This is an automatically translated article.
Mastitis is a fairly common condition for women who are breastfeeding. Common symptoms are pain during breastfeeding and red, swollen breasts, which can be very uncomfortable. The following article will provide information on the signs, causes and treatment of mastitis.
1. What is mastitis?
Mastitis , or inflammation of the breast tissue is a common problem for women who are breastfeeding. Common symptoms include redness, pain, and swelling. Mastitis can occur on its own or as a result of inflammation caused by an infection. Signs of a breast infection include chills, a fever of 101 degrees F or higher, and fatigue. If you think you have an infection, see your doctor as you will most likely need antibiotics to treat the inflammation. With mastitis, it's important to rest as much as possible and keep feeding your baby regularly, even though it can be very painful. Applying cold between feeds and taking anti-inflammatory medications, such as ibuprofen can also help you feel more comfortable and less painful.
2. Common symptoms of mastitis
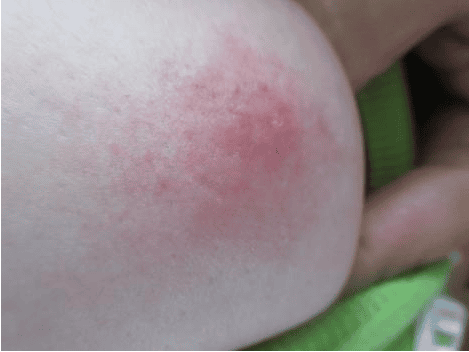
Hình ảnh vú có màu đỏ khi bị viêm
You can detect the following symptoms when the breast is inflamed:
The breast is red when it is inflamed: One of the most common signs of mastitis is a red swollen breast caused by inflammation. If redness is the only symptom, you can take an over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medication, such as ibuprofen. The skin of the breast area will be warm and tender when inflamed: If you have mastitis, the affected breast area may feel very tender and unusually warm. Applying cold between feeds can help you feel more comfortable. The breast becomes swollen when it is inflamed: The affected breast area may be hard and swollen, making breastfeeding difficult. Warming and gently massaging the breast from the swollen area toward the nipple and from the nipple toward the armpit will make it more comfortable.
3. Causes of mastitis
Prolonged engorgement will lead to the risk of mastitis and infection that causes the breasts to become enlarged, swollen and painful. Swollen nipples make it difficult for your baby to latch on to the nipple and can slow down milk flow.
Blocked milk ducts are also one of the causes of mastitis. After you feed your baby, the milk left in the breast can back up into the ducts, inflaming the surrounding tissues and causing a blockage. Clogged milk ducts are a common cause of mastitis. If you feel a small, hard, painful lump in your breast, you may have a blocked milk duct.

Tắc ống dẫn sữa có thể gây viêm vú
4. How to treat mastitis?
Cold and warm: Applying warm or cold compresses (not freezing) between feeds can ease the pain of mastitis. You should note that absolutely do not apply the cold pack directly to the skin, but always wrap the pack in a clean cloth or towel to avoid injuring the skin. This is especially important with mastitis because it can affect the skin's ability to take temperature. Applying a warm compress just before breastfeeding can help the milk flow more evenly.
Continue to breastfeed: It is important for mothers to breastfeed often when the breasts are inflamed, even though it can be painful. Begin breastfeeding with the affected breast. Make sure your baby is positioned well and is latching on as much breast tissue as possible. Gently massage the breast toward the nipple while nursing. If you still have milk in your breasts after breastfeeding, pump or express extra milk to store it.
5. Complications of mastitis while breastfeeding
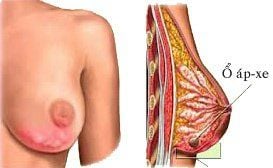
Áp xe vú
Breast Abscess: If an area of the breast remains hard, red and tender despite antibiotic treatment, see your doctor as you most likely have a breast abscess (collection of pus under the skin) that needs drainage. needle aspiration or surgery.
With prompt treatment, mastitis symptoms usually resolve within a few days. To feel better as quickly as possible and prevent a relapse, you need to get plenty of rest. Get help from family and friends so you can focus on taking care of yourself and your baby.
Postpartum care is a continuous, comprehensive process for both mother and baby, including vaginal birth or cesarean section, women need recovery time to ensure that there are no postpartum complications. Inflammation of the milk glands can be effectively prevented, is not a dangerous disease, but women should not ignore the disease because the disease, if not treated, can cause local complications such as breast abscess, worse than sepsis, which can cause serious health problems. high mortality.
After giving birth, the mother's body changes, the mother can suffer from many diseases such as postpartum hemorrhage, urinary incontinence, digestive disorders, bowel and urinary disorders, rectal prolapse,... Especially, If you don't know how to breastfeed, it can lead to inflamed breasts. Therefore, after giving birth, the mother can perform a general health examination at Vinmec International General Hospital. Mothers will have the opportunity to visit with leading specialists, combined with many other specialties to give advice, care, and help improve their postpartum health quickly. In addition, mothers also have the opportunity to use screening services for babies before and after birth; storing cord blood, cord membrane... at Vinmec Institute of Stem Cells and Gene Technology - the world's most advanced and synchronous automatic storage and handling system.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: babycenter.com