This is an automatically translated article.
Interstitial lung disease is a fairly common disease today, early diagnosis and timely treatment are the most effective solutions to defeat interstitial lung disease, avoiding the risk of lung function decline.
1. What is interstitial lung disease?
Interstitial lung disease is also known as diffuse parenchymal lung disease, idiopathic sclerosing alveolar disease, and alveolar inflammatory disease. This is the common name of a group of diseases that damage the interstitial tissues of the lung such as alveolar septum, interalveolar interstitial tissue, and blood vessels. Interstitial lung diseases often have the same clinical symptoms, chronic progression, easily lead to pulmonary fibrosis, eventually affecting the body's ability to breathe.
Interstitial lung disease is more common in women than in men. Inherited diseases of the interstitial lung disease group usually appear in people between the ages of 20 and 40. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis occurs in people over the age of 50.
Interstitial lung disease is classified by causes as follows:
Inhalation toxic substances: silicosis, Berylliosis, Asbestosis, hypersensitivity pneumonitis; Due to drugs: antibiotics, drugs for arthritis, cancer drugs, statin drugs; Infections: Atypical pneumonia, tuberculosis, pneumocystis pneumonia,...;

Thuốc kháng sinh có thể là nguyên nhân gây ra bệnh phổi kẽ
Affiliate organizers: Polyneuritis, dermatomyositis, neurodermatitis, systemic fibrosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatism; Malignancy: Cancerous lymphangitis; Unknown etiology: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, sarcoidosis, Hamman-Rich syndrome.
2. Clinical symptoms of interstitial lung disease
Patients with interstitial lung disease often have symptoms of difficulty breathing with exertion and increased oil, chest tightness, dry cough,... These symptoms are often atypical, easily confused with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. In addition, patients may also have coughing up blood, joint pain, and clubbing fingers.
People with interstitial lung disease may have extra-thoracic symptoms such as painful swelling of joints, peripheral lymph nodes, Raynaud's syndrome, weight loss,... depending on the disease.
3. Diagnosis of interstitial lung disease
Chest X-ray Blood test Blood gas measurement Bronchoscopy Flexible bronchoscopy - alveolar lavage Transbronchial biopsy Surgical lung biopsy (including thoracoscopic biopsy and open lung biopsy)
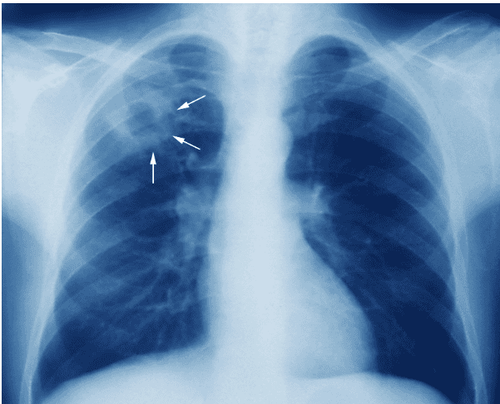
Chụp X-quang giúp chẩn đoán bệnh phổi kẽ
4. Some common interstitial lung diseases
4.1 Hypersensitive pneumonia
The disease occurs due to long-term inhalation of organic dust, with the participation of the immune response and damage to the interstitial space. Depending on the severity and duration, hypersensitivity pneumonitis is divided into acute, subacute and chronic forms. Specifically:
Acute form: The most common form with symptoms such as fever, chills, nausea, fatigue and shortness of breath (easily confused with viral or bacterial infections). The treatment of the disease is mainly symptomatic treatment, stopping contact with the causative agent. Thanks to that, the disease will go away on its own after about 12 hours or a few days. If re-exposure to organic dust, the disease can recur. Subacute form: The slow progression with symptoms such as cough with sputum, fatigue, shortness of breath, weight loss. During treatment, if exposure to organic dust is stopped, the patient can completely recover after a few weeks to a few months. In addition, corticosteroids can be used for patients with subacute hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Chronic: The disease has a chronic onset, with symptoms of cough with phlegm, shortness of breath, fatigue, weight loss and clubbing. If exposure to the causative agent is stopped, the disease may be in remission to some extent. The treatment is still the use of corticosteroids.

