This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Hung - Doctor of Endocrinology - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.Interstitial cystitis is a disease of the bladder, causing the patient to feel pain, urinate frequently, and affect the patient's work and life.
1. What is interstitial cystitis?
Interstitial cystitis is a chronic condition that causes bladder pressure, bladder pain, and sometimes pelvic pain. The pain ranges from discomfort to severe pain.Your bladder is a hollow organ where urine is stored. The bladder expands until it's full and then signals to your brain that it's time to urinate, via the pelvic nerves. This creates the urge to urinate in most people.
With interstitial cystitis, these signals are confused, you will feel the need to urinate more often and with less urine than usual.
Interstitial cystitis commonly affects women and can have a lasting impact on quality of life. Although there is currently no cure, medications and other therapies can help relieve pain caused by interstitial cystitis.
2. Symptoms of Interstitial Cystitis
Patients with interstitial cystitis often do not have the same symptoms.If you have interstitial cystitis, your symptoms can also change over time, due to a number of other factors such as menstruation, sitting for long periods of time, stress, exercise. ..
Common signs in patients with interstitial cystitis include:
Pain in the pelvis, vulva, or posterior vaginal area in women Pain in the scrotum, testicles, penis, or back area penis in men Chronic pelvic pain The need to urinate often, needing to urinate immediately Lower abdominal pain Urethral pain Lower back pain Urinating often, usually in small amounts, throughout the day and night (evening) up to 60 times a day) Pain or discomfort while the bladder is full and pain relief after urinating. Pain during sex With patients with interstitial cystitis, the severity of symptoms varies, the pain is sometimes dull, sometimes very intense. Some people with interstitial cystitis do not have any symptoms.
Although the signs and symptoms of interstitial cystitis can resemble those of chronic urinary tract infections. However, symptoms may get worse if you have interstitial cystitis and a urinary tract infection at the same time.

3. Causes of Interstitial Cystitis
The exact cause of interstitial cystitis is still unknown, but it is likely that many different factors cause this condition. For example, if you have interstitial cystitis, you also have a defect in the protective lining (epithelium) of the bladder. Toxic substances in the urine irritate the bladder wall through leakage in the epithelial layer.Several other factors may contribute to this condition but have not been clearly studied, such as autoimmune reactions, genetics, infections or allergies.
4. Risk of interstitial cystitis
Some factors increase the risk of interstitial cystitis such as:Gender: Interstitial cystitis occurs more often in women than in men. Symptoms in men can be similar to interstitial cystitis, but they are often associated with inflammation of the prostate gland (inflammation of the prostate gland). Skin and hair color: people with fair skin and red hair are at higher risk for interstitial cystitis Age: Most people with interstitial cystitis are diagnosed in their 30s or older. Chronic pain: Interstitial cystitis may be associated with other chronic pain disorders, such as irritable bowel syndrome or fibromyalgia.
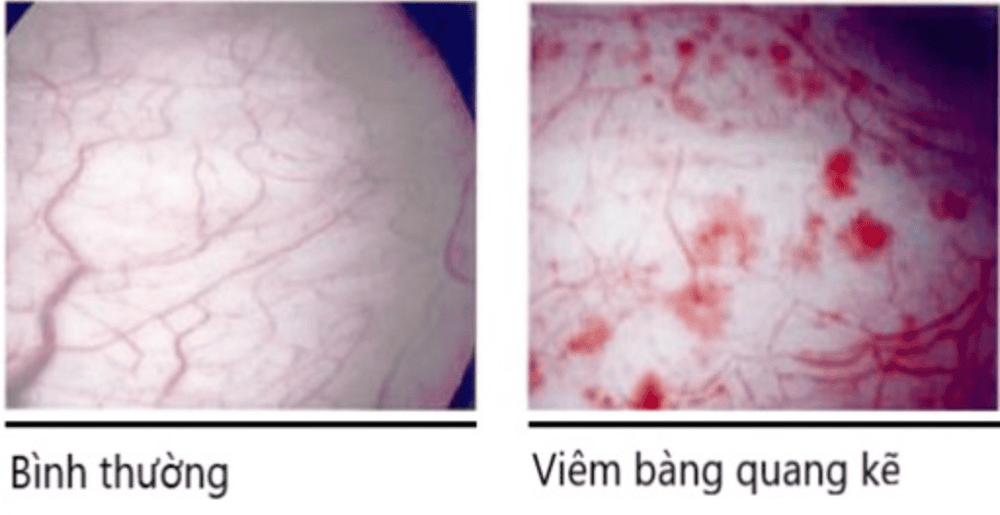
5. Complications from interstitial cystitis
Interstitial cystitis can cause a number of complications such as:Decreased bladder capacity : Interstitial cystitis can cause hardening of the bladder wall, causing your bladder to hold less urine Reduced quality of life : Go Frequent urination and pain can interfere with social, work, and other activities of daily living. Affected Sex: Frequent urination and pain can strain your personal relationships, sexual relations are also affected. Depression: The chronic pain and disrupted sleep associated with interstitial cystitis can be stressful and potentially lead to depression.
6. Diagnosis of interstitial cystitis
Several methods are used to diagnose interstitial cystitis such as:Symptoms of the disease: Your doctor will ask you to describe the symptoms you have and may order a bladder diary with the amount of water you drink with the amount of urine you pass. Gynecological exam: During a pelvic exam, your doctor examines your external genitals, vagina, and cervix to evaluate the internal pelvic organs. Your doctor may also examine your anus and rectum. Urinalysis : analyzing a urine sample to detect signs of a urinary tract infection Cystoscopy : the doctor uses a small tube with a camera attached through the urethra to examine the lining of the bladder Biopsy: During the procedure During a cystoscopy, your doctor may remove a tissue sample (biopsy) from your bladder and urethra for examination under a microscope. This is to check for bladder cancer and other rare causes. Urine cytology: The doctor collects a urine sample and examines the cells to remove cancer cells. Potassium sensitivity test: Your doctor will put water and potassium chloride in your bladder. You are asked to rate pain and urgency on a scale of 0 to 5 after each subcategory. If you feel more severe pain or you have to urinate more often with potassium instillation than with water, your doctor may diagnose interstitial cystitis. In people with normal bladders, there was no difference between small amounts of water or small amounts of potassium chloride. Urinary tract infections can be prevented and treated if the patient detects early signs and actively goes to the doctor for treatment. Absolutely do not self-medicate without a doctor's instructions because it can make the condition worse, causing unnecessary consequences. Currently, Vinmec International Hospital always provides screening packages for urinary tract diseases, this is an effective method to help patients screen for diseases and protect their own health. For pregnant mothers, regular checkups and tests with accurate diagnoses will help detect abnormal signs early and have a thorough treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Article referenced source: Mayoclinic.org