This is an automatically translated article.
Invasive fungal infections can be itchy and uncomfortable, but they are rarely serious. Common infections such as athlete's foot, or ringworm, are caused by fungi, and they are easy to catch. In healthy people, the fungus usually does not spread beyond the surface of the skin, so it is easy to treat.1. Some characteristics of fungal infections
Fungal infections are common throughout the natural world. In humans, a fungal infection occurs when one type of fungal infection invades one or more areas of the body.
Fungi can live in air, soil, water and plants. In addition, some fungi can live naturally in the human body. Like many bacteria, fungi are both beneficial and harmful. When fungal infections enter the body, they can be difficult to eradicate, as they can persist in the environment and infect humans.
2. Symptoms of a fungal infection
Symptoms of an invasive fungal infection will depend on the type, common symptoms include:
Skin changes including redness and possibly cracking or peeling of the skin Itching
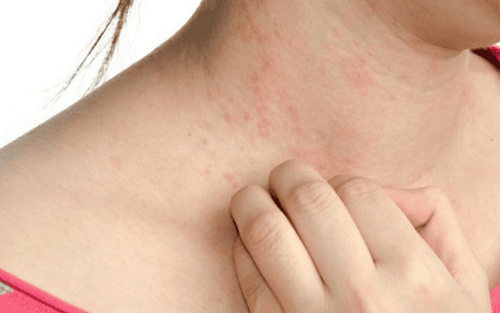
Khi nhiễm nấm xâm nhập có thể gây ngứa
3. Fungi are susceptible to infection
3.1. Athlete's footFungal foot infection is a common fungal infection. Athlete's foot infections are often associated with sport and movement because this is the perfect environment (warm, wet) for the fungus to grow (socks, shoes, sports equipment, locker rooms).
In fact, anyone can be affected by athlete's foot. In particular, fungi are common in warm climates or in the summer months, where they can rapidly multiply.
Symptoms of a fungal infection in athlete's foot can vary from person to person. Typical symptoms include: Redness or blisters on the affected area; The infected skin may soften or the upper layers of the skin may begin to break down; Peeling or cracking of the skin; The skin may peel and itch, sting, or a burning sensation in the infected area.
Diagnosis and treatment: Not all itchy feet are the result of athlete's foot. Doctors usually diagnose an infection by scraping the skin and examining it under a microscope for evidence of any fungus.
There are a few different types of fungus that can cause athlete's foot. Infections can be treated differently depending on the specific fungus that is infecting the skin.
Athlete's foot is usually treated with a topical antifungal ointment. The drug is available to buy without a doctor's prescription. However, severe infections may require additional oral medication. Feet will also need to be cared for and kept dry to help kill the fungus.
Prevention: The methods of preventing athlete's foot are to give the feet plenty of air to breathe and keep them clean and dry. Please wear slippers in public bathrooms and changing rooms to avoid infection.
3.2. Yeast infection
Vaginal yeast infection is a common form of Candida overgrowth in women, usually caused by Candida albicans. Candida overgrowth disrupts the normal balance of bacteria and yeast in the vagina. This bacterial imbalance can be caused by antibiotics, stress, and hormone imbalances, or by poor eating habits.
Candida infections can also often cause fungal toenail infections and rashes.
Symptoms: A yeast infection usually has the following symptoms: Itching and swelling around the vagina with a burning sensation or pain when urinating or having sex; Redness and soreness on and around the vagina; Abnormal vaginal discharge, such as a bluish-gray lump or a discharge that is very watery. A rash can develop over time in some cases. Yeast infections should be treated quickly because symptoms can become severe if left untreated.
Diagnosis and treatment: The classic symptoms of yeast infections make them easy to diagnose. Doctors may ask about medical history, sexually transmitted infections, or recent antibiotic use. The doctor will then examine the vaginal wall and cervix for signs of infection. In case of necessity, cells can be taken from the vagina for definitive diagnosis. Treatment for yeast infections depends on their severity. Standard treatments include topical creams.
Prevention: Avoiding yeast infections starts with a balanced diet and proper hygiene. Wear loose clothing and materials made from natural fibers. Washing underwear in hot water can prevent fungal growth.
3.3. Tinea cruris, commonly known as scabies, is a common systemic fungal infection. These fungi prefer moist environments and thrive in moist areas of the body such as the groin, buttocks, and thighs. Scabies may be more common in the summer and in warm, humid areas.
Scabies is a mildly contagious disease and is usually spread by direct contact with an infected person.
Symptoms: Scabies appears on the body as a red, itchy rash that is often round in shape. Symptoms include: Redness in the groin, buttocks, thighs; rubbing, irritation, itching, or burning in the infected area; Red rash with bulges and raised edges; Cracking, peeling, or flaking of the skin in the infected area
Diagnosis and treatment: Scabies is usually identified based on its appearance. If doctors are unsure, they can take a skin sample to test and confirm a diagnosis. Treatment of scabies often involves topical antifungal ointments and proper hygiene. Many cases of scabies are improved with over-the-counter medications.
Prevention: Scabies can be prevented by using clothing made of natural fibers. Avoid contact with infected people. Avoid sharing personal daily living items such as towels, sports equipment...

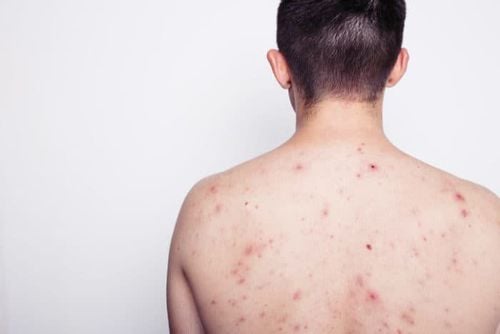
Bệnh ghẻ ngứa ảnh hưởng rất nhiều đến cuộc sống sinh hoạt của người bệnh
Ringworm is a skin infection caused by a fungus that lives on dead tissues, such as skin, hair, and nails. It is also a fungal disease that causes both itchy feet and athlete's foot.
Symptoms: The disease is usually easy to see because of its shape. A red patch that can be itchy or scaly will often turn into a raised, ring-shaped patch of skin over time. It can even spread into multiple rings. The outer surface of the circle is red and bumpy, while the inside may form scabs. The disease is highly contagious and can be transmitted by skin-to-skin contact or by contact with pets. Fungi can also survive on objects such as towels, clothing, and brushes. In addition, the fungus can also infect soil and mud. Therefore, people who play or work with dirt contaminated with the fungus will likely become infected.
Diagnosis and treatment: Various skin conditions can look like circles, so for a definitive diagnosis your doctor will take a skin sample to test for fungus. After confirming the diagnosis, your doctor will recommend treatment depending on the severity of your symptoms.
Creams and ointments are usually used to treat the condition and may not require a prescription. However, a fungal infection of the scalp or a severe one should be treated with a prescription from a dermatologist.
Prevention: Sanitation can help treat and prevent fungal infections. Always keep the skin clean and dry to avoid infections. At the same time, use separate personal items to avoid infection from sick people.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE
Reference sources: webmd.com, medicalnewstoday .com, cdc.gov
MORE
Mold allergy: Symptoms, diagnosis and treatment Diagnosis and treatment of lung fungus Nail fungus: Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment