This is an automatically translated article.
This article is professionally consulted by Master, Resident Doctor Tran Duc Tuan - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital. The doctor has many years of experience in the field of imaging and interventional internal and external blood vessels.Lymphatic malformation is a condition in which the lymphatic vessels are deformed. The trapped fluid forms sacs or cysts. The size of the LM can put pressure on nearby organs. Whole-body ultrasound or MRI is the way to diagnose and evaluate the condition. Not all LMs need treatment. If treatment is needed, options include antibiotics, sclerotherapy, surgery, laser therapy, and compression therapy.
1. What is a lymphatic system malformation?
The lymphatic system is part of the immune system, helping to fight infections and keep fluid balance in the body. The lymphatic system is a network of small vessels that radiate throughout the body to collect fluid (called lymph) and carry it to the lymph nodes, ultimately back into the blood circulation.Lymphatic vessels are irregularly shaped, containing lymphatic fluid called lymphatic malformations (LM-Lymphatic Malformations). LM causes trapped lymph fluid to form a sac or cyst, which can grow over time. Blood from nearby vessels can also enter the cyst, causing the area around the LM to swell. When the LM size is large, it can put pressure on neighboring organs.
LM can appear anywhere on the body. But most common in the neck, face and armpits. They can also appear inside the body's organs or bones. LMs are congenital, which means that the defect is present from birth. LM can be found in the fetus during pregnancy. Some people with LM may be detected later, when it appears as a fluid-filled lump.
There are two types of LM. Macroscopic LMs may consist of one or more cysts 1 cm or more wide. They can be anywhere on the body but are most commonly found just under the skin on the neck or chest and are tender to the touch. They can grow larger due to infection or bleeding inside the cyst. Microcystic LM is a group of cysts that are smaller than macroscopic LM and may feel solid to the touch. Two types of LM can occur on the same body.
LM is not hereditary and is not associated with any other medical condition. However, LM occurs more commonly in children with features such as Down syndrome, Noonan syndrome, Turner syndrome, and overgrowth syndrome.
Symptoms of LM often depend on the size of the malformation and its location. Symptoms may include:
Appearance of a soft, smooth and unchanged skin. It can be found anywhere on the body including the neck, head, mouth, tongue, eyes, chest, abdomen, arms, legs, scrotum, and penis. A lump appears and they grow rapidly. A lump with signs of infection, including redness, warmth, pain, swelling, and discharge (rare). Chronic small bumps, blisters, or bloody scabs on the surface of the skin that may break open and ooze clear blood or lymph fluid. Having a LM in the head, neck, or tongue can make it difficult for the patient to breathe or swallow. Having LM in an arm or leg can cause swelling and pain throughout the entire limb.
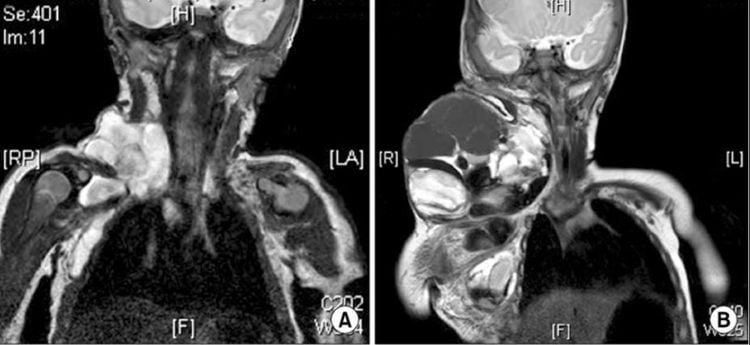
2. Imaging in the evaluation of lymphatic malformations (LM)
Before birth, a LM can be found during an obstetric ultrasound, an Obstetric Ultrasound that provides images of the fetus in a woman's uterus. Through this ultrasound. We can find LM on the skin of the fetus. Imaging modalities are essential to confirm external malformations and to diagnose LM within the body. To diagnose LM, the patient may be offered one or both of the following imaging tests:Ultrasound: This uses sound waves to create images of the inside of the body. This is a non-invasive and highly suggestive method for the diagnosis of lymph node diseases. Ultrasound can not only confirm or rule out the presence of a mass, but can also suggest the nature of the disease on the basis of ultrasound findings. Body Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): An MRI is a way of using a strong magnetic field, radiofrequency pulses, and a computer to create detailed images of structures inside the body. The characteristic of magnetic resonance imaging is that it is a non-invasive form of examination that does not use radiation (x-rays), so there is no radiation exposure. and for high resolution 3D images.
Vinmec International General Hospital put into use the magnetic resonance imaging machine 3.0 Tesla Silent technology. Magnetic resonance imaging machine 3.0 Tesla with Silent technology of GE Healthcare (USA).
Silent technology is especially beneficial for patients who are children, the elderly, weak health patients and patients undergoing surgery. Limiting noise, creating comfort and reducing stress for customers during the shooting process, helping to capture better quality images and shorten the shooting time. Magnetic resonance imaging technology is the technology applied in the most popular and safest imaging method today because of its accuracy, non-invasiveness and non-X-ray use.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: radiologyinfo.org