This is an automatically translated article.
Endoscopic transsphenoidal pituitary surgery is performed through the nose to remove tumors from the pituitary gland and base of the skull. In this minimally invasive surgery, the doctor intervenes through the nostrils and uses a small endoscope with a light source to reach and remove the tumor.Because pituitary tumors can cause hormone disturbances and vision loss, early endoscopic treatment is considered effective and offers many advantages.
1. What is transsphenoidal pituitary surgery?
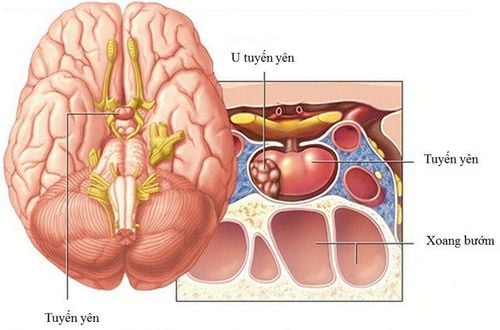
Transsphenoid pituitary surgery is a surgery performed through the nose and sphenoidal sinuses in the nose to remove pituitary tumors.
The entire intervention is done through the endoscope and requires coordination between the neurosurgeon and the ear - nose - throat surgeon.
The traditional endoscopic route is through a skin incision under the upper lip and removal of a large portion of the nasal septum so that the surgeon can directly see the sphenoid sinus area. Meanwhile, minimally invasive endoscopic surgery requires only a small incision in the back of the nasal cavity. In both techniques, the bony wall behind the nose needs to be penetrated to access the pituitary gland. At this point, by looking at the screen, the neurosurgeon will dissect and remove the tumor in the pituitary gland.
2. Who is indicated for laparoscopic pituitary surgery?
Patients are indicated for laparoscopic pituitary surgery if they have the following pathologies:
Pituitary adenoma: a tumor that develops from the pituitary gland, can secrete hormones or not. Craniopharyngioma: a benign tumor that develops from cells near the pituitary stalk, which can invade the third ventricle. Pituitary Cyst: A benign cyst that is essentially a fluid-filled sac, between the anterior and posterior lobes of the pituitary gland. Meningiomas: a tumor that develops from the meninges, the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. Chordoma: a malignant bone tumor that develops from the base of the skull. In the case of patients with proliferative or small nonsecretory tumors (less than 10 mm), surgery may not be necessary. These tumor types need to be considered for a good response to medication or can be evaluated with periodic cranial magnetic resonance imaging to monitor tumor growth.
In contrast, some tumors that are beyond the limits of endoscopic methods should consider craniotomy.
Bệnh nhân u màng não được chỉ định phẫu thuật nội soi tuyến yên
3. How to prepare before laparoscopic pituitary surgery
Before deciding to perform laparoscopic pituitary surgery, the patient needs to be carefully examined many times with a neurosurgeon, an ENT surgeon and an endocrinologist. Also, consultation with an ophthalmologist should be considered if the patient has vision problems.
During the final visit, the surgeon will explain the procedure, risks and benefits of laparoscopic pituitary surgery and answer any relevant questions to address all of your concerns. patients and relatives. Once complete, the patient should sign the consent forms and complete the paperwork.
Next step, a pre-anesthetic doctor will take into account your medical history such as drug allergy, blood clotting function, anesthetic reaction, previous surgery. Patients should also tell their doctor about all prescription and nonprescription medications and herbal supplements they are taking. Because some medications may need to be continued or stopped on the day of surgery or a few days before. Also, stop smoking one week before and two weeks after surgery as these activities can cause problems with blood clotting. At the same time, patients also need pre-operative check-up tests, such as blood tests, electrocardiograms, chest X-rays ... a few days before surgery to assess the health of organs as well as tolerance. upcoming surgery.
4. The process of laparoscopic pituitary surgery
When everything is done and ready, the patient will be transferred to the operating room. An anesthesiologist will explain the effects of the anesthetic and its risks. Next, an intravenous line of isotonic physiological solution will be placed and the anesthetic will enter the body through this line. With complete anesthesia and smooth mechanical ventilation through the endotracheal tube, laparoscopic pituitary surgery will begin.
