This is an automatically translated article.
Aeromonas hydrophila is a gram-negative, rod-shaped heterotrophic bacterium mainly found in warm climates. This is a bacteria that can cause extremely serious consequences that people often call the bacteria a "flesh-eating" bacteria.1. What is aeromonas hydrophila?
Aeromonas hydrophila (AH) is a gram-negative bacillus, capable of causing severe disease similar to other gram-negative bacilli, including gas-producing gangrene, Shigella, Salmonella, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa... In terms of shape, Aeromonas hydrophila bacteria are rod-shaped, ranging in size from 0.5 - 1 micrometer in width and 1 - 3 micrometer in length.
In terms of habitat, Aeromonas hydrophila bacteria reside mainly in warm water environments and in brackish coastal waters in hot and humid areas. They secrete exotoxins like Vibrio cholerae bacteria that cause cholera, so when infected, they will affect the gastrointestinal tract and have clinical symptoms of mild cholera.
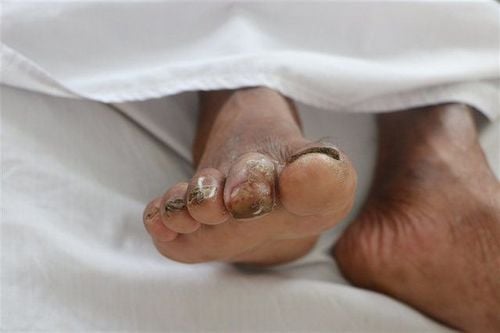
Aeromonas hydrophila bacteria are usually present in fresh or dirty brackish water, muddy water or sewers... and cause diseases for shrimp, fish, frogs, frogs, reptiles mainly; In cases where people at high risk such as cuts, abrasions, boils, sores, etc. come into contact with dirty water, there is a risk of infection.
2. Path of transmission of bacteria aeromonas hydrophila
If drinking dirty water containing Aeromonas hydrophila bacteria or their exotoxins, after passing through the intestinal tract, they can cause the risk of sepsis and multi-organ failure, which often occurs in people who are immunocompromised.
If infected through the skin, Aeromonas hydrophila bacteria invade the wound causing necrotizing inflammation of the skin, fascia, muscle; causing sepsis, multi-organ failure with a high risk of death; at the same time can lead to biliary tract infection, the risk of sepsis is likely to occur if the patient has a history of cirrhosis and is immunocompromised.
After entering the body through wounds on the skin, Aeromonas hydrophila bacteria enter the bloodstream, reach soft tissues or organs in the body, multiply and cause disease through an endotoxin called aerolysin. This toxin binds to a number of receptors in the host cell wall, causing cell damage and tissue necrosis.
To confirm the diagnosis of Aeromonas hydrophila with certainty, it is necessary to perform a culture test, isolate the bacteria or identify the bacteria by PCR (polymerase chain) technique. reactions).
Vi khuẩn aeromonas hydrophila
3. Treatment and prevention of aeromonas hydrophila
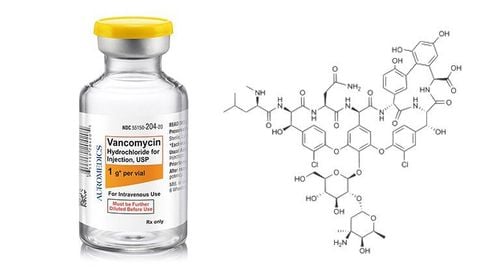
3.1. Treatment of bacterial diseases aeromonas hydrophila Using antibiotics: Aeromonas hydrophila bacteria can still be sensitive to common antibiotics such as sulfamid, chloramphenicol, tetracycline, ciprofloxacin...; however, they are still resistant to some penicillins and cephalosporins. Using antibacterial chemicals: Aeromonas hydrophila bacteria are also easily killed by common bactericidal chemicals. In fact, although bacteria are still sensitive to many antibiotics and are easily destroyed with common bactericidal chemicals, because the disease usually progresses quickly, the infected person is susceptible to necrotizing inflammation of many organs. Parts of the body, therefore, easily lead to sepsis, septic shock, multi-organ failure and often account for a high mortality rate. Currently, with the help of modern emergency and resuscitation facilities and techniques with high response efficiency, it is possible to limit the number of deaths caused by Aeromonas hydrophila bacteria. However, it should be noted that after being cured of the disease, people who have been infected with Aeromonas hydrophila bacteria still have to suffer severe sequelae due to complications of the disease.

Sử dụng thuốc kháng sinh điều trị vi khuẩn aeromonas hydrophila
3.2. Prevention of diseases caused by bacteria aeromonas hydrophila Should not or limit contact with dirty water, especially when on the skin with wounds, cuts, abrasions, sores, boils... If the skin is damaged, it is necessary to clean cuts, lacerations, boils and scratches... with soap and clean water; clean the wound, let it dry, cover the wound with a clean, dry bandage until it heals Deep or other serious wound, need to go to a medical facility to handle the wound properly; Fungal infections of the feet must also be carefully taken care of to avoid the risk of superinfection with Aeromonas hydrophila bacteria. Sanitize the living water environment, do not let the water be contaminated or poisoned. Practice good food hygiene and safety to prevent Aeromonas hydrophila bacteria from entering through the digestive tract. It is necessary to use appropriate labor protection equipment to protect workers who often have to come into contact with the water environment. When there are signs of suspicion, it is necessary to go to a medical facility for early detection, blood cultures and necessary tests should be performed to identify Aeromonas hydrophila bacteria; Make an antibiogram to treat with an effective antibiotic right from the start before it's too late. To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register for an online examination HERE
MORE:
What is Whitmore's disease and symptoms how is it? Prevention of Whitmore's disease as recommended by the Department of Health Is Whitmore's disease dangerous? How to treat?