This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by MSc Nguyen Van Khanh - Pathologist, Laboratory Department - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.
After a breast biopsy, the specimen will be examined under a microscope by a doctor called a pathologist. The results of the pathology will be sent back to your treating doctor. The information in the pathology results will help monitor and treat you. The questions and answers below will help you understand more about the medical terms you see in your pathology results.
1. Explanation of terms
What is adenocarcinoma or adenocarcinoma?
Carcinoma is the term to describe a cancer that originates in the cells that line or cover organs in the body. Breast carcinoma is cancer that originates in the epithelial cells lining the follicles and ducts of the breast. Most breast cancers are carcinomas. Carcinomas that originate in glandular tissue are called adenocarcinomas.
What is invasive carcinoma?
Invasive carcinoma means that it is no longer precancerous (carcinoma in situ) but a true cancer.
Normal mammary gland tissue is made up of milk ducts (tubes) and lactation sacs (lobules). When the cells lining the tubules or lobules change into cancer cells and these cancer cells grow only within the tubules or lobules, they do not break down and invade surrounding tissue. called Carcinoma in situ.
When cancer cells grow and break through the tubes or lobules, it is called Invasive Carcinoma. In invasive carcinoma, the tumor cells may have spread to other parts of your body.
What does invasive ductal carcinoma, invasive lobular carcinoma, carcinoma with ductal and lobular features mean?
Breast carcinoma is divided into two main types: invasive ductal carcinoma and invasive lobular carcinoma. In cases where the tumor may have both tubular and lobular features, it is referred to as mixed ductal and lobular carcinoma. Another term for invasive carcinoma is invasive breast carcinoma of the unspecified type, which is the most common type of invasive ductal carcinoma.
Both invasive ductal carcinoma and invasive lobular carcinoma originate in the cells lining the ducts and lobules. In general, lobular carcinoma and invasive ductal carcinoma are treated differently.
Pathology results mention E-cadherin, what does it mean?
E-cadherin is a test that pathologists use to distinguish whether a tumor is tubular or lobular. E-cadherin was positive for ductal cancers and negative for lobular cancers.
What does well-differentiated, moderately differentiated, or poorly differentiated carcinoma mean?
When viewed under the microscope, pathologists can see a number of features that help predict the growth and metastasis of cancer cells. These features include the arrangement of cells in relation to other cells, whether they form ducts (glandular structure), whether they resemble normal mammary cells (nucleation degree) ) and how many cancer cells are in the process of dividing (multiplier division). These features are combined to determine the degree of differentiation of the cancer.

Well-differentiated carcinoma is a cancer consisting of cells that closely resemble normal cells, do not grow rapidly, and are arranged in small tubules forming ductal carcinoma and cords in lobular carcinoma. These cancers tend to grow, metastasize slowly and have a good prognosis. Poorly differentiated carcinomas are cancers that consist of cells that are unlike normal cells, tend to grow and metastasize more rapidly, and have a poor prognosis. Moderately differentiated carcinomas are cancers with features and prognosis intermediate between the two. What is histology or Nottingham grade?
These degrees are similar to what is mentioned in the distinctions above. Recorded features include gland structure formation, nuclei, and multiplication index. They are then added together to give the histology or Nottingham grade.
If there are 3-5 points, then the cancer is classified as grade 1 (well differentiated). If a score of 6 or 7 is obtained, the cancer is classified as grade 2 (moderately differentiated). If there are 8 or 9 points, then the cancer is classified as grade 3 (poorly differentiated). What is Ki-67?
Ki-67 is a way of measuring how well cancer cells grow and divide. A high Ki-67 (>30%) means that the cancer cells are dividing rapidly, so the cancer is likely to grow and metastasize faster.
What does small ductal, mucinous, ethmoid or micropapillary carcinoma mean?
These cancers are different types of invasive ductal carcinoma that are identified under the microscope by the pathologist.
Small-tubular, mucinous, and ethmoid carcinomas are special types of well-differentiated cancers. They generally have a better prognosis than nonspecific invasive breast carcinomas. Micropapillary carcinoma is a subtype of invasive breast carcinoma and has a poor prognosis. If you have one of these types of cancer, your doctor will recommend different treatments.
Because some tumors can contain many different types, surgery to remove the entire tumor is necessary to determine what type you have. A needle biopsy alone is not informative enough to guide treatment.
Invasion of blood vessels, lymphatic vessels is what? What is D2-40 or CD34?
When looking under the microscope to see cancer cells in small blood vessels or lymphatic vessels, it is called vascular or lymphatic infiltration. When cancer cells grow in these blood vessels, they have a better chance of spreading outside the breast. If the pathology results do not address this problem, it means that there is no vascular or lymphatic invasion. Even if it does, it doesn't mean your cancer has spread. How this symptom affects treatment is best discussed with your treating physician.
