This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Le Xuan Thiep - Radiologist - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital.Contrast nephrography is a diagnostic x-ray imaging technique of the urinary system with intravenous contrast injection to help doctors evaluate a patient's kidneys, ureters, and bladder, when they experience symptoms such as blood in the urine or pain in the side or lower back.
1. Why do patients need nephrography with intravenous contrast?
Intravenous contrast-enhanced pyelogram (English name is Intravenous pyelogram - IVP; French name is Urographie intraveineuse, abbreviated as UIV) is used to take x-rays of the urinary system including parts such as: Kidneys , ureter and bladder .This technique allows the doctor to assess the size and shape of the anatomical structures of the urinary system and determine if they are functioning as well as the excretory function of the kidneys.
The doctor may order an intravenous contrast nephrography if the patient has signs and symptoms such as: Pain in the back or back or blood in the urine, which may be related to: diseases or disorders of the urinary tract.
Intravenous contrast nephrography can diagnose the following conditions:
Kidney stones Bladder stones Prostate enlargement Renal cysts Urinary tract tumors Renal structural disorders such as such as medullary sponge kidney disease.
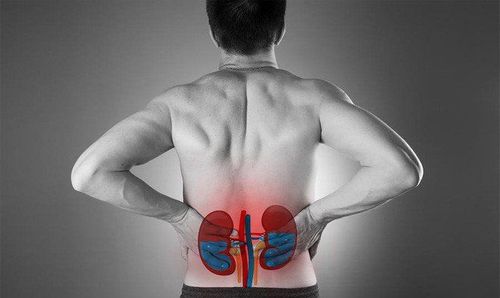
Chụp thận có thuốc cản quang giúp phát hiện các bệnh lý về thận
However, intravenous contrast nephrography is still a useful diagnostic tool in the following cases:
Identify some structural disorders of the urinary tract Detect kidney stones Provide information on the condition urinary tract obstruction
Chụp CT có nhiều ưu điểm vượt trội nên được sử dụng ngày một phổ biến
2. What are the risks of having a contrast-enhanced nephrogram (UIV) performed?
In general, intravenous contrast nephrography is a safe technique, with very rare complications. As with any medical procedure, intravenous contrast nephrography has some complications, including allergic reactions. In some people, the injection of contrast can cause side effects such as:A feeling of warmth all over the body or flushing A metallic taste in the mouth Nausea Itching Rash During the X-ray, the patient will be exposed to low doses of radiation. The amount of this radiation is very small, so the risk of causing cell damage in the body is very low.
However, if you are pregnant or suspect that you may be pregnant, you should tell your doctor before having an intravenous contrast dialysis. Although the risk to the fetus is low, the doctor may consider whether to wait or use another imaging technique.
3. What is the procedure for nephrography with intravenous contrast (UIV)?
3.1 Before the scan Before taking a dialysis with intravenous contrast, the doctor will ask and tell the patient:Are you allergic to anything, especially iodine? Are you pregnant or suspect you are pregnant Have you ever had an allergic reaction to contrast material in the past? The patient may need to avoid eating and drinking for a certain period of time before the contrast agent is injected. In addition, doctors also recommend taking a laxative the night before yesterday's scan.

Bác sĩ tư vấn và dặn dò bệnh nhân trước phẫu thuật
Ask some questions about medical history Check blood pressure, pulse and body temperature Ask the patient to take off hospital gowns and dressings; remove jewelry, eyeglasses, and any metal objects that may obscure the x-ray image. Ask the patient to urinate and go until the bladder is empty. 3.2 During the scan For intravenous contrast nephrography, the patient will lie on his or her back on an examination table. The X-ray machine is usually attached partially or completely to the board. The X-ray image intensifier will be placed on the patient's abdomen. After the patient is comfortably lying on the table, the doctor will begin to take the following steps:
Take X-ray of the urinary tract before injecting contrast. Initiate intravenous contrast injection. X-rays are taken according to the timelines that include (1) the contrast medium going to the kidney, then to (2) the ureter and (3) emptying into the bladder. When the scan is complete, the patient is asked to urinate again. Then, the patient returns to the examination table for the doctor to take an X-ray while the bladder is empty. In some cases, it is possible to add a urine scan to evaluate the urethra: especially in cases of urethral fistula or urethral stricture. 3.3 After the scan When the IV contrast nephrography is complete, the arm vein will be withdrawn. Dr. Le Xuan Thiep has strengths in performing advanced and difficult magnetic resonance and computed tomography techniques such as: coronary computed tomography, cardiac function, cerebral magnetic resonance, cerebral perfusion and organs,..
If you notice any unusual health problems, you should visit and consult a specialist
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.