopic III ventricular septal defect is a method of treating hydrocephalus by creating a hole in the floor of the 3rd ventricle, allowing CSF to drain directly into the basal cisterns.
2.1 Indications/contraindications Indications
Patients with obstructive hydrocephalus; The patient developed an infection after the placement of a ventricular drain; Abdominal treatment of hydrocephalus. Contraindications
Relative contraindications for patients with catheter tip.
2.2 Preparation for surgery Personnel: Neurosurgeon; Means: Skull drill, bone scraper and bone lifter, bone wax; endocardial ventricular system; instrument to break the floor of the third ventricle; Patient: The patient was diagnosed with obstructive hydrocephalus, had the necessary diagnostic imaging tests done, and the doctor shared information about the surgical purpose, procedure, and procedure. ..; Medical records: Complete information about the patient, no contraindications for surgery under anesthesia; Brain MRI before surgery to help doctors understand the imaging features before surgery.
2.3 Performing surgery

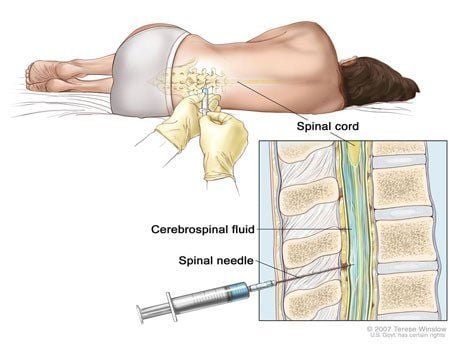
Gây mê trước khi thực hiện phẫu thuật cho bệnh nhân
Check patient records; Checking the right patient, the right disease; General anesthesia of the patient; Place patient in supine position with head elevated 30°; Cranial drilling: In front of coronal joint, 2 - 3cm from midline and about 6 - 10mm wide. Should choose craniotomy in the right position or the side with more dilated ventricles; Cross-section of the epidural, using the endoscopic system; Determine the Monro hole; Identify the floor of the third ventricle, make sure it is thin enough, transparent enough, that the basilar artery and 2 nipple bodies can be visualized. If these structures cannot be observed, the procedure should be discontinued; Select floor openings that meet the technical criteria; Perforation of the floor of the third ventricle; After perforating the floor of the third ventricle, it is important to ensure that the vascular structures are visualized.
2.4 Complications after surgery and how to manage
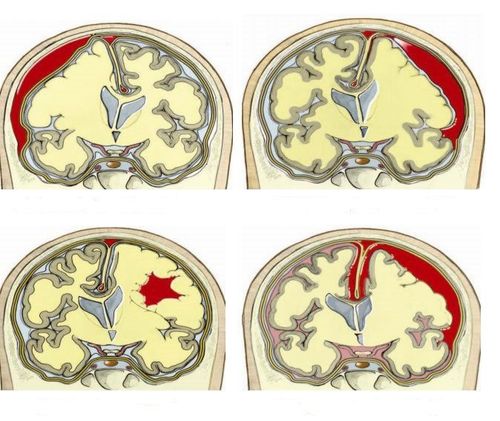
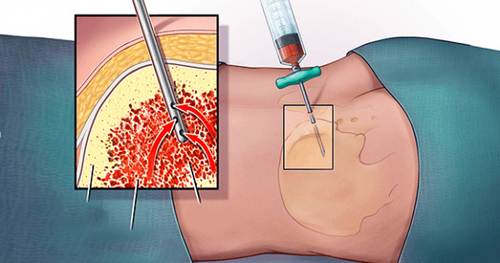
sau phẫu thuật bệnh nhân có thể bị máu tụ trong não
Injury to the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and pituitary stalk: Prophylaxis by identifying structures before and during surgery; Transient III, IV nerve palsy: Manage as indicated; Uncontrolled bleeding (intraventricular haemorrhage): Treat by placing an external ventricular drain; Cardiac arrest: Treat by performing CPR; Meningitis: Management is to identify the causative agent and use appropriate antibiotics; Epilepsy: Prophylaxis is the use of antiepileptic drugs in all cases of invasive brain procedures; Injury to the basilar artery: Treat as indicated; Hematoma in the brain: Depending on the damage can be conservative treatment or surgery. If you experience postoperative symptoms such as: Redness, pain or swelling of the skin along the length of the tube or wound; irritability, drowsiness; nausea, vomiting, headache, double vision; stomachache; fever; recurrence of neurological symptoms before surgery,... the patient should quickly contact the doctor for timely treatment.
Hydrocephalus, when diagnosed early, has a high chance of successful treatment. When being assigned to perform endoscopic surgery to break the floor of the third ventricle for the treatment of hydrocephalus, the patient needs to strictly follow the instructions of the doctor to treat the disease effectively and reduce the risk of complications.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in neurological examination and treatment, patients can completely peace of mind for examination and treatment at the Hospital.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
MORE
How is hydrocephalus diagnosed? Dangerous complications of hydrocephalus Learn about testing cerebrospinal fluid to find the cause of headaches