This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Doctor Tran Quoc Tuan - Head of Resuscitation Unit - ICU - Emergency Resuscitation Department - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital.Intra-articular injection is a simple procedure but requires absolute sterility, carried out at the rheumatology department to treat osteoarthritis, reduce inflammatory response and reduce synovial membrane proliferation.
1. What is an intra-articular injection?
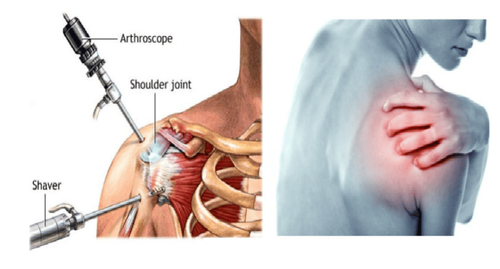
Intra-articular injection is one of the simple, low-cost, safe, and highly effective procedures in treatment and is conducted routinely at joint specialists. Intra-articular injection is a therapy that uses fine needles to insert drugs into joints or adjacent soft tissues for local treatment of some joint diseases.Intra-articular injection is to put drugs directly inside the joint cells to treat diseases related to joints, requires absolutely sterile technique, and must be carried out at medical facilities, minor surgery rooms. under sterile conditions.
The advantages of intra-articular injection technique are:
The drug is put into the joint and has no effect, so the whole body through the blood transfusion will maximize the effects of the treatment drug, so the joint area needs to be treated. treat. Intra-articular injection to reduce inflammatory response, reduce synovial membrane proliferation and supplement mucus in the treatment of osteoarthritis.
Tiêm nội khớp giúp giảm viêm và tăng chất nhầy trong điều trị thoái hóa khớp
2. When to inject intra-articular?
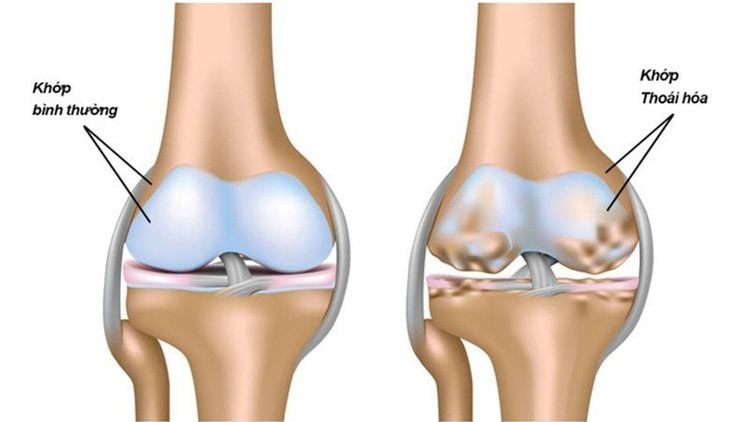
Cases requiring intra-articular injection include:2.1 Indications for intra-articular corticosteroid injection Diseases of the joints with non-infectious synovitis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, juvenile chronic arthritis ,... Seborrheic cystitis Synovial coccyx, especially popliteal coccyx, also known as Baker's cyst Early stage osteoarthritis 2.2 Indications for intra-articular injection of hyaluronic acid Osteoarthritis of the shoulder and knee joints can be injection of finger joints, hip joints,... However, in our country, injection is only applied at shoulder and knee joints.
Cases of contraindications for intra-articular injection:
Joint lesions due to bacterial and fungal infections Infections cannot be excluded Infectious lesions on the skin at injection sites and in areas near the injection site. In addition, caution should be exercised with contraindications of intra-articular corticosteroids such as: diabetes, high blood pressure. These cases must be stabilized before injection and monitored after injection in order to control the epidemic.
Bệnh nhân cao huyết áp cần được điều trị ổn định trước khi tiêm thuốc
3. Intra-articular injection procedure
3.1 Preparation of Instruments:Laboratory under sterile conditions Sterile needles 23G for large joints, and 25G for small joints. Syringe 1.2 ml or 5 ml. Preferably use single-use plastic syringes Alcohol cotton, iodine and sterile adhesive tape Medicines:
Corticosteroids fast acting (short-acting): hydrocortisone acetate, prednisolone acetate. Inject 3 times for a course of treatment. Each injection is spaced 3-4 days apart. Corticosteroids slow-acting (long-lasting): betamethasone, dipropionate Diprospan; Depo Medrol. Inject no more than two injections for a course of treatment, each dose is 7-10 days apart. Novocain or xylocaine: used to numb before injecting corticosteroids or can be used with corticosteroids for pain relief. Anti-shock drugs Dose of corticosteroids: For large joints such as knees and shoulders: inject a dose equivalent to 5mg of prednisolone (eg hydrocortisone acetate: inject 1 ml of the drug). For small joints such as elbows, wrists, ankles: 0.5 ml of the drug. Note: Should not be abused, each course must be injected 3-6 months apart, no more than 2-3 times per year. The most important thing is to treat the main disease. Corticosteroid injections are only symptomatic treatment.
3.2 Procedure Explain the procedure to the patient. Ask patient about medical history and history of drug allergies. Check your medical records, or your rheumatologist's prescription. Before injection, the patient should be examined to reconfirm the indications and rule out contraindications. Determine the injection site. Disinfect the injection area with alcohol iodine or betadine. Inject the correct dose and site.
Tiêm thuốc đúng liều và đúng kĩ thuật
Stop bleeding at the site. Shock treatment if available according to anti-shock regimen Say novocaine (if used with novocaine): bed rest. After the procedure:
Injection site reaction within 24 hours (swelling, pain, redness of the injection site), usually occurring 6-12 hours after the first or second injection: for the patient patients taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, pain relievers. Treat local infection (if present) and review diagnosis or recheck sterile sutures. Skin atrophy, muscle atrophy, change in skin pigmentation at injection site. This complication often occurs with tendon attachments, rarely with intra-articular injections. It can be avoided by not letting the drug spill into the skin, the needle puncture site when there is a skin lesion, should not continue to inject the drug into the old position. The patient needs to be monitored. This complication is not dangerous but affects aesthetics. In summary, intra-articular injection is a simple procedure, but should be absolutely sterile, to treat symptoms such as replenishing mucus, reducing arthritis, and reducing synovial membrane proliferation in pathological conditions. about joints.
After the injection, the patient needs to be monitored, so if there are local reactions or infections, muscle atrophy, skin atrophy, etc., it is necessary to notify the doctor immediately for examination and treatment. timely.
Treatment and prevention of knee osteoarthritis
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.