This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Specialist Doctor I Tran Quoc Vinh - Emergency Doctor - Department of Resuscitation - Emergency - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Acute abdominal pain is one of the typical symptoms and is associated with 80% of gastrointestinal diseases. Symptoms of acute abdominal pain can be a warning sign of a dangerous condition that requires emergency care, but can also be caused by digestive disorders and resolve on their own.
1. Acute abdominal pain
Abdominal pain is a common symptom and 80% of cases are related to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (stomach, intestines, hepatobiliary tract, pancreas). However, extra-gastrointestinal diseases that cause dangerous acute abdominal pain can also be encountered such as: renal colic due to stones (which can cause acute functional renal failure), ectopic pregnancy, shock rupture, arterial dissection. thoracic - abdominal pain, myocardial infarction in the lower wall,... The nature of abdominal pain is often very diverse such as:Abdominal cramps Long-lasting dull pain, intermittent sharp pain,... Abdominal pain is often divided into There are two types: acute abdominal pain and chronic abdominal pain.
2. Acute abdominal pain when to go to the emergency room?
Acute abdominal pain is one of the forms of abdominal pain, abdominal pain comes on suddenly and lasts no more than 2 weeks. This can be a warning symptom of a dangerous condition that needs to be treated promptly, besides, abdominal pain can also be caused by digestive disorders.Severe acute abdominal pain: Some diseases have acute abdominal pain such as: Intestinal infections when the patient is accompanied by other symptoms including high fever and loose, bloody stools, severe cases May be accompanied by hypotension, septic shock. Perforated hollow viscera if the patient has severe abdominal pain accompanied by other symptoms such as abdominal distension, vomiting and inability to defecate. Acute appendicitis if abdominal pain gradually localizes to the right iliac fossa, may be accompanied by fever, vomiting, and loss of appetite. Acute pancreatitis if epigastric abdominal pain spreads to the back, may be accompanied by vomiting... Some dangerous abdominal pain conditions but outside the digestive system such as: dissection of the aorta if there are changes blood pressure in both arms, which can lead to shock... Patients need to go to medical facilities for examination and intervention as soon as possible. Acute abdominal pain may not be dangerous: As in gastrointestinal upset due to mild food poisoning. Patients have symptoms of intermittent abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea in small amounts, and low-grade fever. In these cases, abdominal muscle pain can go away on its own, then the patient needs nutritional supplements and adequate rehydration. However, in the case of high fever and bloody stools is a sign of infection, and should be examined and prescribed antibiotics. Cases of diarrhea, vomiting many times, especially accompanied by low blood pressure need to be hospitalized for examination and treatment.
Đau bụng cấp tính là một trong những dạng đau bụng, xuất hiện đột ngột
3. Some common diseases have symptoms of abdominal pain
Acute abdominal pain is a typical symptom of many different diseases, and the nature of the pain site will also vary. Some typical diseases with symptoms of acute abdominal pain include:3.1. Acute appendicitis
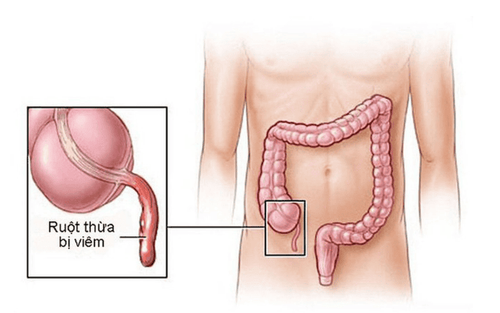
Appendicitis is an acute disease that can occur at any age, causing many dangerous complications, even death, if not treated promptly. The typical symptom of appendicitis is abdominal pain. Abdominal pain will appear in the epigastrium and then spread to the right iliac fossa, then cause dull, continuous and increasing pain, the nature of the pain is cramping and sharp. May be accompanied by fever, vomiting, loss of appetite.
