This is an automatically translated article.
Inflammation and arachnoid cysts are relatively rare diseases. The disease can cause increased intracranial pressure, seizures, coma, convulsions, behavioral changes, loss of balance, cognitive impairment,...1. What is arachnoiditis?
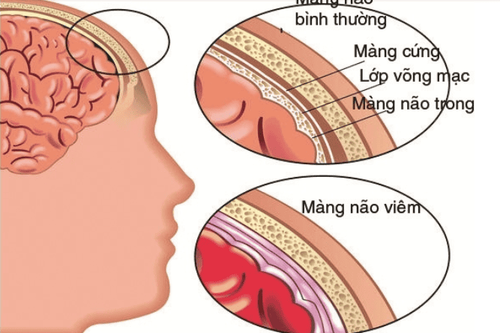
Arachnoiditis occurs due to systemic infection or bacterial infection (otitis, sinusitis), trauma, tumor, meningeal hemorrhage, ... or foreign body. Arachnoiditis can cause local increase in meningeal pressure, formation of cysts or thickened fibrous masses.
Types of arachnoiditis according to location:
Frontal arachnoiditis: Causes hemiplegia, seizures and no other pressures of increased intracranial pressure; Arachnoiditis in posterior fossa : Causes spinal cord compression syndrome, cerebrospinal fluid with albumin-cell dissociation. On myelogram, the typical picture is a rosary-shaped opacity. Sometimes, an accurate diagnosis can only be made with surgery; Arachnoiditis in the visual diagonal area: Causes visual loss, concentric narrowing of the field of view, and central opacity. Sometimes patients have progressive papilledema leading to optic nerve atrophy. Few people have symptoms of pituitary tumor ; Lumbar arachnoiditis causing adhesions: Due to repeated surgical interventions for disc herniation, injection of contrast material or drugs into the canal many times. The patient has low back pain and has cauda equina syndrome. Treatment with surgical removal of the adhesions or corticosteroid injections did not achieve the desired effect.
Viêm màng nhện xảy ra do nhiễm khuẩn toàn thân hoặc ổ nhiễm khuẩn,...
2. What are arachnoid cysts?
2.1 Concepts
Arachnoid cyst is a water cyst located in the spinal cord or brain, containing cerebrospinal fluid, which may or may not communicate with the subarachnoid space. Arachnoid cysts are often congenital, arising from the separation of the arachnoid membrane during pregnancy. Arachnoid cysts are usually benign lesions. Only about 1–5% of arachnoid cysts are associated with trauma or infection.
More than 50% of cases have arachnoid cysts located in the middle cranial fossa. In addition, arachnoid cysts can also be distributed in the pontine-cerebellar angle, suprapubic region, posterior fossa or spinal canal. The cyst is bounded by 2 layers of the inner and outer membranes (made up of leaves of arachnoid cells, endothelial cells, other glial cells,...).
Arachnoid cyst is a rare disease, accounting for only about 1% of intracranial masses. The ratio of boys to girls is 4/1, mainly with cysts on the left side. Symptoms of arachnoid cysts depend mainly on the location and size of the cyst. Mainly the following clinical symptoms:
Increased intracranial pressure: The patient has headache, nausea and vomiting, dizziness,...; Arachnoid cysts increase in size causing symptoms of compression of the cranial nerves, brain or spinal cord; Epilepsy ; Sudden clinical deterioration due to rupture of the arachnoid cyst or bleeding into the cyst (or subdural space); If the arachnoid cyst is near the mid fossa region of the brain, the patient may experience coma, convulsions, hearing and vision disturbances, behavioral changes, developmental delay, inability to control movement, cognitive decline, loss of balance,...

Nang màng nhện là một nang nước nằm trong tủy sống hoặc não, có chứa dịch não tủy
2.2 Diagnosis and treatment
Methods used to diagnose arachnoid cysts include:
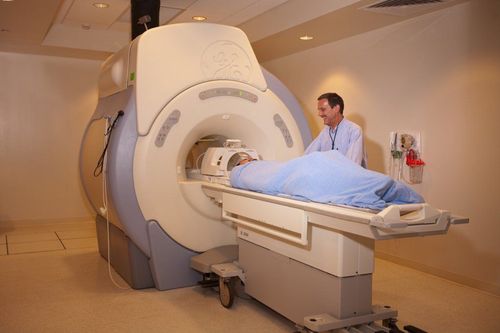
Diagnosis of arachnoid cysts based on clinical symptoms; Tests: Blood count, blood sugar, liver - kidney function, electrolytes,...; Cerebrospinal fluid test; MRI scan of the spine. Regarding the treatment method, if the arachnoid cyst has no symptoms or complications, it may not need to be treated, but only need to periodically monitor the progress of the cyst to intervene when necessary. Currently, there is no cure for cystic atrophy, only surgical removal of the cyst. Depending on the location and size of the arachnoid cyst, surgery may or may not be required. There may also be no surgery, but only intervention to open the cysts so that the fluid drains out and mixes with the cerebrospinal fluid. Timely diagnosis of inflammation and arachnoid cysts plays an important role in giving appropriate treatment to the patient, helping to better protect the patient's health.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, a system of modern equipment and technology. The hospital provides comprehensive and professional medical examination, consultation and treatment services, with a civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space. Customers when choosing to perform tests here can be completely assured of the accuracy of test results.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.