This is an automatically translated article.
The article was consulted professionally with BS. Nguyen Hai Ha - Head of Vaccine Unit - Pediatric Outpatient Department - Pediatric Center - Vinmec Times City International Hospital.Rabies is an acute viral encephalitis disease, transmitted from animals to humans mainly through bites and licks on the damaged skin of animals carrying the virus. Manifestations of rabies in humans are fear of water, fear of wind, convulsions, paralysis and lead to death. Once rabies has occurred, the mortality rate is almost 100% (both human and animal).
1. Rabies virus enters the human body
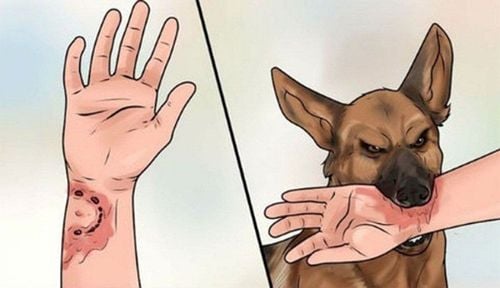
The natural reservoir of rabies virus is warm-blooded mammals such as wolves, jackals, domestic dogs, cats, ferrets, civets, foxes and other mammals. In addition, it may also be present in bats. In Vietnam, rabies virus is mainly transmitted through contact by animals biting, licking on damaged skin or being splashed with saliva on mucous membranes. After entering the human body, the rabies virus will follow the nerves to the brain at a speed of about 0.3mm/hour, causing damage to the central nervous system. The brainstem is infected first, then the hypothalamus, and finally the cortex is damaged. The virus replicates in the brain, then moves along the nerves to other organs such as the salivary glands, kidneys, lungs, heart, liver...In the salivary glands, the virus multiplies in large numbers, creating a source of infection. most dangerous disease. From the day the virus enters the human body, the incubation period varies greatly from person to person, from 1 week to over 1 year, even in some cases over 6 years, the average incubation period is 1-3 months, rare. cases less than 9 days or more than 1 year. The incubation period depends on the amount of virus, the severity of the wound, and the distance from the bite to the central nervous system. In fact, the highest rate of rabies development and death is from bites to the face, the average rate of death is in the hands, the lowest is in the legs.
2. Some common characteristics in patients
Initially, the patient feels headache, restlessness, sobbing, screaming, unreasonably depressed, fear, fever, malaise, and unusual sensory changes at the wound site of the animal bite. The disease progresses to paralysis or paralysis. The swallowing muscles of the esophagus are constricted when drinking water, the later stage can cause spasms in the neck and throat when seeing the image of water, so the patient is very afraid of water, the patient is delirious and convulsive. The illness usually lasts from 2 to 6 days and then dies due to paralysis of the respiratory muscles.
3. How to recognize rabies in humans from time to time
Incubation period: calculated from the time a dog (or an animal with rabies) bites and licks the damaged skin until the disease develops, this is a valuable time to save the patient's life. Signs of this period are almost absent, if the incubation period is short, the only sign is a bite or scratch on the skin. Therefore, it is the most important thing for people who are bitten by an animal to go to the doctor and get vaccinated against rabies right after being bitten. The prodromal period (onset): is the initial manifestations of rabies in humans before the onset of the disease, the patient shows signs of anxiety, mood changes, itching, and pain at the bite site. . Note that by this point, most patients have forgotten about being bitten by a dog (or other animal). Full-fledged period: rabies usually has two basic disease forms, which are aggressive and paralytic. Symptoms of rabies in humans can be aggressive or spastic: the patient will show a psychomotor agitation, the patient will become violent, mad, quarrelsome, destructive and rapidly progress to coma and death. Patients with spasticity, tremors of extremities, convulsions, spasms of the throat and larynx causing symptoms of fear of water, a feeling of thirst, do not dare to drink, just seeing or hearing the sound of running water also causes increased throat spasms. and very painful. This spasm increases every time there is a very small stimulus such as: wind blowing, electric fan, taste of food, light... The patient's face is always tense, panicked, eyes bright and red, hearing, may have genital irritation, penile erection in men. Patients begin to gradually increase fever, sweating, increased sputum secretion, cardiovascular and respiratory disorders, hallucinations. These symptoms progressed gradually and died after 3-5 days due to cardiac arrest, respiratory arrest.Symptoms of rabies in paralyzed people: common in patients bitten by rabies dogs who have been vaccinated but vaccinated quite late, the virus has entered the brain to cause disease. Patients usually have no symptoms of fear of water or wind. Initially, there may be pain in many areas of the spine, then there is Landry's syndrome (first paralysis of the lower extremities, then sphincter disorders, then paralysis of the upper limbs). When the damage spreads to the medulla oblongata, the patient will develop cranial nerve palsy, stop breathing and cardiac arrest, and die. The course of the disease is about 4-10 days.
