This is an automatically translated article.
The article was consulted professionally with MSc. Doctor Vu Thi Duyen - Doctor of Nephrology - Endocrinology, Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Lactic acidosis during diabetes treatment is a rare but serious complication that can be fatal when it occurs. Therefore, patients need to be especially careful when using the drug during treatment.
1. What is lactic acidosis?
Lactic acidosis is caused by a build-up of excess lactic acid in the blood. Normally, the main sources of lactic acid production are red blood cells, skeletal muscle, skin, and brain. The liver and kidneys perform the reverse conversion of lactic acid into glucose and oxidize it. Excess production of lactic acid or reduced elimination of lactic acid by the body causes accumulation of lactic acid in the body leading to lactic acidosis.Lactic acidosis is a common condition in patients with decompensated heart failure, respiratory failure, liver failure, sepsis, intestinal or extremity infarction,... This condition is also seen in patients with diabetes. type2 is treated with metformin.
2. Risk of lactic acidosis in patients with type 2 diabetes
When treating type 2 diabetes, Metformin is the preferred drug to use right from the time of diagnosis when there are no contraindications. Metformin can be combined with all other classes of hypoglycemic drugs such as sulfonylurea, insulin, thiazolidinedione, glinide for the same purpose of controlling blood sugar. However, metformin is contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment because of the increased risk of lactic acidosis and possibly death. The risk of metformin accumulation and metformin-associated lactic acidosis increases with the severity of renal failure because metformin is eliminated primarily by the kidneys.
Metformin được chống chỉ định dùng cho bệnh nhân suy thận nặng vì có thể làm tăng nguy cơ nhiễm toan axit lactic
3. Diagnosing acidosis
Clinical symptoms: Rapid breathing, profuse sweating, cold and moist skin, abdominal pain, sweaty breath, nausea or vomiting, confusion and coma. Increased pulmonary ventilation. Blood pH < 7.3. Serum bicarbonate < 15 meq/L. Anion gap > 15 meq/L. There are no ketone bodies in the serum. Serum lactate > 5 mmol/L.4. How should patients with type 2 diabetes avoid lactic acidosis?
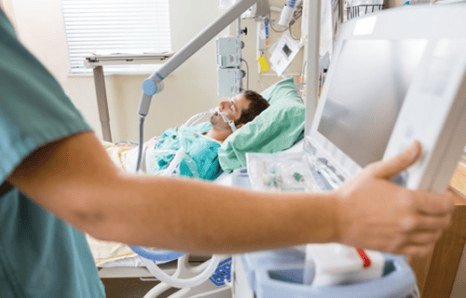
Để xử trí nhiễm toan lactic, bệnh nhân sẽ được cấp cứu, hồi sức tích cực và lọc máu để loại bỏ bớt axit lactic ra khỏi cơ thể
Need to know the contraindication of metformin in subjects with renal failure with high risk of lactic acidosis: glomerular filtration rate < 60 ml/min. Metformin should not be used in patients with all forms of acute metabolic acidosis (lactic acidosis, diabetic ketoacidosis) pre-diabetic coma, an acute condition that may affect renal function. (dehydration, severe infection, shock), hepatocellular failure, alcoholism, acute alcohol poisoning. Before initiating treatment with metformin, it is necessary to estimate the glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and monitor the glomerular filtration rate at least once a year in all patients receiving metformin. Renal function should be assessed at least once a year in patients with normal renal function and every 3-6 months in patients at risk of developing renal failure and in elderly patients. Patients on metformin therapy should be screened and vigilant for associated risk factors such as cardiogenic shock, hypovolemic shock, severe heart failure, deep coma, and sepsis. Adjust dosage and monitor renal function closely in patients with moderate renal impairment (glomerular filtration rate 30-60 mL/min). Temporarily discontinue metformin therapy when the patient is indicated for the use of iodinated contrast media, surgery under general anesthesia, spinal anesthesia, or epidural anesthesia. The patient must adhere to the prescribed dose of medication. When signs of lactic acidosis appear, such as: cramps, muscle weakness, severe myasthenia gravis, vomiting, pain in the abdomen or chest, shortness of breath, hypothermia, decreased heart rate, etc. Stop treatment immediately and notify the doctor to determine the blood lactate level. Lactic acidosis is one of the serious and serious medical complications that can occur when treating type 2 diabetes with metformin. In order to prevent the above complications, patients with type 2 diabetes need to strictly follow the instructions of the consulting doctor during the treatment process and have regular endocrinology examination. When there are any warning signs of lactic acidosis, the patient should go to the doctor immediately for timely and effective examination and treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.