This is an automatically translated article.
Articles by Dr. Dr. Truong Ngoc Hai - Resuscitation Doctor - Emergency Resuscitation Department - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
In 2019, the American Association for Hemodialysis (ASFA) issued the 8th recommendation to significantly expand the indications for TPE in many critical conditions such as sepsis with multi-organ failure, acute liver failure, pancreatitis acute elevation of triglycerides, poisoning...[52]. These diseases are mostly rare, so clinical trials evaluating the effectiveness of the indications are still limited. Pathological differences lead to many centers having specific indications for which efficacy has not yet been demonstrated.
In addition, resuscitated patients often have hemodynamic instability, coagulation disorders, and electrolyte disturbances that can reduce the effectiveness of plasma exchange. Therefore, there is a need for more reports on the clinical indications, methods of implementation and safety of TPE in many different centers.
1. Indications for plasma exchange according to ASFA 2019
For TPE to be a reasonable choice in many dialysis techniques, at least one of the following conditions must be met [51]:
The substance to be removed is of sufficient size (>15,000 Da) for the techniques to be removed. Other, less expensive dialysis cannot be minimally effective. The substance to be eliminated has a relatively long half-life, so that elimination reduces plasma concentrations for a therapeutically significant period. The substance to be eliminated is very toxic and/or unresponsive to conventional treatment, therefore prompt removal from the body is imperative.
Hình ảnh: Các biện pháp lọc máu và chất mục tiêu
*Khối lượng phân tử đơn vị dalton, “Nguồn: Williams, 2014” [76]
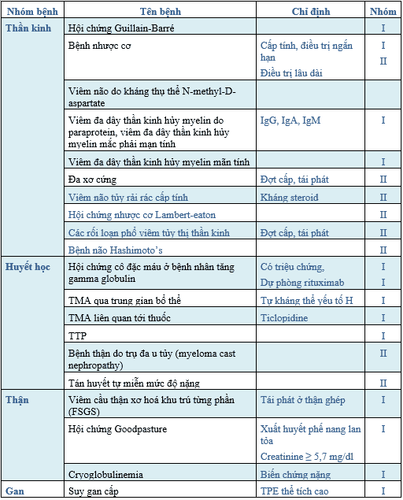
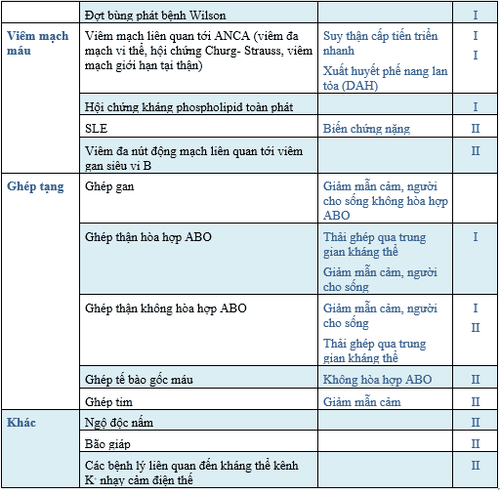
Năm 1986, ASFA đã xuất bản hướng dẫn thực hành đầu tiên về sử dụng phương pháp phân tách máu trên ấn bản đặc biệt của Journal of Clinical Apheresis. Kể từ 2007, các hướng dẫn này được cập nhật mỗi ba năm dựa trên việc xem xét một cách kỹ lưỡng, kịp thời các bằng chứng mới nhất về sử dụng phân tách máu trên lâm sàng với ấn bản gần đây nhất (lần thứ 8) được xuất bản vào năm 2019. Trong phiên bản này, ASFA vẫn tiếp tục duy trì 84 bệnh lý, mở rộng với 157 chỉ định phân thành bốn nhóm trong khuyến cáo về chỉ định [52].
