This is an automatically translated article.
There are many techniques to examine the spine including: conventional X-ray, CT, MRI... Each technique has its own advantages and disadvantages. However, radiographs of the spine are now considered the most basic indication in many distinct clinical settings.
1. Anatomy of the human spine
Human spine anatomy includes 7 cervical vertebrae (C1-C7), 12 thoracic vertebrae (D1-D12), 5 dorsal vertebrae (L1-L5), 5 sacral vertebrae (S1-S5), 4 coccyx vertebrae.
Each vertebral segment will have different shapes and characteristics, but the general structure of each vertebra will basically include structures such as vertebral body, pedicle, transverse process, spinous process, joint apex...
To survey the spine in detail and comprehensively, it is necessary to take X-rays of the spine in many different positions, including:
Cervical spine including upright, inclined, oblique, open-mouthed positions, flexion and flexion and each position has different advantages:
The remaining vertebrae (thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccyx) usually X-ray the spine is basically straight and tilted.
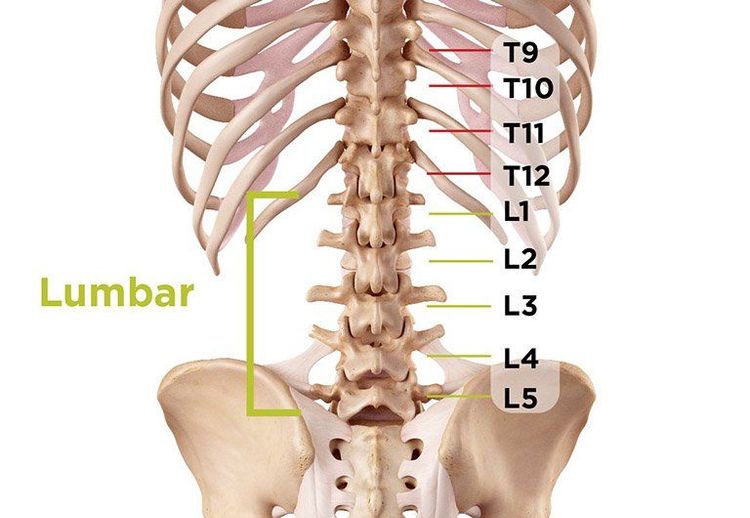
Hình ảnh giải phẫu cột sống thắt lưng
2. Some common diseases when taking X-rays of the spine
X-ray of the spine is the first indicated imaging modality to evaluate abnormalities in the spine. Through imaging of the spine on X-ray films, doctors can diagnose some of the following diseases:
X-ray of cervical vertebrae, thoracic vertebrae, lumbar vertebrae, sacral vertebrae, coccyx in various positions straight, side view:
Detect diseases such as spondylolisthesis, vertebral body rupture, vertebrae slip or collapse... Congenital malformations such as kyphosis scoliosis, double spines, vertebral body adhesions... Some other diseases such as primary or metastatic tumor, spinal tuberculosis... X-ray of the cervical spine is 3⁄4 slanted: Oblique is the position when the X-ray is projected at a 45-degree angle relative to the vertical plane of the spine. Spine. This special position helps to detect graft-hole narrowing when the patient has clinical signs of nerve root compression or vertebral artery compression.
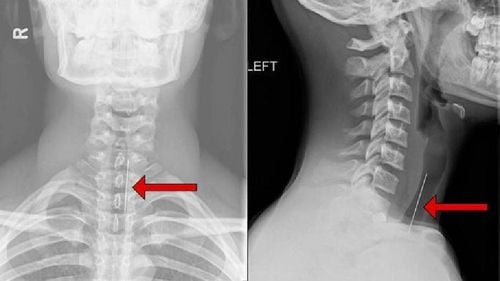
X-ray of the cervical spine in the open-mouth position: A special technique to help diagnose fractures of the periodontal process in cervical vertebrae C1 and C2.

Thoái hóa cột sống là bệnh lý thường gặp về cột sống
3. Indications of X-ray method of spine
Indications for X-ray of the spine are very diverse, the most common are patients with pain in the corresponding spine in common diseases such as: spondylolisthesis or abnormally changed shape of the spine... Indications for X-rays of the spine include:
3.1. Spine deformity
Curvature of the spine: On X-ray film of the spine in straight posture, the image of the spine is misaligned, some vertebrae are rotated or the vertebral body is deformed in a wedge shape; Spinal kyphosis: Usually detected on X-ray of the spine in the inclined position when the spine curve changes and protrudes posteriorly; Spinal deformities due to transition disorders: Some abnormalities can be detected such as 8 cervical vertebrae, and ribs at C7 (causing brachial nerve compression), lumbar vertebrae D12, lumbar spondylolisthesis. S1 or L5 cochlear... Double spine: Usually due to incomplete ossification process, common in vertebra L5 or S1 when the image of the spinous process splits in two. Open waist: The same cause as double fracture, due to incomplete ossification of the posterior arch of the vertebrae, common in 2 vertebrae L4 and L5. On the X-ray film of the spine in the 3/4 position, there is a characteristic image of "broken dog's neck". This disease often causes complications of spondylolisthesis. Congenital fusion of two vertebral bodies: To distinguish secondary vertebral body adhesions (due to tuberculosis), congenital fusion of two vertebral bodies in both the intervertebral disc space and the posterior arch, and at the same time, the spine is not kyphosis due to the absence of rupture. destroy the living body.