Ho có đờm là triệu chứng phổ biến của viêm phổi tăng cảm thể bán cấp
4.2 Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is an interstitial lung disease of unknown etiology, the histopathological lesion is diffuse interstitial inflammation and pulmonary fibrosis. This disease is common in people 50-70 years old. Patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis present with progressive shortness of breath, later stages of cyanosis of the skin and lips, hypoxia, chronic cardiopulmonary disease, pulmonary hypertension, and heart failure. The survival time of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is usually less than 5 years.
4.3 Eosinophilic pneumonia
This is eosinophilia in the lung parenchyma. The diagnostic criteria for the disease are eosinophilia in the peripheral blood and in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid or in lung biopsies. The disease may have no known cause.
Some of the causes of eosinophilic pneumonia are:
Toxic and drug-induced eosinophilic pneumonia: The main causative agents are NSAIDs and antibiotics. Pathogenic toxins can be scorpion stings, aluminum salts or metal particles, inhaling drugs, inhaling organic matter during rubber production; Loeffler syndrome: Due to a roundworm parasitic infection, the larvae travel through the bloodstream to the alveoli before entering the small intestine. Larvae are localized at the apex of the lung, disappearing on their own after about 2 weeks. Symptoms include dry cough, feeling of heat behind the breastbone, restlessness, discomfort, possible fever, coughing up blood and sputum, shortness of breath, wheezing, etc. The treatment of diseases caused by this cause includes: treat symptoms and use deworming drugs; Churg-Strauss syndrome: Characterized by sinusitis, bronchial asthma, and peripheral blood eosinophilia.
Tình trạng viêm phổi tăng bạch cầu ái toan có thể được gây ra bởi hội chứng Churg-Strauss
4.4 Interstitial pneumonia
Complications of lung injury such as interstitial pneumonia, pulmonary fibrosis, pulmonary edema, bronchospasm, pleural effusion,... can all be caused by drugs. Some drugs that cause interstitial pneumonia belong to groups such as antibiotics, cancer chemotherapy drugs, immunosuppressants, and arthritis drugs. In addition, radiation therapy for cancer can also cause interstitial pneumonia.
Patients with interstitial pneumonia often present with shortness of breath, cough (first dry cough, then hemoptysis), wheezing, chest pain. Extrapulmonary symptoms can include muscle and bone pain, fatigue, joint pain, fever, edema, dry eyes, dry mouth, sensitive skin to light,...
5. Methods of treating interstitial lung disease
Treatments are selected according to the type of disease and its cause. Treatment usually includes:
Medication: The patient may be prescribed anti-inflammatory or anti-fibrotic drugs depending on the cause of the interstitial lung disease. Use oxygen: Help the patient breathe easier, prevent or minimize complications caused by low oxygen levels in the blood, improve sleep, lower blood pressure on the right side of the heart. Surgery: If other treatments do not work, patients with interstitial lung disease may be indicated for lung transplant surgery.
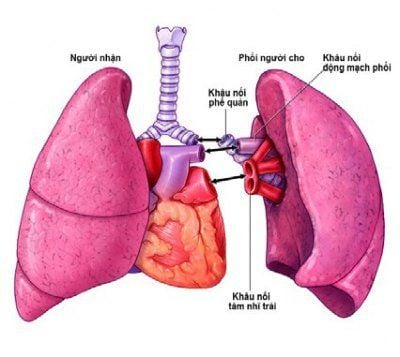
Ghép phổi là một phương pháp điều trị bệnh phổi kẽ
6. Measures to prevent and control interstitial lung disease
A healthy lifestyle will help to cope with and limit the progression of interstitial lung disease. Some notes for patients include:
Quit smoking and avoid inhaling automatic smoke Having a healthy, nutrient-rich diet with enough calories needed for the body's needs Immunization: Infection Because breathing can worsen symptoms of interstitial lung disease, everyone should get a pneumonia shot and a flu shot every year Exercise: Working hard at sports will help you stay healthy. resistance to chronic diseases. Interstitial lung disease greatly affects the quality of life of patients. Therefore, when there are signs of suspected disease, patients should go to the doctor immediately to get an accurate diagnosis and have a positive and effective treatment plan.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit. examination and treatment at the Hospital.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
SEE MORE
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: What you need to know Overview of common lung diseases What disease does a persistent dry cough warn of?