Nhóm I: TPE là liệu pháp điều trị đầu tay, có thể sử dụng đơn độc hoặc phối hợp với các biện pháp điều trị khác. Nhóm II: TPE là liệu pháp điều trị thứ hai, có thể sử dụng đơn độc hoặc phối hợp với các biện pháp điều trị khác. Nhóm III: Vai trò của TPE chưa rõ ràng. Quyết định điều trị được cân nhắc trên từng trường hợp cụ thể. Nhóm IV: Những bệnh lý mà bằng chứng công bố cho thấy hoặc gợi ý TPE có hại. Ở các khoa HSTC, thường áp dụng các chỉ định TPE thuộc nhóm I, II theo khuyến cáo
TTP
TTP là bệnh lý gây huyết khối toàn thân ảnh hưởng chủ yếu các mạch nhỏ. Nguyên nhân chính là do hình thành các kháng thể gây thiếu hụt trầm trọng ADAMTS13 (<10%), vốn duy trì sự phân phối bình thường các multimer von Willebrand. Phần nhỏ còn lại đột biến gen làm suy giảm chức năng của ADAMTS13. Ban đầu TTP được định nghĩa bởi ngũ chứng: giảm tiểu cầu, thiếu máu tán huyết vi mạch, rối loạn tri giác, suy thận và sốt. Tuy nhiên, cần nghĩ ngay đến chẩn đoán này nếu lâm sàng ghi nhận giảm tiểu cầu không rõ nguyên nhân và thiếu máu tán huyết vi mạch. Thang điểm PLASMIC hỗ trợ tiên đoán thiếu hụt ADAMTS13 nghiêm trọng gồm các biến số: tiểu cầu <30 ×109/L, creatinine <2,0 mg/dL, INR <1,5, MCV <90 fL [11]. Tỉ lệ tử vong rất cao khoảng 90% nếu không được điều trị do đó nên điều trị ngay trong 4-8 giờ khi nghi ngờ TTP và các nguyên nhân gây tán huyết vi mạch khác có khả năng thấp[62]. Nếu TPE không có sẵn lập tức thì có thể truyền FFP 25-30 ml/kg nếu dung nạp. Corticosteroid có thể được sử dụng để hỗ trợ điều trị . Rituximab có thể sử dụng để điều trị TTP kháng trị hoặc tái phát. Caplacizumab, N-acetylcysteine và ADAMTS13 tái tổ hợp là các điều trị bổ sung đầy hứa hẹn. Bệnh nhân TTP có khuynh hướng tạo huyết khối hơn là xuất huyết, nếu có chỉ xuất huyết da niêm do vậy chỉ nên truyền tiểu cầu nếu có xuất huyết đe dọa tính mạng . Đối với TTP bẩm sinh, đặc trưng bởi sự suy giảm hoạt động của ADAMTS13 và không tồn tại kháng thể, việc điều trị chỉ đơn giản là truyền FFP 10-15mL/kg hoặc kết tủa lạnh (chứa ADAMTS13). TPE nên được thực hiện mỗi ngày cho đến khi số lượng tiểu cầu >150×109/L, và LDH bình thường trong 2-3 ngày liên tiếp [52].
Suy gan cấp
Suy gan cấp có thể xảy ra ở gan bình thường hoặc trên nền bệnh gan mãn tính. Hai nguyên nhân phổ biến nhất là ngộ độc acetaminophen và viêm gan siêu vi. Các nguyên nhân khác gồm viêm gan tự miễn, bệnh nặng, hội chứng Budd-Chiari cấp tính, sốc nhiệt... Tỉ lệ tử vong trong suy gan cấp là 50-90% do rối loạn chuyển hóa cấp tính, bệnh não gan và rối loạn đông máu nặng. Tỉ lệ tự phục hồi sau suy gan cấp phụ thuộc vào nguyên nhân: tỷ lệ phục hồi cao trong gan nhiễm mỡ thai kỳ, ngộ độc acetaminophen và viêm gan siêu vi A; viêm gan siêu vi B có tiên lượng trung bình; các thuốc khác và chưa rõ căn nguyên tự hồi phục ít hơn 20% [68].