D2-40 and CD34 are special tests that the pathologist can use to identify these types of vascular invasion. These tests are not necessary in cases of obvious invasion.
What does tumor size mean?
If an entire tumor or cancerous area is operated on, the pathologist will tell how big the cancer is by measuring its length (largest diameter), or measuring it under a microscope , or measured on macroscopic examination (with the naked eye). The size of the tumor in the mammary gland is part of determining the stage of the cancer, which has prognostic and therapeutic implications.
Core biopsies only cover part of the tumor, so the pathology results for core biopsies will not provide tumor size. After surgery (conservative mastectomy or total mastectomy), the tumor size will be more accurately measured.
What does u stage mean?
Cancer stage is a measurement of how aggressive and metastatic it is. The standard staging system for breast cancer used is the TNM stage:
T represents the primary tumor (primary tumor) N represents metastasis to nearby lymph nodes M represents metastasis (spread to the lymph nodes) other distal parts of the body) If tumor staging is based on surgical specimens and evaluated by a pathologist, the letter p (for pathology) is placed before the letters T and N.
The T classification (T0, Tis, T1, T2, T3, or T4) is based on the size of the tumor and whether the tumor invades the skin covering the mammary gland or invades the chest wall below the mammary gland. The higher the T number, the larger the tumor and/or the more extensive invasion of tissues near the breast. (Tis is carcinoma in situ). Therefore, the entire tumor must be taken to assess the T classification, information that is not covered on core biopsies.
The N classification (N0, N1, N2, or N3) indicates whether the cancer has spread to lymph nodes near the breast and how many nodes have metastasized. The higher the number after N, the more lymph nodes that have metastasized cancer. If no lymph nodes are removed for examination, then classified as NX, the letter X is used to mean that no information is available for evaluation.
The M classification (M0, M1) is usually based on laboratory and imaging findings, and is not part of the pathological report. In a pathological outcome, the M classification is often omitted or classified as MX (again the X means no information available for evaluation).
When the categories T, N and M are defined. This information is combined together to give an overall stage of the cancer. The stages are represented by Roman numerals starting from period I (earliest period) to stage IV (latest period). Non-invasive cancer (carcinoma in situ) is called stage 0.
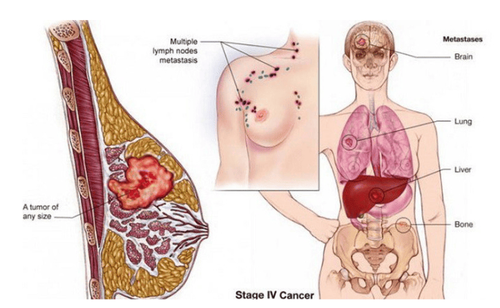
What is the lymph node mentioned in your pathology report?
If breast cancer has metastasized, it usually first reaches the lymph nodes near the breast under the arm (called axillary lymph nodes). If you have any large lymph nodes under your arm (detected on physical examination or with an imaging test such as ultrasound or mammography), they may be biopsied at the same time as the tumor biopsy. your breast. The doctor will use a needle to take a sample of cells from the lymph node. The cells will be checked to see if they contain cancer cells. If cancer cells are present, it is ductal carcinoma or lobular carcinoma.
During surgery to treat breast cancer, lymph nodes under the arm if present are also removed. These lymph nodes will be examined under a microscope to see if they contain cancer cells. Results must report how many lymph nodes were removed and how many of them contained cancer (eg, 2/15 lymph nodes had metastatic cancer).
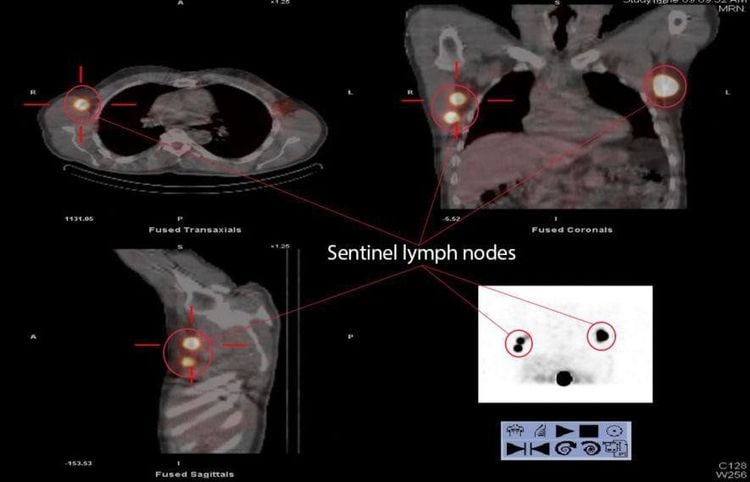
What is the sentinel lymph node?
