This is an automatically translated article.
The article was consulted with Specialist Doctor II - Nguyen Thi Minh Tuyet - Head of Obstetrics and Gynecology Department - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.According to statistics, the rate of deep vein thrombosis in pregnant women is about 0.1-0.2%. The risk is higher in the last 3 months of pregnancy and the first 3 weeks after giving birth. So how dangerous is deep vein thrombosis in pregnant women?
1. What is Deep Vein Thrombosis?
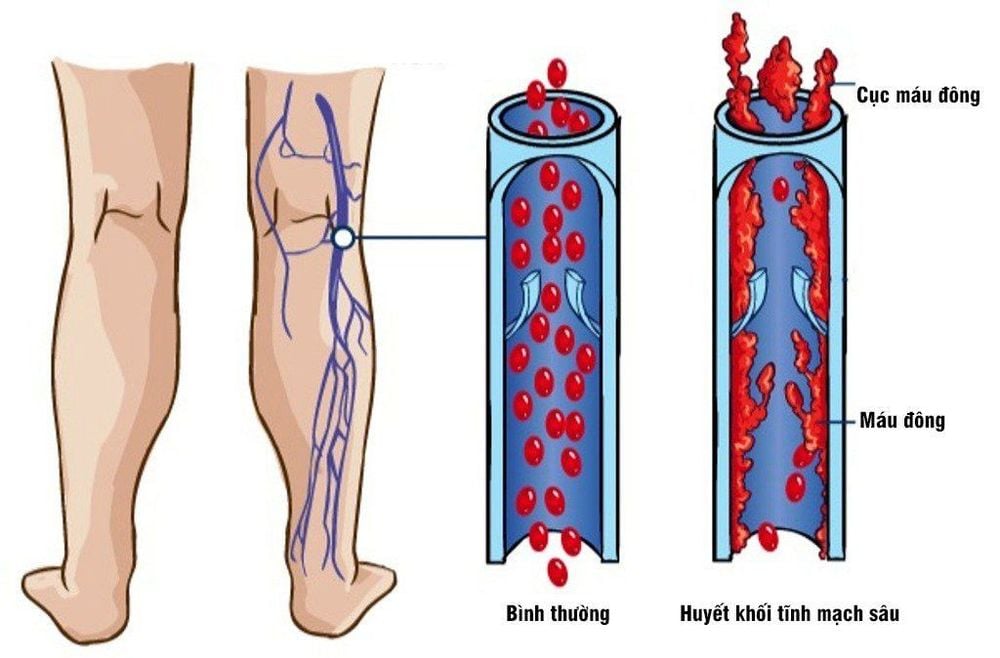
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition in which a blood clot forms in the deep veins of the body. Deep vein thrombosis can occur anywhere, but is most common in the deep veins of the legs.Deep vein thrombosis follows the blood flow to the heart, is contracted by the heart and pushed to the lungs, causing pulmonary embolism. Pulmonary embolism is a dangerous complication with a high risk of death.
2. Why are pregnant women at risk of deep vein thrombosis?
Pregnant women have changes in the clotting process, blood tends to increase blood clotting to protect pregnant women from bleeding in the uterus and stop bleeding during childbirth. Because the blood clots more easily, there is an increased risk of deep vein thrombosis in pregnant women.Pregnancy blocks blood flow from the legs back to the heart, causing blood stagnation, reduced circulation is also a cause of increased risk of deep vein thrombosis in the legs.
The risk of venous thrombosis in the first and second trimesters is similar, increases in the last 3 months and 3 weeks after birth, the disease usually occurs after birth and decreases after the first 6 weeks.
Trắc nghiệm: Bạn có hiểu đúng về dấu hiệu mang thai sớm?
Các dấu hiệu mang thai sớm không phải chỉ mỗi trễ kinh mà còn có rất nhiều dấu hiệu khác như xuất huyết âm đạo, ngực căng tức,… Điểm xem bạn biết được bao nhiêu dấu hiệu mang thai sớm thông qua bài trắc nghiệm này nhé!
3. Which women are at high risk?
There is a history of venous thromboembolism, a family history of venous thrombosis. Smoking or frequent exposure to secondhand smoke. Age over 35 Pre-eclampsia. Overweight or obese. BMI > 30 at first visit Traveling long distance during pregnancy Pregnant with twins or more. Sedentary for long periods of time. Congenital high risk of hypercoagulability. Intrauterine growth retardation. Emergency cesarean section in the previous time. Mother has medical diseases such as diabetes, lupus erythematosus, cancer, sickle cell disease.
4. Signs of deep vein thrombosis in pregnant women
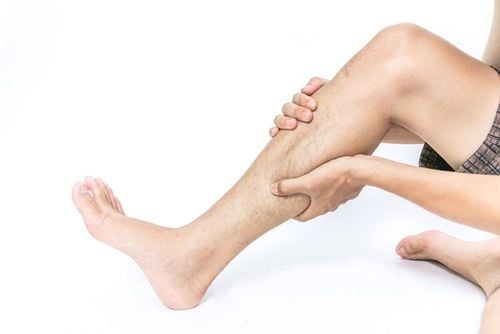
Signs of deep vein thrombosis in pregnant women are often unclear, usually with the following signs:Calf pain, mild pain or severe pain, pain increases when walking. Changes in skin color in the area of VTE tend to turn blue-black or an unusual color. Leg swelling usually occurs in one leg, compare the difference between the two legs The sensation of skin heat in the leg, the area of thrombosis is usually hotter than other areas. See the superficial veins dilated more than usual Manifestations when there are complications including: Unexplained shortness of breath, coughing a lot, sometimes coughing up blood, chest pain... are manifestations when deep vein thrombosis causes pulmonary embolism complications. When you have these symptoms, you need to go to the hospital immediately for timely treatment. Detection of deep vein thrombosis in the leg by doppler ultrasound of the leg vessels.
5. Is deep vein thrombosis in pregnant women dangerous?
Deep vein thrombosis in pregnant women is a dangerous disease, which can cause many complications affecting the life of mother and fetusComplications of deep vein thrombosis in pregnant women include:
For the fetus: Blood clots in the placenta interfere with fetal nutrition, causing miscarriage, slow fetal growth, risk of premature birth, premature rupture of membranes.
For mother: Cerebral vascular occlusion, pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction increase the risk of maternal mortality.
6. How to prevent deep vein thrombosis in pregnant women
Regularly exercise during pregnancy when there are no contraindications. If you are in a high-risk group, you need to be examined and detected early. Stay away from smoking. Do not smoke, minimize exposure to secondhand smoke. Weight control. Have a reasonable diet, limit high fat intake, eat lots of green vegetables and fruits, drink lots of water. Deep vein thrombosis in pregnant women is very dangerous. Pregnant women with high-risk factors should be checked for detection and receive preventive treatment to avoid the risk of affecting the health of mother and baby.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.