Đối với suy gan cấp có khả năng tự phục hồi thấp, điều trị tiêu chuẩn vẫn là hỗ trợ bắc cầu chờ ghép gan. Nếu gan ghép không có sẵn, các hệ thống hỗ trợ gan có thể được sử dụng tuy nhiên hiện vẫn chưa chứng minh làm cải thiện sống còn ở nhóm bệnh nhân này. Hệ thống hỗ trợ gan bao gồm các hệ thống dựa trên tế bào và không dựa trên tế bào. Nhiều hệ thống hỗ trợ gan dựa trên tế bào đã được thử nghiệm lâm sàng ví dụ như gan nhân tạo, hệ thống hỗ trợ gan ngoài cơ thể, thiết bị hỗ trợ gan dạng mô-đun (MELS) [41]. Các liệu pháp không dựa trên tế bào bao gồm TPE, thẩm tách albumin, liệu pháp trao đổi huyết tương chọn lọc, hệ thống tái tuần hoàn hấp phụ phân tử (molecular adsorbents recirculation system (MARS)) được FDA chấp nhận sử dụng trong điều trị quá liều và ngộ độc thuốc [32].
Trong suy gan tối cấp, TPE giúp loại bỏ các độc tố gắn kết với albumin và không liên kết như axit amin thơm, amoniac, nội độc tố, indol, mercaptan, phenol được cho là gây ra hôn mê gan, hội chứng tăng động, giảm kháng lực mạch hệ thống và lưu lượng máu não. Ngoài ra, TPE loại bỏ các chất trung gian gây viêm, ổn định tình trạng đông máu nhờ bổ sung các yếu tố đông máu và loại bỏ các yếu tố kích hoạt tăng đông như chất hoạt hóa plasminogen mô, fibrin và sản phẩm thoái giáng fibrinogen. Một RCT trên bệnh nhân suy gan cấp bị bệnh não gan cho thấy MARS và TPE+MARS cho hiệu quả lâm sàng tương đương. Tuy nhiên, TPE + MARS làm giảm mức bilirubin toàn phần trong huyết thanh hiệu quả hơn [31]. Tương tự, phối hợp TPE, lọc hấp phụ và lọc máu liên tục giúp loại bỏ hiệu quả các chất chuyển hóa, đặc biệt là bilirubin, hơn các kết hợp khác không có TPE [43]. Nghiên cứu tiến cứu đa trung tâm, đối chứng ngẫu nhiên của Larsen (2016) gồm 183 bệnh nhân từ 3 trung tâm ghép gan lớn (London, Helsinki, Copenhagen) đánh giá hiệu quả của TPE lưu lượng cao (TPE-HV) trong điều trị suy gan cấp. Nghiên cứu cho cải thiện sống còn không ghép gan, 59% so với 48% ở nhóm điều trị tiêu chuẩn (p <0,001) khi TPE-HV với thể tích 15% cân nặng (8-12L) mỗi ngày trong 3 ngày. TPE-HV giúp cải thiện huyết động, giảm đáp ứng viêm với tỉ lệ biến chứng tương đương so với nhóm điều trị nội khoa chuẩn. Tuy nhiên, cần lưu ý rằng TPE-HV trước ghép gan không cải thiện sống sót so với những bệnh nhân được điều trị chuẩn [40].
Nhiễm trùng huyết
Nhiễm trùng huyết là rối loạn đáp ứng viêm toàn thân đối với nhiễm trùng trong đó có nhiều hóa chất trung gian gây rối loạn chức năng đa cơ quan (MODS), rối loạn đông máu nội mạch lan tỏa (DIC), và rối loạn điều hòa miễn dịch. Theo thống kê tại Mỹ từ năm 2004-2009, tỷ lệ nhiễm trùng huyết là 300-1031/100000/năm với tỷ lệ tử vong 15-30%. Các yếu tố nguy cơ của nhiễm trùng huyết bao gồm tuổi cao, bệnh lý mãn tính, suy giảm miễn dịch, dụng cụ xâm lấn [19]. Cytokine và các chất trung gian khác như yếu tố hoại tử u (TNF), TGF-β interleukin, leukotrienes, prostaglandin, nội độc tố tham gia đáp ứng viêm trong nhiễm trùng huyết. Rối loạn đông máu, tắc vi mạch và thiếu máu mô như có vẻ liên quan với sự mất sự cân bằng của ADAMTS13 và các multimer von Willebrand [29].
