This is an automatically translated article.
Intubation techniques in adults help patients maintain the airway because trauma, disease, or infection causes acute airway arrest. This is a difficult technique, but very important in patient resuscitation.
1. When to intubate an adult?
Intubation techniques in adults are performed in necessary cases, when the patient has acute apnea in:
Disorder of consciousness; Injury; Respiratory failure; Loss of respiratory protection; Maintain breathing. It should be noted not to intubate in cases such as: patients with laryngeal lesions, or with deformities, maxillofacial trauma. Intubation for the elderly needs special attention. In addition, you can refer to the article on intubation for children here.

Đặt ống nội khí quản để duy trì khả năng hô hấp cho bệnh nhân
2. Necessary tools for intubation
The tools and equipment that need to be fully prepared to perform the intubation procedure are as follows:
Oxygen source; Electrocardiogram monitor; Capillary blood oxygen meter; Laryngeal lamp and tongue; Sputum suction device; Endotracheal tube; 10ml syringe; Guide rods; Instrument to fix the endotracheal tube. Equipment to check endotracheal tube position. For adult patients, the laryngeal tongue can be selected as curved (size 3 or 4) or straight (size 2 or 3). The size of the endotracheal tube is different between male and female patients, in men it is 8 - 8.5 mm in diameter, 7.5 - 8 mm in women.
In this technique, the exact position of the endotracheal tube is extremely important, so in addition to the requirement of trained and experienced technicians, it is necessary to support equipment to check the position as well as monitor the delivery. correct inlet.
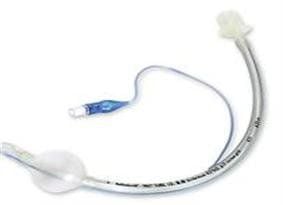
Kích thước ống nội khí quản đa dạng
3. Perform endotracheal intubation in adults
Do the following trick:
3.1. Measurement of capillary blood oxygen concentration.
Continuous electrocardiogram monitoring.
3.2. Check equipment: laryngoscope, endotracheal tube cuff, sputum suction device. Select the endotracheal tube and insert the guide rod into the lumen of the endotracheal tube.
3.3. Specific anatomical assessment of the patient's airway. Evaluation criteria: oral cavity size, tooth movement, neck, distance from chin to laryngeal cartilage. Remove dentures if present.
3.4. Assess cervical spine injury, place the patient in an appropriate position.
If there is no injury, the patient is placed with a pillow under the occipital, lying in a sniffing position, so that the oropharyngeal - larynx axis is straight.
3.5. Suction oral sputum and increase blood oxygenation first.
Use 100% oxygen to increase blood oxygenation for 1-2 minutes, at the same time monitor on the meter.
3.6. Adjust the bed height, suitable for the position performed by the technician.
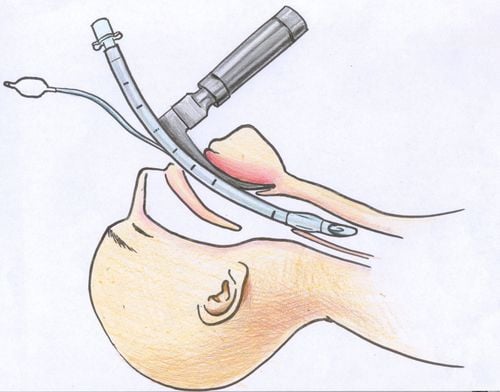
3.7. Prepare the left hand to hold the laryngoscope and the endotracheal tube in the right hand. 3.8. Insert the blade of the lamp into the right corner of the patient's mouth.
With the lamp blade straight, bring it straight down to the center of the tongue, using the tip of the lamp blade to lift the epiglottis. With the curved lamp blade, slide the blade to the left and then insert it into the small slot, lifting the indirect lamp blade cover.

Kỹ thuật đặt ống nội khí quản đường miệng
3.9. Raise the lamp handle, examine the larynx so that it is perpendicular to the lamp blade. Be careful not to pull the lamp handle back because it will damage your teeth.
3.10. Observe the 2 vocal cords, now insert the endotracheal tube according to the guide rod, stop when the cuff passes the 2 vocal cords.
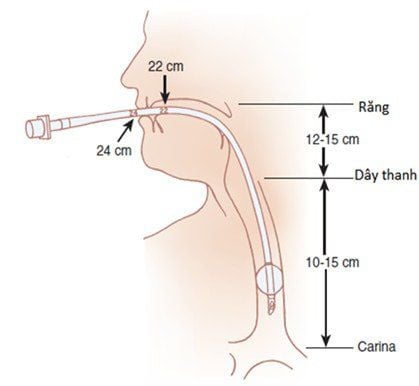
The exact position of the endotracheal tube is about 23cm in men and 21cm in women, measured from the corner of the mouth.
3.11. Carefully pull out the guide rod to avoid injury. Pump cuff 10 cc gas.
3.12. Check the position of the endotracheal tube.
3.13. Fixed endotracheal tube.
4. Possible complications when intubation
Technicians performing endotracheal intubation need to understand the possible complications and try to limit and overcome them if they occur:
Arrhythmia; Hypertension ; Decrease oxygen, increase blood CO2; Insert the tube into the bronchus or esophagus (wrong position); Increased intracranial pressure; Drainage of the funnel cartilage; Tooth trauma; mucosal damage; Increases cervical spine injury. In performing endotracheal intubation, sedation and muscle relaxants may be used to make the technique clearer. It is necessary to understand the indications, contraindications as well as complications of drug use.

Có thể sử dụng thêm thuốc an thần để đặt nội khí quản được thuận tiện
Chest X-ray is used as a laboratory method to provide images to check the depth, as well as the correct position of the endotracheal tube. It is recommended to leave the tip of the tube about 2cm above the carina.
If the patient has cervical spine injury, it is important to put in a stable, straight lying position for easy endotracheal intubation.
Vinmec International General Hospital is a general hospital with the function of examining, treating and recovering many diseases with modern standard medical equipment. Accordingly, the technical equipment is also invested in innovation suitable for each procedure and surgery in order to minimize possible dangerous complications, including the intubation procedure. manage. Especially with a team of highly qualified and well-trained doctors and nurses, they will bring optimal treatment results to customers.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.