Laparoscopic pituitary surgery usually has six steps and usually takes 2 to 3 hours.
Step 1: Prepare the patient The patient lies on the operating table with the appropriate position. The nasal cavity and the surrounding area are cleaned with an antiseptic solution.
Step 2: Incision The otolaryngologist places the endoscope on one side of the nostril and inserts it straight into the back of the nasal cavity. The images from the camera are viewed on a monitor outside the body that helps the surgeon control the instruments.
A small portion of the nasal septum that separates the left and right nostrils will be removed. At the same time, the anterior bony wall of the sphenoid sinus was also perforated and opened.
Step 3: Accessing the Pituitary Gland Just behind the posterior wall of the sphenoid sinus is the pituitary gland. Accordingly, this layer of bone will also be removed to reveal the dura layer of the skull. By opening the sclera, the entire pituitary gland and tumor will be exposed.
Step 4: Remove the tumor Through a small hole the tumor will be removed in pieces by the neurosurgeon with long endoscopic hand tools.
After all visible tumors are removed, the surgeon conducts the laparoscopy further to look and examine the underlying tumor. Some tumors may grow sideways into the cavernous sinus. At this point, it can be difficult to completely remove these parts of the tumor without causing damage to the nerves and vascular bundles. Therefore, any remaining tumor may be subsequently treated with additional radiation therapy.
At some hospitals, the surgery can be done in a special operating room equipped with a magnetic resonance scanner. This will give surgeons a real picture of the brain to know exactly how much tumor has been removed before the end of the intervention. This technology has the advantage of allowing for more complete tumor removal and may reduce the need for a second surgery.
Step 5: Autologous fat grafting (optional) After the tumor is removed, the surgeon will prepare to close the sphenoid sinus wall. If necessary, a small skin incision is made in the abdominal wall to remove some of the autologous fat tissue to fill in the space left by tumor removal.
Step 6: Close the wall of the sphenoid sinus The hole in the wall of the sphenoid sinus will be replaced by a bone graft from the nasal septum. However, composite grafts are sometimes used when a suitable septum piece is not available or the patient has had a previous laparoscopic pituitary surgery.
In addition, a biological glue is used on the graft in the sphenoid sinus, which promotes healing and prevents the leakage of cerebrospinal fluid from the brain parenchyma into the sphenoid sinus and paranasal spaces.
Finally, a soft splint may be placed in the nose along the septum to control bleeding and prevent swelling. These splints also prevent adhesions that can lead to chronic nasal congestion.

Phẫu thuật nội soi tuyến yên cần thực hiện tại bệnh viện lớn và uy tín
5. How to care and monitor after laparoscopic pituitary surgery?
After surgery, the patient will be taken to the recovery room, where vital signs are monitored until the patient is fully awake and transferred to a separate room for continued monitoring in the hospital. At this point, the patient was also encouraged to get out of bed as soon as possible.
Some people may experience nasal congestion, nausea, and headaches after laparoscopic pituitary surgery. Common pain relievers and anti-allergics can control these symptoms.
The day after surgery, the endocrinologist will examine you to check that the pituitary gland is producing the proper levels of hormones. Otherwise, hormone replacement medications may be offered. At the same time, the entire intervention area will also be re-examined by cranial magnetic resonance imaging.
If everything goes well, in just one or two days, the patient will be discharged from the hospital.
Laparoscopic pituitary surgery through the sphenoid line is a simple and fairly common way to remove the tumor at this location. Minimalist interventions both help to improve the pathology, while limiting trauma to the brain parenchyma as well as shortening the recovery time, minimizing pain for the patient as well as achieving high aesthetics by means of medical equipment. Endoscopic.
Customers who need examination and treatment can directly go to Vinmec Health System nationwide or contact for an appointment HERE.
In April & May 2021, when there is a need for examination and treatment of pituitary tumors at Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital, customers will enjoy double incentives:
- Free specialist examination
- 50% discount for customers with post-examination treatment indications. The program is limited to the corresponding technique of each hospital and to customers who perform this treatment technique for the first time at Vinmec.