Điều trị chủ yếu là hỗ trợ huyết động (bù dịch, vận mạch) và hô hấp, kiểm soát ổ nhiễm, sử dụng kháng sinh. Các phương pháp điều trị khác bao gồm corticosteroid, IVIG, thuốc kháng đông và thuốc điều hòa miễn dịch chưa thật sự chứng minh được hiệu quả điều trị [18]. TPE cho thấy cải thiện chức năng các cơ quan bằng cách loại bỏ hóa chất trung gian gây viêm và chống tiêu sợi huyết, bổ sung các protein chống đông và ADAMTS13. Một số gợi ý điều trị sớm mang lại hiệu quả hơn và giúp ổn định huyết động. Các nghiên cứu quan sát ghi nhận tỷ lệ sống còn ở nhóm TPE là 60-87% so với đối chứng dự đoán hoặc lịch sử từ 20-40% [52]. Nghiên cứu Fortenberry trên đối tượng trẻ em, tiến hành phân tích đa biến ghi nhận TPE làm giảm tỷ lệ tử vong 28 ngày bằng với OR = 0,45 với p = 0,02 [20]. Mặc dù ghi nhận những dấu hiệu tích cực, khá ít RCT đánh giá vai trò của TPE trên đối tượng nhiễm trùng huyết, đa phần gặp trở ngại trong việc thu nhận đối tượng vào nghiên cứu, thiết kế có độ tin cậy thấp và do vậy còn rất khó có thể đưa ra một khuyến cáo mạnh về sử dụng TPE như là liệu pháp bổ sung trên nhóm đối tượng này [60].
2. TPE designations group I, II according to ASFA 2019
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
TÀI LIỆU THAM KHẢO
Tiếng Việt:
Hoàng Đức Chuyên (2012), Nghiên cứu đặc điểm lâm sàng và điều trị viêm tụy cấp tăng triglyceride, Luận văn Thạc sĩ Y học, Trường Đại Học Y Hà Nội. Nguyễn Minh Đức (2017), Nghiên cứu đặc điểm lâm sàng, chẩn đoán điện và kết quả điều trị hội chứng Guillain – barré bằng phương pháp thay huyết tương , Luận văn Tiến sĩ Y học, Viện Nghiên Cứu Khoa Học Y Dược Lâm Sàng 108. Huỳnh Thị Thu Hiền (2020), "Liệu pháp thay huyết tương ở bệnh nhân nặng", Tạp chí Y Học Thành Phố Hồ Chí Minh , 24 (2), tr. 202-206. Thông Võ Duy (2021), “Tăng trirelycerie máu rất nặng ở bệnh nhân viêm tụy cấp: yếu tố nguy cơ và kết cục lâm sàng”, Tạp chí Y học Việt Nam , 2, tr. 49-55. Lê Quang Thuận (2017), Nghiên cứu hiệu quả điều trị viêm gan nhiễm độc cấp nặng bằng biện pháp thay huyết tương tích cực , Luận văn Tiến sĩ Y học, Viện Nghiên Cứu Khoa Học Y Dược Lâm Sàng 108. Võ Thị Đoan Thục (2020), Nghiên cứu hiệu quả của thay huyết tương trong điều trị viêm tụy cấp nặng do tăng triglyceride máu tại Bệnh viện Chợ Rẫy , Luận văn Chuyên khoa 2, Đại Học Y Dược Huế. Tiếng anh:
7. Ahmed S., Kaplan A. (2020), "Therapeutic Plasma Exchange Using Membrane Plasma Separation", Clin J Am Soc Nephrol , 15 (9), pp. 1364-1370.
