This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by MSc Nguyen Vinh Toan - Ear - Nose - Throat Doctor, Interspecialty Department - Vinmec Times City International HospitalChronic otitis media is a persistent infection in the lining of the middle ear, it is caused by an ongoing inflammatory response in the middle ear with granulation tissue formation and is often associated with an unresolved bacterial infection. or resistant bacteria.
1. Chronic otitis media is divided into two main types
+ Chronic purulent otitis media
+ Otitis media with Cholesteatoma
When otitis media does not respond to medical treatment with local and systemic methods, surgery with the aim of making the ear dry, avoid complications and preserve the structure and function of the ear.
1.1 Indications for surgery include Perforation lasting more than 6 weeks
Ear discharge persisting for more than 6 weeks despite adequate medical therapy Having cholesteatoma Evidence of chronic mastoiditis Conduction hearing loss Principle The basis of surgery in chronic otitis media is to clean the lesions and restore hearing.

2. Common surgical methods for chronic otitis media
2.1 Surgery to patch the tympanic membrane (Myringoplasty) The commonly used materials for tympanic membrane repair are autologous materials such as temporal muscle fascia, tarsal cartilage, and coronal cartilage.
2.2 Tympanoplasty combined with Tympanoplasty 2.3 Mastoidectomy Cortical Mastoidectomy is surgery to remove the outer part of the mastoid bone and clean out the mastoid cells. cells in mastoid sinus, enlarged striatum, striatum
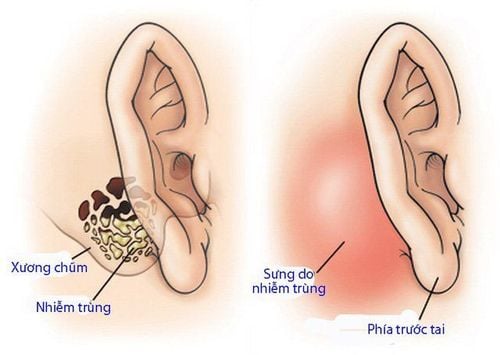
Vị trí xương chũm nhiễm trùng
Canal wall up mastoidectomy is surgery to remove mastoid cells, keep the posterior wall of the ear canal, and access the middle ear through the facial recess (short incus of the incus, nerves). atrial cord, cord VII) cleans lesions, especially cholesteatoma, preserves the structure of the ear canal wall to prevent potential complications that may be caused by surgery. Mastoidectomy) Includes modified mastoidectomy: Preserve the fibula and the remaining tympanic membrane to restore hearing. The classic mastoidectomy is to remove all the ossicles, tympanic membrane, and mastoid cells to form a common space, occlusion of the eustachian tube is usually applied when there is a widespread Cholesteatoma mass.
3. Postoperative care for chronic otitis media
In cases of simple tympanic membrane patching, you are usually discharged from the hospital early in the day or after one day, cleaning the incision daily with an antiseptic, the insertion materials in the ear canal are usually removed after 7-10 days. If the ear canal is repaired immediately, it is necessary to avoid water entering the ear. For radical surgery, it is advisable to periodically visit to detect recurrent cholesteatoma, clean the surgical cavity to avoid the accumulation of scales that cause infection.
Người có bệnh lý về tai nên đến gặp bác sĩ chuyên khoa trong thời gian sớm
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.
SEE ALSO:
Complications of otitis media with purulent discharge: When should surgery be performed? Fever after mastoid otitis media is okay? Why is otitis media easy to recur?