Gù đốt sống là một dạng dị dạng cột sống
3.2. Degenerative spine disease
Osteoarthritis is a very common degenerative joint disease, especially in people over 40 years old. Mechanism of spondylolisthesis, the fibrous capsule around the disc degenerates over time, so the disc bulges and protrudes outward, the ligaments are stretched and bone spurs form due to calcification around the disc. The features of degeneration on spine radiographs include:
The disc fissure changes little at first but gradually narrows due to subchondral bone degeneration; Bone spurs in vertebral bodies, common in cervical and lumbar vertebrae; Bone bridge: This phenomenon occurs when two bone spurs close together stick together; Subchondral sclerosis with dark opacities of the spine at the superior and inferior edges of the vertebral body.
3.3. Disc herniation
Herniated disc is a disease that occurs due to herniation of the nucleus pulposus due to tearing of the outer fibrous capsule and causing compression of the spinal canal and nerve roots. The disease is common in the lumbar or cervical spine but is rare in the thoracic spine.
C Conventional X-ray of the spine often difficult to detect disc herniation. At that time, the patient may be assigned to take an X-ray of the nerve root envelope with the following images:
Central disc herniation: Image of complete contrast-enhanced amputation at the level of the degenerated disc; Displaced disc herniation: X-ray of the nerve root capsule in the 3⁄4 position shows a concave contrast-enhanced column of contrast at the location of the herniation.
Thoát vị đĩa đệm gây ảnh hưởng đến cuộc sống sinh hoạt của người bệnh
3.4. Spinal cord injury
Spinal trauma can be detected when taking X-ray of the spine, often caused by traffic accidents, daily life or occupational accidents... The recorded spine image has the following characteristics:
Body rupture vertebral column: Transverse fracture line of vertebral body; Collapse of the vertebral body: The height of the vertebral body decreases, collapses. Collapsed vertebrae are often more dense than normal, most of the time, the body is wedge-shaped; Sliding vertebral body: Can slide forward, backward or sideways. Spondylolisthesis can cause dangerous complications such as compression or complete severing of the spinal cord; Other special cases are common such as: fracture of C2 periodontal process, fracture of transverse process in lumbar vertebrae, fracture of posterior arch and fracture of spinous process less common.
3.5. Tuberculosis of the spine
Of bone and joint tuberculosis, spinal tuberculosis accounts for the highest rate, most commonly found in vertebrae D9-D10 and L1-L2. The image of the spine in this pathology usually goes through 3 stages:
Early stage: Disc stenosis can be seen both on radiographs of the straight and inclined spine. Initially, the disc space may be narrow, so it should be compared with adjacent vertebrae. Full-blown stage: Disc stenosis with images of the spine being destroyed by tuberculosis attacking the vertebral body. The vertebral body has features of rough edges, wedge-shaped and deformed physiological curves (kyphosis); Recovery phase and sequelae: Tuberculosis of the spine causes vertebrae to stick together, loss of disc space.
Hình ảnh bệnh lao cột sống
3.6. Ankylosing spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis usually begins with sacroiliac arthritis, then progresses to hypoattenuating vertebrae. About 3 years later, the disease progressed to a new stage, the ligaments were calcified, and the spine joints were attached. The image of the spine when the anterior longitudinal, interspinous, and lateral ligaments are calcified is often the "bamboo spine" or "train track".
X-ray of the spine is very important to help doctors accurately diagnose diseases related to the spine, the solid and flexible fulcrum of the body. However, patients should inform their doctor about their health status, so that the doctor can understand and have clear indications before conducting a spine X-ray, to avoid unnecessary consequences. this.
Vinmec International General Hospital has applied X-ray technique in examination and diagnosis of many musculoskeletal diseases. X-ray technique at Vinmec is carried out methodically and according to standard procedures by a team of highly qualified medical professionals, modern machinery system, thus giving accurate results, making a significant contribution to diagnosis and staging of the disease.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.