8. Apter A. J., Kaplan A. A. (1992), "An approach to immunologic reactions associated with plasma exchange", J Allergy Clin Immunol , 90 (1), pp. 119-24.
9. Basic-Jukic Nikolina, Kes Petar, Glavas-Boras Snjezana, et al. (2005), "Complications of Therapeutic Plasma Exchange: Experience With 4857 Treatments". Therapeutic apheresis and dialysis : official peer-reviewed journal of the International Society for Apheresis, the Japanese Society for Apheresis, The Japanese Society for Dialysis Therapy , 9, pp. 391-395.
10. Beech C., Kumar D., Hendrickson J., et al. (2019), "Cryoglobulinemia as a Possible Primer for TRALI: Report of a Case". Lab Med, 50 (3), pp. 313-319 .
11. Bendapudi P. K., Hurwitz S., Fry A., Marques M. B., et al. (2017), "Derivation and external validation of the PLASMIC score for rapid assessment of adults with thrombotic microangiopathies: a cohort study", Lancet Haematol , 4 (4), pp. 157-164.
12. Calça Rita, Gaspar Ana, Santos Afonso, et al. (2020), "Therapeutic plasma exchange in patients in a portuguese ICU", Portuguese Journal of Nephrology & Hypertension , 34 (1), pp. 21-25.
13. Clebone A. (2019), "Transfusion reactions and cognitive aids". Curr Opin Anaesthesiol , 32 (2), pp. 242-246.
14. Colling M., Sun L., Upadhyay V., et al. (2020), "Deaths and complications associated with the management of acute immune thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura", Transfusion , 60 (4), pp. 841-846.
15. Cordoba J. P., Larrarte C., Medina M. C. (2015), "Experience in therapeutic plasma exchange by membrane filtration at an academic center in Colombia: Registry of the first 500 sessions", J Clin Apher , 30 (6), pp. 347-52.
16. Daga Ruiz D., Fonseca San Miguel F., González de Molina F. J., et al. (2017), "Plasmapheresis and other extracorporeal filtration techniques in critical patients", Medicina Intensiva , 41 (3), pp. 174-187.
17. Erkurt M. A., Sarici A., Kuku I., et al. (2021), "The effect of therapeutic plasma exchange on management of HELLP Syndrome: The report of 47 patients", Transfus Apher Sci , 60 (5), pp. 1-3.
18. Evans L., Rhodes A., Alhazzani W., et al. (2021), "Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021 ", Intensive Care Med , 47 (11), pp. 1181-1247.
19. Fleischmann C., Scherag A., Adhikari N. K., et al. (2016), "Assessment of Global Incidence and Mortality of Hospital-treated Sepsis. Current Estimates and Limitations", Am J Respir Crit Care Med , 193 (3), pp. 259-72.
20. Fortenberry J. D., Nguyen T., Grunwell J. R, et al. (2019), "Therapeutic Plasma Exchange in Children With Thrombocytopenia-Associated Multiple Organ Failure: The Thrombocytopenia-Associated Multiple Organ Failure Network Prospective Experience", Crit Care Med , 47 (3), pp. 173-181.
21. Freireich E. J. (2011), "Leukocyte transfusion and the development of the continuous-flow blood cell separator", Transfus Med Rev , 25 (4), pp. 344-50.
22. Gajic O, Rana R., Winters J. L, et al. (2007), "Transfusion-related acute lung injury in the critically ill: prospective nested case-control study" . Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 176 (9), pp. 886-891.
23. Gashti C. N., Andreoli D. C., Patel D. (2018), "Membrane-based therapeutic plasma exchange (mTPE): Technical and clinical experience", J Clin Apher , 33 (1), pp. 38-45.
24. Guyton (2016), Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology 13th , W B Saunders, Philadelphia, chapter 25, pp. 307-308 .
25. Hafer C., Kielstein J. T. (2017), "Pro: High dose of therapeutic plasma exchange-mind the gap!", Nephrol Dial Transplant , 32 (9), pp. 1457-1460.