Viêm ruột thừa có thể gặp ở mọi lứa tuổi khác nhau và gây ra nhiều biến chứng nguy hiểm
3.2. Acute pancreatitis
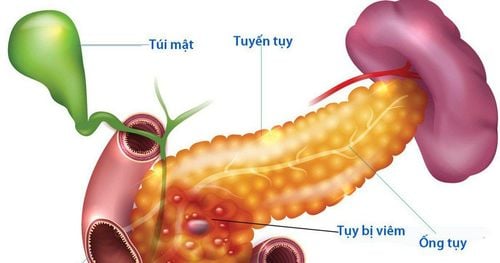
The typical symptom of acute pancreatitis is severe pain in the epigastrium just below the nose of the sternum. Causes of acute pancreatitis are usually gallstones, alcohol, and hypertriglyceridemia. Patients often have pain that comes on suddenly, and within a few minutes reaches intense pain, often radiating to the back. Abdominal pain in acute pancreatitis can last up to several days.Abdominal pain often increases when the patient has strong pressure such as coughing, vigorous movement or deep breathing. In addition, symptoms associated with acute pancreatitis include:
Dehydration Increased pain sensation in the abdominal wall, bruising, bleeding under the skin of the abdominal wall Vomiting Fever Prolonged acute pancreatitis can cause lower blood pressure. In more severe cases of acute pancreatitis, it can lead to acute renal failure, cardiac and pulmonary dysfunction (ARDS), hypovolemia, and sepsis, even death. .
3.3. Gastritis acute
Acute gastritis is clinically manifested as severe pain in the epigastrium. The nature of the pain can be excruciating, burning, but sometimes dull, bloated, and difficult to digest. In addition, accompanying symptoms such as:Nausea; Vomiting a lot, vomiting immediately after eating, vomiting with sour liquid, even with blood; Swollen tongue; Foul mouth. The cause of acute gastritis is a bacterial infection in the gastric mucosa or the effect of toxic agents. This condition is only a limited inflammatory response taking place in the mucosa and is rapidly changing and initiating. But if this process takes place in waves, it can cause chronic inflammation when the stomach lining is destroyed, and compromise the function of the immune system.
3.4. Kidney stones, nephritis
Kidney stones, nephritis, also known as pyelonephritis, is caused by sequelae of urinary tract infections that cause urethritis and move to the renal pelvis. Besides, the cause of kidney stones and prostate tumors can also be stagnation and obstruction of the flow of urine. Symptoms of abdominal pain in kidney stones, nephritis are:Low back pain. The spasm radiates down to the groin, pelvis and even the external genitalia. Urination, diarrhea. Abnormal urine color, and even blood in the urine. For small stones (< 7 mm) that may not require treatment, the patient can drink plenty of fluids to push the stones out. If the patient does not have to undergo surgery, it is necessary to prevent complications other than recurrent stones, leading to kidney failure, sepsis and septic shock.
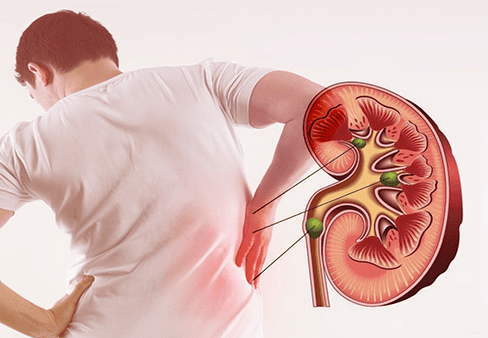
Sỏi thận là do di chứng của nhiễm khuẩn tiết niệu và di chuyển lên bể thận
3.5. Gynaecological disease
Acute lower abdominal pain can be a symptom of gynecological diseases, stemming from many different causes. Patients often have symptoms such as:Lower abdominal pain; Pain spreading to the lumbar region, vulva; Burning sensation; Pain in the bladder; Painful urination, difficulty urinating; Rectal pain; Feeling of wanting to defecate; Vaginal itching. Bleeding, abnormal vaginal discharge Menstruation delay, menorrhagia In addition, some gynecological diseases will have symptoms that are often more difficult to detect, and less visible to the outside, such as:
Damage to the cervix; Injury to the uterine body: posterior flexion of the uterus, uterine torsion, uterine fibroids, and necrosis; Genital prolapse ; Chronic adnexitis; Inflammation of the sacrum or ovaries; Endometrial optimism ; Ectopic pregnancy Varicose veins of the pelvis,... In short, acute abdominal pain is a symptom of many different diseases. To classify and recognize a dangerous condition depends on its nature and other accompanying symptoms. When acute abdominal pain occurs and is accompanied by unusual signs and symptoms, the patient should immediately go to a medical facility for examination and appropriate treatment measures.