4. What to do when bitten by an animal?
When bitten by a dog, cat (or animal), there are 2 things to do: treat the wound and vaccinate against tetanus, rabies prevention and anti-rabies serum. In addition, it is necessary to closely monitor the health of the biting animal.4.1. Wound treatment: It is necessary to separate the clothes from the bite, use scissors to cut off the fabric at the bite site (if any). This helps limit the animal's saliva from sticking more into the wound. Rinse the wound under running water for 15 minutes, the warmer the better. After that, clean the wound with 70% alcohol, iodide alcohol or Povidone-Iodine, absolutely do not try to squeeze blood. Do not rub the wound, avoid making the wound worse. Do not apply leaves, kerosene or any other substance to the wound. After cleaning the wound, the patient should use a medical gauze or clean cloth to bandage the wound to stop the bleeding and prevent bacteria from entering. However, the bandage should not be too tight, making it difficult for blood to circulate. If the wound needs stitches to stop bleeding, it should be sewn sparsely, not cosmetically. Some bite wounds require antibiotics prescribed by a doctor to prevent infection. 4.2. Vaccinating against tetanus, rabies and anti-rabies sera: Patients should immediately go to medical facilities to receive tetanus vaccine, rabies vaccine and anti-rabies serum (if the wound is wound). grade III) immediately after being bitten by a dog. The vaccination schedule according to the route and type of rabies vaccine will be appropriately advised by the doctors depending on the grade of the wound and the post-exposure prophylaxis regimen. Post-exposure rabies vaccination will have 2 regimens: intramuscular and intradermal
Intramuscular injection, rabies vaccination regimen when exposure is confirmed (bitten): Persons who have not received pre-exposure prophylaxis infection: 5 injections (0.5ml/dose) on days 0, 3, 7, 14, 28. In case of exposure level III, it is necessary to combine injection of anti-rabies serum. Persons vaccinated in the last 5 years: 2 injections on days 0 and 3. People who have been vaccinated irregularly or for more than 5 years: Get 5 injections on days 0, 3, 7, 14, 28 and possibly injection of anti-rabies serum. Intradermal injection, rabies vaccination regimen, dose 0.1ml x 2: Persons who have not received pre-exposure prophylaxis: 4 injections: injection in different limb positions, 0.1ml each side, on days 0 , 3, 7 and 28. People who have had prophylactic vaccination: Inject 0.1ml on days 0 and 3.
5. Treatment when rabies has occurred
Until now, there is no medicine that can save a patient's life when rabies has occurred. Treatment at this time is only symptomatic treatment such as sedation and leaving the patient to lie in a quiet, separate place.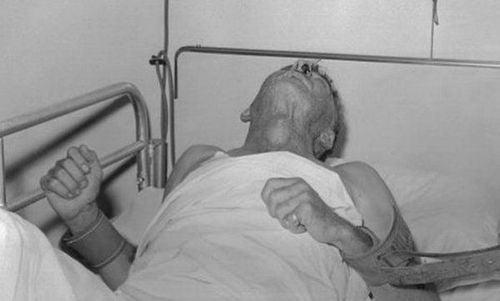
6. Preventing rabies when caring for sick people
Rabies is a very dangerous disease, when caring for patients, family members or medical staff should wear full protective equipment such as hats, clothes, gloves, boots..., wash hands thoroughly with soap after care and disinfected with alcohol. Patient items should be incinerated. Iron items, beds, cabinets, floors... need to be cleaned with soap and sprayed with disinfectant.Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.