This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Ngo Dac Thanh Huy - Cardiologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine, Vinmec Danang International General HospitalIndications for treatment of arrhythmias with extrathoracic electric shock will depend on the symptoms and severity of the patient. In some cases, it is possible to combine methods for cardiovascular emergency such as: medication, defibrillation, cardioversion, implantation of pacemaker - automatic defibrillator (ICDs), resynchronized pacemaker heart, pacemaker implantation, and surgery.
1. Introduction to cardioversion technique
Cardiac cardioversion is one of two cardiothoracic emergency cardioversion techniques first performed in the 1950s. In emergencies, this CPR can save lives. patient. The success rate of cardioversion will be very high if the physician selects the patient carefully, diagnoses the heart rhythm correctly, uses the right electrode plate, determines the optimal level of energy/anesthesia, minimizes thromboembolic events and at the same time preserve the patient's airway, preventing possible electric shock complications.Cardiac cardioversion is performed on patients with incompatible pacemakers or defibrillators, resulting in cardiac dysfunction (acute/chronic change in pacing threshold, sensitivity). Although cardioversion seems simple, if not performed correctly, it can have serious consequences for the patient.
2. Mechanism and indications for performing cardioversion
2.1 Mechanism Simply understood, extrathoracic shock is a method of cardiovascular emergency that allows to quickly extinguish and stabilize most cardiac arrhythmias in the patient's body. Extrathoracic shock induces depolarization of all excitable myocytes, while severing re-entry loops or inactivating peripheral foci of activity by electrically reactivating intracardiac cells. cardiac muscle cells. The effectiveness of the extrathoracic shock depends on the potential applied and the resistance of the tissues. Some factors that can decisively affect resistance are coordination status, patient morphology and patient's thorax.The cardioversion mechanism is the synchronous release of energy onto the R wave of the QRS. Usually the energy will be lower in the shock shock. Avoid discharges during myocardial repolarization (T waves) that cause ventricular fibrillation. The peak of the T wave is the end of the absolute refractory process, the myocardial fibers in this stage are also transitioning to a state of repolarization, so they will be very vulnerable to damage, even causing ventricular fibrillation.
Currently, synchronous cardioversion with 2-phase machines is preferred to use more than 1 phase. In particular, the amount of energy used in arrhythmias is also relatively different. However, they are basically lower than that of asynchronous electric shock.
2.2 Indications Electroconversion cardioversion is indicated in cases of patients with supraventricular arrhythmias with hemodynamic instability such as: Atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, supraventricular tachycardia with re-entry loop....
Several studies have demonstrated that cardioversion in pregnant women is safe and does not affect the heart rate or other developmental problems of the fetus.
Some specific contraindications to cardioversion in cardiovascular emergencies such as tachycardia due to catecholamine/digitalis poisoning, ventricular extrasystoles, junctional tachycardias.
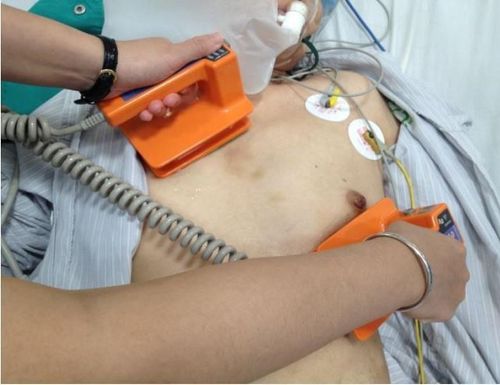
3. Procedure for performing cardioversion
3.1 Preparation In the case of planned cardioversion, the patient will be advised to fast for 6-8 hours to avoid aspiration pneumonia. The patient was given short general anesthesia to avoid pain. Arrange tools and staff to support the patient's breathing. 3.2 Performing cardioversion Electroconversion electrodes can be placed in the anterior/posterior position: in which there will be 1 plate in the 3-4 intercostal space close to the left sternal border, 1 plate in the lower position. left shoulder blade. If placed in the anterior/lateral position, one pole plate will be placed in the 2nd intercostal space close to the right sternal border and one in the 5-6th intercostal space at the apex of the heart.After the shock machine shows signs of shock synchronized with the QRS complex, the doctor will press the discharge button. Depending on the type of tachycardia in the patient, the energy level of the shock can be selected accordingly. 2-phase cardioversion is more effective than single-phase because when done, the current will sweep through the patient's heart again in the opposite direction.
For open heart surgery, the doctor can use an electric shock plate placed directly into the heart of the patient to shock the rhythm or defibrillation, however, the energy level will be lower.
4. Complications that can be encountered during cardioversion
Complications of cardioversion may include:Muscle pain in the area where the shock plate is placed; Respiratory depression due to sedation; Pulmonary edema ; Damage to the heart muscle; Ventricular fibrillation due to general anesthesia; Thromboembolism; Unsustained ventricular tachycardia; Atrial arrhythmias; Heart block; slow heart rate; Transient left bundle branch block; Myocardial necrosis; Cardiac dysfunction; Transient hypotension; Pulmonary edema and skin burns. In summary, cardioversion is a relatively safe and effective method of cardiovascular emergency. However, to prevent unwanted complications, it is necessary to closely monitor the patient's overall condition and vital signs.
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the most prestigious medical treatment units for cardiovascular diseases in Vietnam. The Cardiology Department of Vinmec always receives much praise and satisfaction from domestic & international customers. As a pioneer address to successfully apply the world's most advanced techniques in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
A team of highly qualified and experienced specialists: Doctors with qualifications from Master to Professor, Doctorate, reputable in medical treatment, surgery, interventional cardiac catheterization. Intensive training at home & abroad. In particular, Prof. TS.BS Vo Thanh Nhan - Cardiology Director of Vinmec Central Park was recognized as the first and only expert in Vietnam to be awarded the "Proctor" certificate on TAVI. State-of-the-art equipment, comparable to major hospitals in the world: The most modern operating room in the world; The most modern silent magnetic resonance imaging machine in Southeast Asia; The CT machine has a super-fast scanning speed of only 0.275s/round without the use of drugs to lower the heart rate; The 16-sequence PET/CT and SPECT/CT systems help detect damage to the cardiovascular organs early even when there are no symptoms of the disease. Applying the most advanced advanced cardiovascular techniques in the world in treatment: Painless open heart surgery; Percutaneous aortic intervention without general anesthesia; Treatment of mitral regurgitation through the catheter has a success rate of 95%; Ventricular-assisted artificial heart transplantation for patients with end-stage heart failure prolongs quality of life beyond 7 years. Cooperating with leading cardiovascular centers in Vietnam and the world such as: National Heart Institute, Cardiology Department of Hanoi Medical University, University of Paris Descartes - Georges Pompidou Hospital (France), University of Pennsylvania (France), University of Pennsylvania (France), University of Pennsylvania (France). United States)... with the aim of updating the most modern cardiovascular treatments in the world.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.