26. Hafer C., Golla P., Gericke M., et al. (2016), "Membrane versus centrifuge-based therapeutic plasma exchange: a randomized prospective crossover study", Int Urol Nephrol , 48 (1), pp. 133-138 .
27. Hisamichi Mikako, Kawarazaki Hiroo, Oroku Masato, et al. (2016), "Risk factors for allergic reaction at initial therapeutic plasma exchange in a single-center study: beware of high rates of severe allergic reaction", Renal Replacement Therapy , 2 (1), pp. 2-5.
28. Horvatits T., Drolz A., Trauner M., et al. (2019), "Liver Injury and Failure in Critical Illness", Hepatology , 70 (6), pp. 2204-2215.
29. Hotchkiss Richard S., Moldawer Lyle L., Opal Steven M., Reinhart Konrad, Turnbull Isaiah R., et al. (2016), "Sepsis and septic shock", Nature Reviews Disease Primers , 2 (1), pp. 1-21.
30. Hu Lunyang, Wang Baoli, Jiang Yong, et al. (2021), "Risk factors for transfusion-related acute lung injury". Respiratory Care , pp. 08829.
31. Huang Y. K., Tan D. M., Xie Y. T., et al. (2012), "Randomized controlled study of plasma exchange combined with molecular adsorbent re-circulating system for the treatment of liver failure complicated with hepatic encephalopathy", Hepatogastroenterology , 59 (117), pp. 1323-1326.
32. Kandiah P. A., Olson J. C., Subramanian R. M. (2016), "Emerging strategies for the treatment of patients with acute hepatic failure", Curr Opin Crit Care , 22 (2), pp. 142-151.
33. Kaplan A. (2012), "Complications of apheresis", Semin Dial , 25 (2), pp. 152-158.
34. Kaplan A. A. (2013), "Therapeutic plasma exchange: a technical and operational review ", J Clin Apher , 28 (1), pp. 3-10.
35. Kes P., Janssens M. E., Bašić-Jukić N., Kljak M. (2016), "A randomized crossover study comparing membrane and centrifugal therapeutic plasma exchange procedures, Transfusion , 56 (12), pp. 3065-3072.
36. Khandelwal P., Thomas C. C., Rathi B. S., Hari P., Tiwari A. N., et al. (2019), "Membrane-filtration based plasma exchanges for atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome: Audit of efficacy and safety", J Clin Apher, 34 (5), pp. 555-562.
37. Kuldanek S. A., Kelher M., Silliman C. (2019), "Risk factors, management and prevention of transfusion-related acute lung injury: a comprehensive update", Expert Rev Hematol , 12 (9), pp. 773-785.
38. Kundrapu S., Datla S., Griffin V., Maitta R. W. (2019), "Adverse events during apheresis: A 10-year experience at a tertiary academic medical center", J Clin Apher , 34 (5), pp. 528-536.
39. Lahmer T., Messer M., Schnappauf C., Rasch S., Fekecs L., et al. (2017), "Impact of Therapeutic Plasma Exchange on Hemodynamic Parameters in Medical Intensive Care Unit Patients: An Observational Study", Artif Organs , 41 (2), pp. 204-209.
40. Larsen F. S., Schmidt L. E., Bernsmeier C., Rasmussen A., Isoniemi H., et al. (2016), "High-volume plasma exchange in patients with acute liver failure: An open randomised controlled trial" , J Hepatol , 64 (1), pp. 69-78.
41. Lee K. C., Stadlbauer V., Jalan R. (2016), "Extracorporeal liver support devices for listed patients", Liver Transpl , 22 (6), pp. 839-48.
42. Lemaire A., Parquet N., Galicier L., Boutboul D., Bertinchamp R., et al. (2017), "Plasma exchange in the intensive care unit: Technical aspects and complications", J Clin Apher , 32 (6), pp. 405-412.
43. Li Mao-Qin, Ti Jun-Xiang, Zhu Yun-Hang, et al. (2014), "Combined use of non-biological artificial liver treatments for patients with acute liver failure complicated by multiple organ dysfunction syndrome", World journal of emergency medicine , 5, pp. 214-217.
