This is an automatically translated article.
Injury to the arteries of the extremities is a major injury caused by traffic accidents and is mostly seen in men. Because these injuries quickly lead to anemia, it is important to know the symptoms to quickly get timely treatment. If left late, it will cause sequelae of loss of limb function, amputation, even death.
1. Causes of limb artery injury
Injuries to the arteries of the extremities are mainly seen in the lower extremities. Accordingly, in order to find out the exact cause of the limb artery, it is necessary to distinguish two types according to the mechanism of action to cause arterial injury as follows:
Indirect trauma due to fracture, dislocation: This injury accounts for the majority of patients. limb artery injury. When the head of the bone-joint fractures, when displaced, it will tear and crush the artery that runs close to the bone. Locations of fractures, dislocations or arterial damage by this mechanism include the area around the elbow joint in the upper extremities; the area around the knee joint in the lower extremities (fracture of the lower third of the femur, fracture of the femoral condyle, fracture of the tibial plateau, fracture of the upper third of the tibia, dislocation or subdislocation of the knee). Therefore, it is important to systematically look for acute limb ischemia in the presence of fractures in these regions. Direct trauma: This injury accounts for less than 10% of limb artery injuries. Due to the direct impact of blunt or blunt objects in the area of the limb through which the artery passes, it causes severe contusion of the soft part of the limb at the site of the impact - including the artery, which may be accompanied by a corresponding fracture or laceration of the skin.
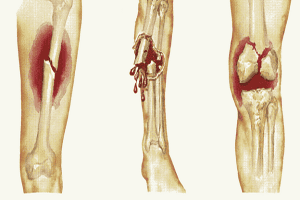
Đầu xương gãy có thể làm tổn thương đoạn động mạch chạy sát xương
2. Diagnosis of limb artery injury
Diagnosis of limb artery injury is mainly based on clinical evidence, in which the most important is limb embolism syndrome. Accordingly, vascular Doppler ultrasound is the main subclinical investigation. Indications for angiography when encountering difficult cases.
2.1. Clinical diagnosis of arterial injury Due to the trauma of fractures and soft tissue contusions, there are some changes in clinical symptoms. Vascular lesions can be easily missed because obvious signs of fractures and damage to other organs can be observed. However, if a limb artery injury is thought about and a careful examination is done, a clinical diagnosis of a limb artery injury can still be made.
Function
Injury or indirectly due to fracture - dislocation, especially around the knee and around the elbow or directly due to strong trauma to the vascular path. Physical signs of fracture - dislocation, or severe soft-tissue contusion (pain, reduced limb mobility). Signs of limb artery injury: signs of numbness, decreased sensation in the extremities. More severe is complete loss of locomotion and sensation in the extremities. Body as a whole
Manifestations of fractures and other organ trauma, possibly with traumatic shock. If you come late, you may also experience signs of infection and toxicity due to the cause of limb necrosis.
Hoại tử chi có thể dẫn tới nhiễm trùng và gây sốc chấn thương toàn thân
Injury site
Signs of fracture such as swelling, deformity, misalignment. Or contusion and muscle hematoma - the soft tissue in the area of direct impact lies in the arterial path.
Lower extremities
Acute ischemic syndrome of extremities resembling arterial wounds. Some of the symptoms of a fracture can be confused with those of an arterial injury, such as edema and muscle pain, decreased limb mobility, and difficulty in palpating the peripheral pulse.
2.2. Subclinical exploration of limb artery trauma Doppler ultrasound: Ultrasound has high diagnostic value and is convenient because it is an exploratory diagnosis that does not cause bleeding, however, it requires equipment and people to do echocardiography. blood. Ultrasound results show narrowing - occlusion of arteries, intravascular thrombus, associated venous injury, vascular condition outside the lesion.
Selective angiography: Angiography shows arterial disruption, accessory circulation, and pulse below the lesion. Selective angiography has very high diagnostic value but has very limited indications because it is an exploratory diagnostic method with bleeding, prolonging the duration of limb ischemia. Multi-slice computed tomography can be substituted with rendering, but is often used in some difficult arterial injuries.
