This is an automatically translated article.
If left untreated, adrenal cysts can damage other organs, especially the cardiovascular system, and even lead to death. Endoscopic adrenal cystectomy is an effective treatment for this condition.
1. What is an adrenal cyst?
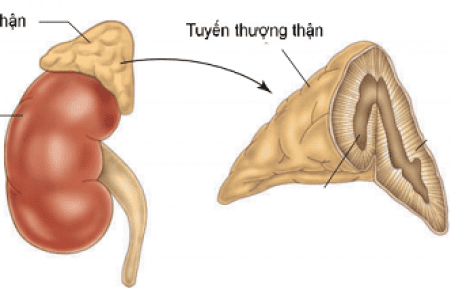
The adrenal gland is an endocrine gland located behind the peritoneum, above the 2 kidneys, has the function of producing important hormones, helping to balance water - electrolytes, regulate blood pressure, fight stress,... Adrenal gland or adrenal adenoma is a benign tumor that develops in the adrenal gland. Adrenal tumors can develop at any age, but are more common between the ages of 20 and 50.
In patients with adrenal tumors, the tumor releases hormones, causing persistently high blood pressure. In addition, the patient also has other symptoms such as headache, heart palpitations, sweating, shaking, shortness of breath, pale skin, anxiety, constipation, weight loss,...
High blood pressure due to adrenal tumors can damage many organs, especially the tissues of the brain, kidneys and cardiovascular system. If left untreated, it can lead to heart disease, kidney failure, stroke, acute respiratory failure, damage to the eye nerves, or cancer. Surgical removal of the tumor is the mainstay of treatment for cases of adrenal tumors. Before surgery, the patient will be used to treat high blood pressure to avoid complications during surgery. And laparoscopic surgery is the most commonly indicated method.

U tuyến thượng thận thường là lành tính
2. Endoscopic adrenal cyst surgery
2.1 Indications/contraindications
Indications
Cases of adrenal cysts discovered incidentally, size 3 - 7cm.
Contraindications
Patients with contraindications to endoscopic surgery: Have respiratory diseases, cardiovascular diseases, blood clotting disorders; Patients with invasive malignancies, venous thrombosis, or lymph node metastases; Pregnant women in the last 3 months.
2.2 Preparing for surgery
Personnel performing: laparoscopic surgeon, anesthesiologist, resuscitation assistant; Technical facilities: Laparoscopic surgery system, basic laparoscopic surgical instruments, vascular welding knife,...; Patients: Shared about the purpose of surgery, steps taken, possible complications; get clinical examination, do clinical tests to detect adrenal cysts; cooperate with endocrinologists and cardiologists for preoperative treatment; coordinate with the anesthesiologist in resuscitation examination and risk classification; Medical records: Complete according to prescribed procedures.
2.3 Performing surgery
Step 1: Check the patient's profile and patient, make sure the right person and the right disease;
Step 2: Perform surgery. There are two options: intraperitoneal surgery or retroperitoneal surgery.
2.3.1 With intraperitoneal surgery
Left adrenal cystectomy:
Patient's position is suitable for technique; Place 3 trocars along the left costal margin and add 1 additional trocar if necessary. The location of trocar placement and the number of trocars varies depending on the tumor nature and the surgeon's judgment; Inflation of the peritoneal cavity: Open inflation technique, pressure 10-12mmHg, initial pumping speed is 2-3 l/min; Posterior abdominal peritoneal opening; Resection of the splenic kidney ligament and the splenic colonic ligament. Cut the attachment of the spleen superior and lateral to move the spleen easily; Dissection of the renal vein and the left main adrenal vein; Clamping, cutting the middle of the left adrenal vein; Removal of the arteries supplying the adrenal gland when the adrenal gland is dissected freely; Separation of attachment between adrenal gland and kidney by hook; Take the specimen, pass it through the 10mm trocar hole, and transfer it to the pathology department for cytology; Drain and suture the trocar holes. Right adrenal cystectomy:
Patient's position is suitable for technique; Place 3 trocars along the right costal margin, 1 more trocar can be placed to raise the liver if necessary; Cut the right triangle ligament to raise the liver, expose the superior renal pole, open the posterior abdominal peritoneum, lower the hepatic flexure, raise the liver, show the inferior vena cava and the right adrenal gland posterior to the liver; Perform the same procedure to remove the left adrenal cyst.
2.3.2 With retroperitoneal access surgery
Right adrenal cystectomy:
The patient is under endotracheal anesthesia, the position is suitable for the technique; Place trocar: Trocar 1 (10mm) is placed near the beginning of rib XI, below rib XII; trocar 2 (10mm or 5mm) is placed at the angle formed by the paravertebral mass with rib XII, trocar 3 (10mm or 5mm) is placed on the iliac crest; The position of trocar 1 is the separation of the peritoneum from the abdominal wall: Make 1-2cm skin incision at the tip of rib XI, below rib XII, use electric knife or Kelly to separate muscle and weight until the lumbar thoracic fascia is visible. Then cut the thoracic fascia with scissors or an electric knife and use your fingers to dissect, creating a space between the posterior Psoas fascia and the Gerota fascia; Insert a gastric tube with a glove on the tip or a Foley tube with a condom on the tip into the space between the posterior fascia of Psoas and the fascia of Gerota; Inflate about 200 - 300ml through the catheter to create the retroperitoneal space; Place the 10mm trocar with the blunt end into the newly created retroperitoneal space, inflate to a pressure of 12-13 mmHg; Open the Gerota scale, then identify the renal hilum and superior renal pole; Exposing, dissecting the right adrenal gland from the right upper pole; Clamp the right main adrenal vein and cut; Right adrenal gland dissection; Clamping and resection of arterial branches supplying blood to the right adrenal gland; Take the specimen, pass it through the 10mm trocar hole, and transfer it to the pathology department for cytology; Drain and suture the trocar holes. Left adrenal cystectomy: Do the same.

Sau phẫu thuật, bệnh nhân cần theo dõi cẩn thận để tránh tai biến như tắc ruột
2.4 Monitoring and handling of accidents
Monitor the condition of the whole body, urine, electrolytes, drainage of the adrenal fossa and adrenal hormones; Early complications after surgery: Bleeding, abdominal wound infection, subcutaneous emphysema, intestinal obstruction: Correct treatment regimen depending on the lesion. Laparoscopic adrenal cyst surgery has many advantages over open surgery: Short hospital stay, small surgical scars, and patients' early recovery. To reduce complications during treatment, patients should follow all instructions of their doctor before, during and after surgery.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, for detailed information and to book an appointment for medical examination and consultation, customers can call the hotlines of the hospitals or register for an online consultation with Vinmec International General Hospital HERE.