The sentinel lymph node is the first node near the breast that is most likely to harbor cancer cells when they metastasize. Your surgeon will find and remove sentinel lymph nodes during a breast lumpectomy. Checking sentinel lymph nodes is a way to check for spread of cancer to the lymph nodes under the arm without having to remove too many of them.
If there are no cancer cells in the sentinel lymph nodes, there is little chance that the cancer has spread to other lymph nodes, so no further lymph node collection is needed.
If the sentinel node contains cancer, the pathology will show how many nodes are cancerous as well as the size of the cancer in the lymph nodes. In some cases, if cancer is in the sentinel lymph nodes, you may need additional treatment, such as surgery to remove more lymph nodes under your arm or radiation therapy to the underarm area. You should discuss this with your treating physician.
What are solitary tumor cells in a lymph node?
This means only scattered cancer cells in the lymph nodes are found by routine microscopic examination or by other special tests. Having single tumor cells does not affect your tumor stage or change your treatment plan.
What does pN0(i+) result mean?
This means that solitary tumor cells are found in the lymph nodes by special staining methods.
What does micro-metastasis in lymph nodes mean?
This means that there are cancer cells in the lymph nodes that are larger than solitary tumor cells but smaller than normal metastases. If micrometastasis is present, classify N as pN1mi. This can affect the stage of your cancer, so your treatment plan may need to change. Please discuss further with your treating physician.
What are the special tests like Cytokeratin, CK5/6, p63, SMA?
These are special tests that a pathologist uses to help diagnose invasive breast cancer or identify metastatic cancer in the lymph nodes. Not all cases require these tests. Whether or not your pathology results refer to these tests has no bearing on diagnostic accuracy.
What do the following terms, if present on pathology, mean?: common ductal hyperplasia, adenopathy, fibroadenoma, stellate scar, complex fibrous lesion, papillomatosis, tumor papillary, apocrine metaplasia, cyst, columnar cell change, collagen bridge, mammary duct dilation, cystic fibrosis change.
All of these terms are noncancerous (benign) changes seen under the microscope by pathologists. They are not important when biopsies show invasive breast cancer.
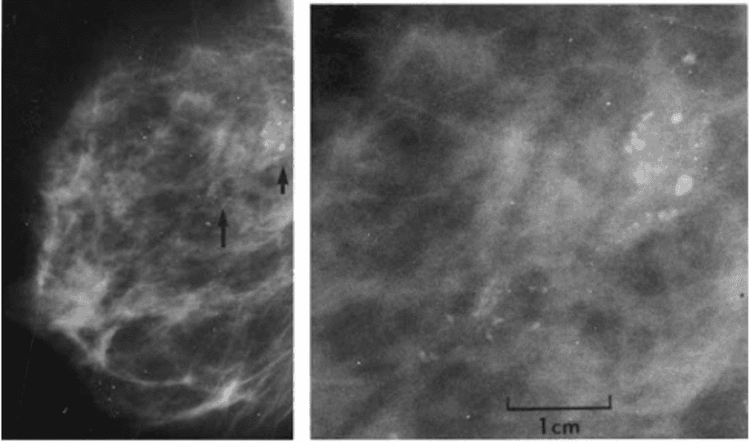
What is calcification or microcalcification?
Microcalcification or calcification is mineral deposition that can be present in both noncancerous and cancerous mammary gland lesions. They can be seen either on a mammogram or under a microscope. Since some calcifications are seen in areas containing cancer, their presence on mammograms is an indicator for biopsies of this area.
The pathologist then looks at the tissue sample removed and makes sure it contains calcifications. If there is calcification, the doctor understands that the biopsy sample was taken in the correct area of the lesion (that is, the abnormal areas containing calcification on the mammogram).
Microcalcifications and calcifications are important only because they are sometimes found in areas where cancer is present. When they are found alone (without disturbing changes in the tubules or lobules), they are not important.
In addition to cancer, in the pathology results, there are more lesions of atypical tubular hyperplasia, atypical lobular hyperplasia, ductal carcinoma in situ, intraductal carcinoma, and lobular carcinoma. lobular tissue in situ, what do they mean?
These are terms for atypical or precancerous changes that may be seen on biopsy but are not as serious as invasive cancer. If they are found along with invasive cancer, they are usually not important.
However, they may need to be surgically removed altogether as part of the treatment. If they are seen on open biopsies or they are close to the surgical site, further surgery may be required to remove more tissue.
What does estrogen receptor (ER) or progesterone receptor (PR) mean?
