This is an automatically translated article.
The term transient ischemic attack may not be as common as a stroke, but the extent of the damage and complications it causes are also very serious. So is transient ischemic attack dangerous or what to do to prevent this disease?
1. What is a transient ischemic attack?
Previously, transient ischemic attack was defined as “focal neurological deficits of sudden onset of vascular origin lasting less than 24 hours”. However, through many subclinical diagnoses and many specific patient cases, in 2009 the American Stroke Association recognized and used a clearer definition of a transient ischemic attack as "ischemic attack". transient ischemic attack is a brief episode of neurological dysfunction due to retinal ischemia or ischemia, symptoms usually lasting less than 1 hour, and no evidence of cerebral infarction. This definition is now also recognized and used in Vietnam.
Cơn thiếu máu não cục bộ thoáng qua gây ảnh hưởng đến sức khỏe cũng như tinh thần của người bệnh
2. Manifestations of patients with transient ischemia
Patients with transient ischemia often have some of the following signs:
Symptoms of patients with damage to the anterior cerebral circulation system (carotid system): Blindness or transient darkening of one eye . Hemiplegia and hemisensory disturbances. Language disorder. Symptoms of patients with damage to the posterior cerebral circulatory system (vertebral-basal artery system): Weakness of the extremities or hemiplegia (may be transferred from one area to another) Hemiparesis (may be rotated) from one region to another). Weakness or loss of vision Co-ordination and balance disorders. The above symptoms of patients with transient ischemic attack are usually of sudden onset, mainly lasting from 2 to 20 minutes and then disappear on their own.

Bệnh nhân thiếu máu cục bộ thoáng qua có thể bị mất thị lực
3. Causes of transient cerebral ischemia
Through studies related to transient ischemic attack, some causes are given such as:
Due to occlusion of cerebral artery branch. This is the leading cause of atherosclerosis. Due to a decrease in global or local perfusion. This condition may be caused by orthostatic hypotension; causes of narrowing of the carotid or vertebral-basal arteries; arrhythmia; increased blood viscosity;
4. How is transient ischemic attack diagnosed?
Imaging: CT scan of the skull will rule out small brain bleeding or brain tumor with clinical presentation resembling transient ischemic attack. Several non-invasive probes such as ultrasound have been developed to study cerebral circulation and to image large vessels to the skull. Carotid doppler ultrasound is useful in detecting internal carotid stenosis, but angiography remains an important method for examining the cerebrovascular system. Magnetic resonance angiography can detect stenosis of the great vessels but is not as sensitive as angiography. Therefore, if the CT scan of the skull is normal, there is no cause of a blood clot in the heart, and if age and general condition indicate that the patient is at high risk, then a bilateral carotid angiogram should be considered for evaluation. Carotid cerebral infarction, ultrasound helps to screen patients for research.
Other tests: Clinical and laboratory tests need to evaluate hypertension, heart disease, hematological disorders, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, peripheral vascular disease. Tests include blood count, fasting blood sugar, blood cholesterol, serology for syphilis, electrocardiogram, cardiopulmonary scan. Contrast echocardiography if cardiac origin, blood culture if endocarditis is suspected. Monitor electrocardiogram if paroxysmal, transient arrhythmia is suspected.
Tình trạng thiếu máu não thoáng qua được chẩn đoán thông qua phương pháp CT scan
Differential diagnosis: Migraine: often with aura, headache accompanied by nausea, photophobia, fear of noise. Symptoms develop slowly over 30 minutes or so. Syncope: usually in patients with a history of cardiovascular disease. Sudden brief loss of consciousness, without other focal neurological symptoms. Partial seizures: usually localized in one part and then spread to other parts. Diagnosis is based on electroencephalogram. Transient global amnesia/TGA: common in the elderly. Sudden loss of memory in the right direction, keep asking the same question over and over. The storm lasted for several hours. Hypoglycaemic episodes: usually in patients with a history of diabetes being treated. A quick diagnosis can be made in the absence of a test by intravenous glucose injection or drinking sugar water.
5. Is transient ischemic attack dangerous?
Transient ischemic attack has "transient" clinical symptoms but is a high risk marker for true stroke. Therefore, patients need to be treated early and investigated for risk factors to have a good preventive treatment plan.
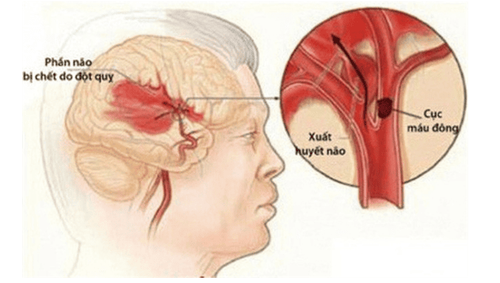
Đột quỵ não là một biến chứng nguy hiểm của tình trạng thiếu máu não cục bộ thoáng qua
6. What to do to prevent transient ischemic attack?
Although it can lead to dangerous complications, transient ischemic attack is preventable if you maintain healthy living habits such as:
Exercise: adults need regular exercise regularly to improve health and enhance the body's resistance, not just to prevent ischemic heart disease. Diet: reducing salt and increasing potassium (if blood potassium does not increase) help limit hypertension. Eat a lot of vegetables, fruits and vegetables, limit animal fat. Limit beer and alcohol. Quit smoking if you are a smoker. Obesity: it is recommended to maintain a body mass index (BMI) of 18.5-25. In case of BMI over 30, it is necessary to take measures to lose weight. Periodic health check every 6 months to detect risk factors. Besides, it is necessary to thoroughly treat risk factors if possible:
Dyslipidemia: combine a reasonable diet with treatment with Statins, can combine with Fibrate group if necessary to bring blood lipids to normal levels. often. Diabetes: Combination of dietary modification with blood sugar control medication. Maintain HbA1C below 6.5%. Atrial fibrillation: advise patients with atrial fibrillation how to self-detect signs of atrial fibrillation. Asymptomatic carotid stenosis: Carotid endarterectomy or carotid stenting when stenosis is greater than 70% on Doppler ultrasound or more than 60% on digitized angiography.

Tập thể dục giúp ngăn ngừa thiếu máu não cục bộ thoáng qua
Periodic health check-ups help to detect diseases early, so that there are treatment plans for optimal results. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has general health checkup packages suitable for each age, gender and individual needs of customers with a reasonable price policy.
Results of the patient's examination will be returned to the home. After receiving the results of the general health examination, if you detect diseases that require intensive examination and treatment, you can use services from other specialties at the Hospital with quality treatment and services. outstanding customer service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.