Siêu âm mạch máu
3. Treatment of limb artery injury
The general rule when treating a limb artery injury is to surgically restore blood flow as soon as possible.
3.1 First aid after injury Immobilize broken bones with splints. Resuscitate against shock, give fluids - blood if necessary. Administer anticoagulation, but not when there is a risk of bleeding (VT - extensive soft tissue contusion, bleeding trauma to other organs). Accordingly, it is necessary to ensure that the bleeding is firmly stopped before using the drug. The best drug is Heparin intravenously at a dose of 100 - 200 units / kg / 24 hours. May be administered in the following ways: Mix the total dose /24 hours + 9‰ saline serum into a 20 - 50 ml syringe, divided into small intravenous doses 2 - 4 hours apart. Dilute the total dose/24 hours into a 500 ml serum vial and administer slowly over 24 hours. Doctors and nurses use electric syringes, the way to mix medicine is calculated according to the total dose of 24 hours. In addition, Calciparin can be replaced with the same total dose as Heparin. Antibiotics, tetanus prevention drugs if there are skin wounds. Refer the patient to a line that has a real capacity for vascular therapy. 3.2. Surgical treatment Anesthesia: An endotracheal anaesthetic is recommended, but regional anesthesia may be used. Anastomosis to restore arterial circulation: Fix the broken bone before anastomosis with the simplest technique to fix the fracture relatively. Posterior bones can be fixed to reduce limb ischemia. Vascular dissection, cutting the injured artery until the healthy part. Anastomosis restores arterial circulation, often requiring a reversible graft of the great saphenous vein. Suture damage to veins and nerves, if any, but limit skin closure. Open the lower scale if there are signs of swelling - muscle pain. If the fixation of the bone is not very stable, it is possible to strengthen 1 tray of fixed limb powder. Amputation: Indicated when there are symptoms of anemia that is not completely reversible.
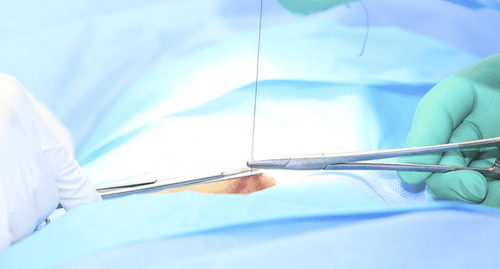
Khâu nối phục hồi lưu thông động mạch sau chấn thương
3.3.Postoperative treatment Anticoagulation: usually only maintained with intravenous Heparin within 24 hours, then replaced by oral anticoagulation (aspegic, vitamin K antagonist). In case of severe anemia, treatment with Heparin should be prolonged for several days. Heparin should be maintained longer.
Transfer to complete treatment of broken bones if necessary, after vascular stabilization.
Complications:
Wound infection: widening the wound, changing the dressing and taking good care, high risk of arterial anastomosis. Progression of muscle and soft tissue necrosis: due to severe ischemia or crushing. Need surgical removal of muscle - necrotic tissue. Arterial anastomosis: Should be ligated and treated for local infection, anticoagulation with Heparin. Consider resuming the vessel, then 2. Occlusion of the arterial anastomosis: usually due to the suture technique, it is necessary to re-operate soon. Acute renal failure: usually in the case of a very severe ischemic limb but trying to anastate the vessel, often in arterial trauma, early amputation is indicated. Injury to the arteries of the extremities is a major injury caused by traffic accidents and is mostly seen in men. Because these injuries quickly lead to anemia, it is necessary to have a timely treatment and treatment plan.
Vinmec International General Hospital is a general hospital with the function of examining and treating pathological diseases, as well as providing emergency and lifesaving surgery for many difficult cases. At Vinmec, endoscopic diagnosis and treatment with modern medical methods have been carried out with high efficiency, minimizing complications of recurrent disease. The great success is because Vinmec is always fully equipped with modern facilities, examination and treatment procedures are carried out by a team of experienced and qualified doctors that will bring about treatment results. optimal for customers.
To register for medical examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.