Receptors are proteins found on cells that can bind to certain substances circulating in the blood, such as hormones. Normal breast cells and some breast cancer cells have receptors that bind to the hormones estrogen and progesterone. These two hormones often promote the growth of breast cancer cells.
An important step in the evaluation of breast cancer is testing a portion of cancer removed during a biopsy (or surgery) to see if they have estrogen and progesterone receptors. Cancer cells may contain either receptors, or both, or none.
Breast cancers that contain estrogen receptors are often called ER-positive (or ER+) cancers, while cancers that contain progesterone receptors are called PR-positive (or PR+) cancers. Women with hormone receptor-positive cancer tend to have a better prognosis and are more likely to respond to hormone therapy than women with breast cancer without these receptors.

All breast cancers and precancerous breast cancers should be tested for these hormone receptors, with the exception of lobular carcinoma in situ.
ER and PR results are reported separately and are reported as follows:
Negative, weak positive, positive Percentage positive Percentage positive whether weak, moderate, or positive strong. You should discuss with your treating physician how the test results affect your treatment plan.
What is HER2/neu or HER2?
Some breast cancers have too much of a growth-promoting protein called HER2/neu (commonly referred to as HER2). The HER2/neu gene directs cells to make this protein. Tumors with increased HER2/neu levels are called HER2-positive.
Cells in HER2-positive breast cancer have too many copies of the HER2/neu gene, resulting in an increased amount of the HER2 protein above normal. These cancers tend to grow and metastasize faster than other breast cancers.
All new breast cancer diagnoses should be tested for HER2, because women with HER2-positive breast cancer are more likely to benefit from treatment with drugs that target the HER2 protein , such as trastuzumab (Herceptin), lapatinib (Tykerb), pertuzumab (Perjeta), and T-DM1 (Kadcyla).
Biopsy or surgical samples are usually tested in one of two ways:
Immunohistochemistry : In this test, special antibodies bind to HER2 proteins present in the specimen, causing cells to Cells change color if they have multiple copies. This color change can be observed under a microscope. Results are reported as 0, 1+, 2+, or 3+. Fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH): This test uses fluorescent DNA fragments that attach to copies of the HER2/neu gene in cells, which can then be counted under a special microscope.
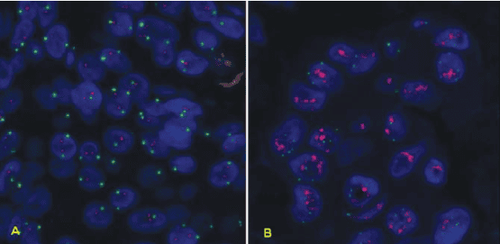
Many breast cancer specialists think that FISH is more accurate than immunohistochemistry. However, this test is more expensive and takes longer to do. Usually immunohistochemistry is the test used first:
If the result is 0 or 1+, the cancer is considered HER2-negative. Women with HER2-negative tumors are not indicated for treatment with HER2-targeting drugs (such as trastuzumab). If the result is 3+, the cancer is HER2-positive, so the patient may benefit from treatment with drugs that target HER2. If the result is 2+, the HER2 status of the tumor is unclear. This means that more FISH testing is needed to further clarify the HER2 results. A new type of test, called chromogenic in situ hybridization (CISH), is performed similarly to FISH, by using small DNA primers to count the number of HER2/genes neu in breast cancer cells and without the use of a special microscope, this test can be cheaper than FISH. Currently, this test is not widely used by immunohistochemistry and FISH.
If you have HER2-positive cancer, your treating doctor must add some medications to your treatment. The test results will influence your treatment plan, so it's best to discuss this with your treating doctor.
What is the surgical cut or ink color mentioned in the results?
When the entire tumor is removed, the outer edges (or surgical sections) of the specimen are stained with ink, each of which is stained with a different color of ink. The pathologist analyzes slides of the tumor under the microscope to assess the distance from the tumor cells to the marker (edges or sections of the specimen).
If the cancer cells touch the ink (also called a positive cut), it means that the cancer has not been completely removed and further surgery or other treatments may be needed.
Occasionally, all of the invasive cancer has been resected, but there may be precancerous or other serious lesions on or near the resection, such as ductal carcinoma in situ or carcinoma. lobular carcinoma in situ.
If your pathology results show a positive surgical resection, your treating doctor will talk to you about the next best course of treatment.
Your treating physician orders a molecular test to be performed on your specimen. What does that mean?
Molecular tests such as Oncotype DX® and MammaPrint® can help predict the prognosis for some breast cancer types, but not all cases require this test. If one of these tests is done, the results will be discussed with your treating doctor. The results will not affect your diagnosis, but may affect your treatment plan.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space. Customers when choosing to perform tests here can be completely assured of the accuracy of test results.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Article referenced source: American Cancer Society