44. Lockwood C. M., Rees A. J., Pearson T. A., et al. (1976), "Immunosuppression and plasma-exchange in the treatment of Goodpasture's syndrome", Lancet , 1 (7962), pp. 711-5.
45. Mateen Farrah, Gastineau Dennis (2008), "Transfusion Related Acute Lung Injury (TRALI) after Plasma Exchange in Myasthenic Crisis". Neurocritical care , 8, pp. 280-282.
46. Meyer D. E., Reynolds J. W., Hobbs R., et al. (2018), "The Incidence of Transfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury at a Large, Urban Tertiary Medical Center: A Decade's Experience". Anesth Analg , 127 (2), pp. 444-449.
47. Miklaszewska M., Korohoda P., Zachwieja K., et al. (2017), "Filter Size Not the Anticoagulation Method is the Decisive Factor in Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy Circuit Survival", Kidney Blood Press Res , 42 (2), pp. 327-337.
48. Millar Jonathan E., Fanning Jonathon P., McDonald Charles I., et al. (2016), "The inflammatory response to extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO): a review of the pathophysiology", Critical Care , 20 (1), pp. 387.
49. Mokrzycki M. H., Balogun R. A. (2011), "Therapeutic apheresis: a review of complications and recommendations for prevention and management", J Clin Apher , 26 (5), pp. 243-8.
50. Mortzell Henriksson M., Newman E., Witt V., et al. (2016), "Adverse events in apheresis: An update of the WAA registry data", Transfus Apher Sci , 54 (1), pp. 2-15.
51. Noiri Eisei (2014), “Complication”, The Concise Manual of Apheresis Therapy , Springer, Japan, chapter 17, pp. 177-224.
52. Padmanabhan A., Connelly-Smith L., Aqui N., Balogun R. A., Klingel R., et al. (2019), "Guidelines on the Use of Therapeutic Apheresis in Clinical Practice - Evidence-Based Approach from the Writing Committee of the American Society for Apheresis: The Eighth Special Issue", J Clin Apher , 34 (3), pp. 171-354.
53. Palma-Garcia L., Velasquez-Rimachi V., Pezo-Pezo A., Roig J., Perez-Villegas J. (2018), "Therapeutic plasma exchange: Experience in a third level hospital, 2013-2016, Lima (Peru)" . J Clin Apher , 33 (4), pp. 480-485.
54. Paton E., Baldwin I. C. (2014), "Plasma exchange in the intensive care unit: a 10 year retrospective audit", Aust Crit Care , 27 (3), pp. 139-144.
55. Paugam-Burtz C., Levesque E., Louvet A., Thabut D., Amathieu R., et al. (2020), "Management of liver failure in general intensive care unit", Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med , 39 (1), pp. 143-161.
56. Puppe B., Kingdon E. J. (2014), "Membrane and centrifugal therapeutic plasma exchange: practical difficulties in anticoagulating the extracorporeal circuit", Clinical kidney journal , 7 (2), pp. 201-205.
57. Rajagopal K. (2019), "Left Ventricular Distension in Veno-arterial Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: From Mechanics to Therapies", Asaio j , 65 (1), pp. 1-10.
58. Ranganathan Lakshmi, Menon Rema, Ramakrishnan Nagarajan, et al (2019), "Therapeutic Plasma Exchange Practices in Intensive Care Unit", Indian journal of critical care medicine , 23 (7), pp. 336-338.
59. Reeves H. M., Winters J. L. (2014), "The mechanisms of action of plasma exchange", Br J Haematol , 164 (3), pp. 342-51. .
60. Rimmer Emily, Houston Brett L., Kumar Anand, Abou-Setta Ahmed M., Friesen Carol, et al. (2014), "The efficacy and safety of plasma exchange in patients with sepsis and septic shock: a systematic review and meta-analysis", Critical care , 18 (6), pp. 699-699.
61. Roubinian N. (2018), "TACO and TRALI: biology, risk factors, and prevention strategies", Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program , 2018 (1), pp. 585-594.
62. Sarode Ravi, Bandarenko Nick, Brecher Mark E., Kiss Joseph E., Marques Marisa B., et al. (2014), "Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: 2012 American Society for Apheresis (ASFA) consensus conference on classification, diagnosis, management, and future research", Journal of Clinical Apheresis , 29 (3), pp. 148-167.
63. Schmidt J. J., Asper F., Einecke G., et al. (2018), "Therapeutic plasma exchange in a tertiary care center: 185 patients undergoing 912 treatments - a one-year retrospective analysis", BMC Nephrol , 19 (1), pp. 12.
64. Schwab P. J., Fahey J. L. (1960), "Treatment of Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia by plasmapheresis", N Engl J Med , 263, pp. 574-9.
65. Sengul Samanci N., Ayer M., Gursu M., et al. (2014), "Patients treated with therapeutic plasma exchange: a single center experience"., Transfus Apher Sci , 51 (3), pp. 83-89.
66. Shumak Kenneth H., Rock Gail A. (1984), "Therapeutic Plasma Exchange", N Engl J Med, 310 (12), pp. 762-771.
67. Simetka O., Klat J., Gumulec J., Dolezalkova E, et al. (2015), "Early identification of women with HELLP syndrome who need plasma exchange after delivery", Transfus Apher Sci , 52 (1), pp. 54-59.
68. Stravitz R. Todd, Lee William M. (2019), "Acute liver failure", The Lancet , 394 (10201), pp. 869-881.
69. Szczeklik W., Wawrzycka K., Włudarczyk A., et al. (2013), "Complications in patients treated with plasmapheresis in the intensive care unit", Anaesthesiol Intensive Ther, 45 (1), pp. 7-13.
70. Toy P., Gajic O., Bacchetti P., et al. (2012), "Transfusion-related acute lung injury: incidence and risk factors", Blood , 119 (7), pp. 1757-67.
71. Tschope C., Ammirati E., Bozkurt B., Caforio A. L. P., Cooper L. T., et al. (2021), "Myocarditis and inflammatory cardiomyopathy: current evidence and future directions", Nat Rev Cardiol , 18 (3), pp. 169-193.
72. Vlaar A. P., Hofstra J. J., Determann R. M., et al. (2011), "The incidence, risk factors, and outcome of transfusion-related acute lung injury in a cohort of cardiac surgery patients: a prospective nested case-control study". Blood , 117 (16), pp. 4218-25.
73. Vlaar Alexander P. J., Toy Pearl, Fung Mark, et al. (2019), "A consensus redefinition of transfusion-related acute lung injury", Transfusion , 59 (7), pp. 2465-2476.
74. Wakelin Stuart, Janssens Michiel Etienne (2018), "Centrifugal and Membrane Therapeutic Plasma Exchange – A Mini-review", European Oncology & Haematology , 14 (2), pp. 105.
75. Wallace D. J. (1999), "Apheresis for lupus erythematosus", Lupus , 8 (3), pp. 174-180. .
76. Williams M. E., Balogun R. A. (2014), "Principles of separation: indications and therapeutic targets for plasma exchange" , Clin J Am Soc Nephrol , 9 (1), pp. 181-90.
77. Winters J. L. (2012), "Plasma exchange: concepts, mechanisms, and an overview of the American Society for Apheresis guidelines", Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program , 2012 , pp. 7-12.
78. Yilmaz A. A., Can O. S., Oral M., et al. (2011), "Therapeutic plasma exchange in an intensive care unit (ICU): a 10-year, single-center experience", Transfus Apher Sci , 45 (2), pp. 161-166 .
79. Zhao Y., Garrity D., Graves M., Linden J., St Pierre P., et al. (2019), "Optimization of infusional calcium gluconate for prevention of hypocalcemic reactions during therapeutic plasma exchange" , J Clin Apher , 34 (6), pp. 656-660.